1 引言
III-V族化合物半导体材料具有电子迁移率高[1]、少子寿命短[2]、抗辐射能力强[3]及电阻温度系数小[4]等优点,在半导体器件、集成电路等方面有重要的应用。半导体III-V族二元合金半导体材料不具备在发射光波长为1.3~1.55 μm的通信窗口直接跃迁能带的特性。而对于由III-V族二元合金GaAs-InAs组成的三元合金半导体材料InxGa1-xAs(x为三元合金中In的原子数分数),在室温下带隙可以在0.87 μm(GaAs)到3.5 μm(InAs)范围内调谐,这使得其相对于其他材料,在能带结构工程及各种光电器件(如光纤通信系统、红外发光二极管、光电探测器[5-9])中更具吸引力。化合物的光电特性与材料界面的应变存在密切的关系,由于InxGa1-xAs与GaAs衬底存在晶格失配,随着In组分的增加失配应力将持续增加,这使得在GaAs衬底上外延高结晶质量的InxGa1-xAs薄膜成为研究的热点与难点。目前,国内一些课题组使用分子束外延(MBE)[10-12]、金属有机化学气相沉积(MOCVD)[13-15]、电共沉积等方法制备InxGa1-xAs薄膜[16],由于存在晶格失配,大多数研究都集中在低In组分,但针对通信波段1.55 μm附近的高In组分的InxGa1-xAs薄膜鲜有报道。
本文利用配有反射高能电子衍射仪(RHEED)原位监测装置的MBE设备生长出高结晶质量的InxGa1-xAs薄膜,在生长过程中对GaAs衬底进行脱氧处理,外延GaAs缓冲层及外延InxGa1-xAs薄膜进行实时监控并记录。对生长出的InxGa1-xAs薄膜进行X射线衍射(XRD)测试,显示生长出的为高结晶质量的单晶薄膜。光致发光(PL)测试显示峰位出现蓝移,说明在InxGa1-xAs薄膜中可能存在压应变。最后拉曼(Raman)光谱显示GaAs-like横向光学声子(TO)的峰相比于GaAs-like 纵向光学声子(LO)的峰出现明显的展宽,证实了在InxGa1-xAs薄膜中存在应变。
2 实验
本实验是在超高真空(~2.2×10-8 Pa)MBE及RHEED联合系统中实现,所使用的衬底为n-型GaAs(100)基片。在生长前先对衬底进行除气处理:首先,将衬底放入进样室(loadlock)中,200 ℃下加热处理2 h去除基片上吸附的水汽;其次,将衬底转移到预处理室(buffer)中,400 ℃下加热2 h进行预除气;最后,把即将进行薄膜生长的衬底转移到生长室中,且在高温环境中再次进行30 min除气处理。在生长实验开始之前,用束流器(BFM)对外延所需的各个材料源的束流进行校准,得到生长所需的束流。用热偶标称温度对衬底所需的温度进行校准。GaAs衬底在550 ℃下脱氧处理后,降温到450 ℃,As束流压(BEP)为1.7×10-4 Pa,V/III束流比为22,生长出GaAs缓冲层,生长时间为15 min。降低生长温度至350 ℃,生长出InxGa1-xAs薄膜,As束流压为1.3×10-4 Pa,Ga束流压为7.9×10-6 Pa,In束流压为1.9×10-6 Pa,生长时间为30 min。在整个过程中通过RHEED进行实时监测并记录。对生长出的InxGa1-xAs薄膜,采用德国布鲁克公司D8 DISCOVER X射线衍射仪进行测试获得InxGa1-xAs薄膜及GaAs衬底的XRD图,从中可以得出InxGa1-xAs三元合金的组分及结晶质量。用配有InGaAs探测器的HORIBA iHR550光谱仪记录PL光谱,用655 nm波长半导体二极管激光器作为激发源,采用LabRAM HR Evolution, HORIBA光谱仪得到InxGa1-xAs薄膜Raman光谱图。
3 结果与讨论
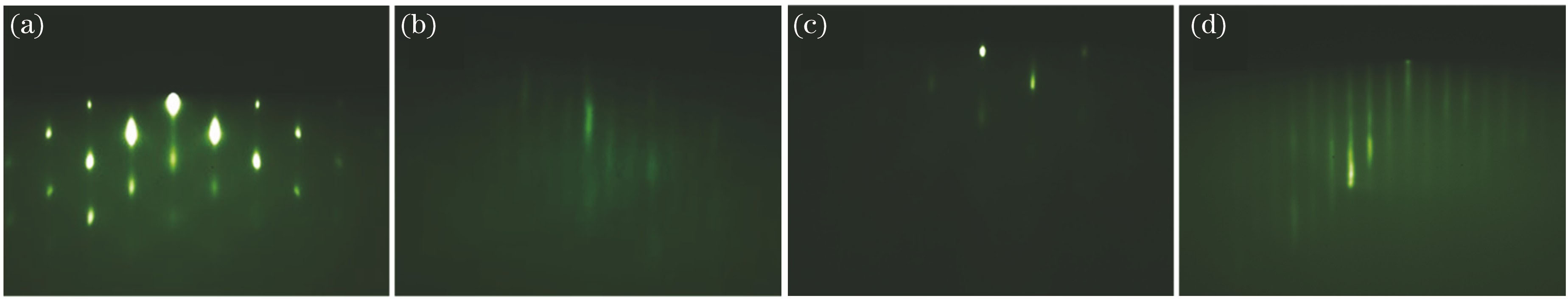
图1为衬底处理及样品生长整个过程中的RHEED衍射图样实时监测图。图1(a)中GaAs衬底在温度为450 ℃,As束流的保护下进行脱氧处理,RHEED衍射图样显示为明亮的透射斑点,这说明在富As条件下,衬底表面进行了完全脱氧处理,且衬底表面呈现三维岛状结构。在GaAs缓冲层生长过程中,由于在GaAs衬底表面,原子之间存在吸附、脱附、迁移、结合等过程,随着缓冲层的生长,三维岛状结构将向二维层状结构转变,在RHEED衍射图样中表现为在劳厄环上的衍射斑点为主、而在斑点的基片表面法线方向有较弱的条纹拉长趋势,如图1(b)所示。图1(c)为In开始加入生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜的RHEED衍射图样,RHEED衍射图像上显示透射斑点被拉长成条纹状,这是因为在GaAs缓冲层和InxGa1-xAs薄膜接触层之间存在一定的晶格失配,且在InxGa1-xAs薄膜的几个原子层表面有较大的粗糙度。随着InxGa1-xAs薄膜生长时间的增加,准三维结构逐渐向二维层状结构过渡,最后图1(d)中RHEED衍射图像显示InxGa1-xAs薄膜为亮度较弱的拉长的条纹,且背景颜色微微变亮。文献[
17]通过隧穿透射电镜(STM)证实薄膜表面呈现原子级平整度。因此,RHEED衍射图像显示生长出晶格失配较大的、高结晶质量的InxGa1-xAs薄膜。
图 1. 生长过程中的RHEED衍射图像。(a)进行脱氧处理的GaAs衬底;(b)生长的GaAs缓冲层;(c) In组分加入生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜;(d)生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜
Fig. 1. RHEED diffraction pattern during growth. (a) Deoxidation processing of GaAs substrate; (b) growth of GaAs buffer layer; (c) growth of InxGa1-xAs film by adding In component; (d) growth of InxGa1-xAs film
下载图片 查看所有图片
图2中显示InxGa1-xAs薄膜的光学照片及对应的XRD图。图2(a)为在5 cm GaAs衬底上生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜的光学照片,将整个薄膜区域等分成四个不同的区域,分别标记为1、2、3、4。而四个区域最外侧环形区域由于有卡托压住片子边缘因此无法生长出InxGa1-xAs薄膜。图2(b)中的插图是所生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜的结构。为使InxGa1-xAs薄膜的结晶质量更好,先在除气完成的GaAs衬底上生长出GaAs缓冲层,使整个GaAs缓冲层表面平整,图1(b)中的再构线显示其具备完整的平面。图2(b)对应图2(a)InxGa1-xAs薄膜四个不同区域及对应GaAs衬底的XRD图,从图2(b)中可以得到GaAs衬底的衍射峰2θ对应的角度为33.13°,而在GaAs衬底上生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜对应的衍射峰2θ为31.76°,对应的衬底为33.10°,InxGa1-xAs薄膜和GaAs衬底对应的半峰全宽分别为0.137°和0.094°,所以得到的InxGa1-xAs薄膜是均匀的高结晶质量薄膜。
图 2. InxGa1-xAs薄膜的光学照片及对应的XRD图。(a)光学照片;(b) XRD图像
Fig. 2. Optical photograph of InxGa1-xAs film and corresponding XRD image. (a) Optical photograph; (b) XRD image
下载图片 查看所有图片
确定InxGa1-xAs薄膜对应的衍射峰后,查阅数据手册[18]可知,InAs晶格常数为0.6058 nm(300 K),根据布拉格公式
式中,d为晶面间距,θ为入射X射线与相应晶面夹角,n为衍射级数,λ为波长,及面间距公式
式中,h、k、l为密勒指数,a为晶格常数,可以计算出GaAs和InxGa1-xAs对应的晶格常数分别为0.5648 nm和0.5858 nm。根据Vegard's law(韦德)公式
可以得到InxGa1-xAs三元合金中In的组分(原子数分数)x[19],其中晶格常数a的下角标为对应的半导体材料。InxGa1-xAs外延层的应变ε定义为两层晶格常数的相对差异[20]:
可以得到在三元合金InxGa1-xAs薄膜中In的组分为0.51,薄膜中存在的应变为-3.58%,因此在薄膜中存在的应力为压应力。
根据300 K时III-V族三元合金的带隙随组分变化的依赖关系,直接带隙材料InxGa1-xAs的禁带宽度Eg值为[20-21]
对于每一种特定组分的半导体材料,均有一本征吸收的长波限,此波限可以表示为
根据XRD的结果得到InxGa1-xAs薄膜In组分为0.51,对应的室温发光波长约为1604 nm。图3为三元合金InxGa1-xAs薄膜在温度T=300 K下的光致发光谱图,图3中Ec为导带能级,Ev为价带能级,上角标代表对应的半导体材料,从图中可以得到发光峰位对应的位置为1560 nm。
在室温下,ΔEc随In组分的变化关系式表示为[22]
根据室温下GaAs的带隙,InxGa1-xAs薄膜的带隙及对应的ΔEc可以得到生长的GaAs/InxGa1-xAs异质结构的能带结构示意图,如图3中插图所示。根据PL光谱及对应的能带可以计算出当三元InxGa1-xAs合金中发光波长约为1560 nm时,In的组分为0.49,这与XRD的测试结果存在偏差。这可能是由于GaAs缓冲层和InxGa1-xAs薄膜之间的失配较大导致存在的应力使得InxGa1-xAs薄膜的发光峰出现了蓝移,因此从光谱测试结果中推算出三元合金中In的组分偏小。
图 3. InxGa1-xAs薄膜室温下的PL光谱,插图为室温下发光对应的能带图
Fig. 3. PL spectra of InxGa1-xAs film at room temperature, inset shows energy band diagram corresponding to luminescence at room temperature
下载图片 查看所有图片
为了进一步证明在三元合金InxGa1-xAs薄膜中存在应变,对InxGa1-xAs薄膜进行Raman光谱分析。图4中深红色为对应GaAs衬底的Raman光谱,从光谱可以得到衬底的Raman峰存在两种模式,分别是GaAs TO和GaAs LO,对应的峰位分别为268.8 cm-1和290.4 cm-1。在InxGa1-xAs合金中显示出双模式声子特性,涉及到InAs-like 和GaAs-like 模式,但是它们分别存在两种模式,即为like TO和like LO[23-25]。图4中黑色对应为InxGa1-xAs薄膜的Raman光谱,从谱线上可以得到其由多个模式的峰组合而成。为了确定多个Raman光谱峰的来源,对InxGa1-xAs薄膜的Raman光谱进行分峰处理,得到主要存在三个峰:红色、蓝色和粉红色的光谱。这三个模式的峰对应的峰位分别为233.1、256.8、270.2 cm-1。根据文献[
25-27],这三个峰位对应的模式分别为InAs-like LO、GaAs-like TO、GaAs-like LO。在三元合金InxGa1-xAs薄膜中, InAs-like TO、InAs-like LO、GaAs-like TO、GaAs-like LO模式对应的Raman峰位ω随着In组分的变化方程为(其中下角标代表Raman峰模式)
根据(8)~(10)式可以得到InxGa1-xAs三元合金薄膜对应的Raman光谱存在三种模式的峰,与文献中对应的模式一致。可以计算出在InxGa1-xAs三元合金中In的组分为0.55左右,与XRD和光谱比较都有误差,这可能是由于激光作用在薄膜表面使表面出现局部过热,造成In组分偏高,本文对此不作过多的讨论。图4中InxGa1-xAs薄膜的Raman光谱中GaAs-like TO模式的峰出现明显的展宽,这说明在InxGa1-xAs薄膜中存在应力,这与文献[
25]的结果一致。
图 4. InxGa1-xAs薄膜及GaAs衬底在室温下的Raman光谱
Fig. 4. Raman spectra of InxGa1-xAs film and GaAs substrate at room temperature
下载图片 查看所有图片
4 结论
使用分子束外延设备生长了InxGa1-xAs薄膜,并通过RHEED进行实时监测。RHEED衍射图样显示InxGa1-xAs薄膜具有明显的再构线且薄膜表面呈现原子级别的平整度,XRD测试显示生长的InxGa1-xAs薄膜具有高结晶质量,且计算出三元合金中In组分为0.51,InxGa1-xAs薄膜中存在压应力,且应变大小约为-3.58%。PL光谱测试InxGa1-xAs薄膜由于压应变存在,发光峰位出现蓝移且发光峰位为1560 nm。Raman光谱显示InxGa1-xAs薄膜存在多个模式,GaAs-like TO模式峰出现明显的展宽,说明在三元合金InxGa1-xAs薄膜中存在应变。
参考文献
[1] Lester L F, Hwang K C, Ho P, et al. Ultrafast long-wavelength photodetectors fabricated on low-temperature InGaAs on GaAs[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 1993, 5(5): 511-514.
Lester L F, Hwang K C, Ho P, et al. Ultrafast long-wavelength photodetectors fabricated on low-temperature InGaAs on GaAs[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 1993, 5(5): 511-514.
[2] Gupta S, Whitaker J F, Mourou G A. Ultrafast carrier dynamics in III-V semiconductors grown by molecular-beam epitaxy at very low substrate temperatures[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1992, 28(10): 2464-2472.
Gupta S, Whitaker J F, Mourou G A. Ultrafast carrier dynamics in III-V semiconductors grown by molecular-beam epitaxy at very low substrate temperatures[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1992, 28(10): 2464-2472.
[3] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, et al. Superior radiation resistance of In1-xGaxN alloys: Full-solar-spectrum photovoltaic material system[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(10): 6477-6482.
Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, et al. Superior radiation resistance of In1-xGaxN alloys: Full-solar-spectrum photovoltaic material system[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(10): 6477-6482.
[4] Ohno H, Munekata H, Penney T, et al. Magnetotransport properties of p-type (In, Mn)As diluted magnetic III-V semiconductors[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 68(17): 2664-2667.
Ohno H, Munekata H, Penney T, et al. Magnetotransport properties of p-type (In, Mn)As diluted magnetic III-V semiconductors[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 68(17): 2664-2667.
[5] Heimbuch M E, Holmes A L, Reaves C M, et al. Tertiarybutylarsine and tertiarybutylphosphine for the MOCVD growth of low threshold 1.55 μm InxGa1-xAs/InP quantum-well lasers[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1994, 23(2): 87-91.
Heimbuch M E, Holmes A L, Reaves C M, et al. Tertiarybutylarsine and tertiarybutylphosphine for the MOCVD growth of low threshold 1.55 μm InxGa1-xAs/InP quantum-well lasers[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1994, 23(2): 87-91.
[6] 夏宁, 方铉, 容天宇, 等. 表面硫钝化对GaAs材料光响应特性的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(6): 0603002.
夏宁, 方铉, 容天宇, 等. 表面硫钝化对GaAs材料光响应特性的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(6): 0603002.
Xia N, Fang X, Rong T Y, et al. Effect of surface sulfur passivation on photoresponse characteristics of GaAs materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(6): 0603002.
Xia N, Fang X, Rong T Y, et al. Effect of surface sulfur passivation on photoresponse characteristics of GaAs materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(6): 0603002.
[7] Ponomarev D S, Khabibullin R A, Yachmenev A E, et al. Intensive terahertz radiation from InxGa1-xAs due to photo-dember effect[J]. International Journal of High Speed Electronics and Systems, 2016, 25(3): 1640023.
Ponomarev D S, Khabibullin R A, Yachmenev A E, et al. Intensive terahertz radiation from InxGa1-xAs due to photo-dember effect[J]. International Journal of High Speed Electronics and Systems, 2016, 25(3): 1640023.
[8] Lee H J, Jang I K, An W C, et al. Enhanced output power of InGaAs/GaAs infrared light-emitting diode with GaxIn1-xP tensile strain barrier[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(12): 1582-1588.
Lee H J, Jang I K, An W C, et al. Enhanced output power of InGaAs/GaAs infrared light-emitting diode with GaxIn1-xP tensile strain barrier[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(12): 1582-1588.
[9] Kim D K, Lee H J, An W C, et al. Dependence of laminar flow fluctuation on indium composition in In0.07GaAs/GaAs quantum wells for 940-nm infrared light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2018, 72(9): 1020-1024.
Kim D K, Lee H J, An W C, et al. Dependence of laminar flow fluctuation on indium composition in In0.07GaAs/GaAs quantum wells for 940-nm infrared light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2018, 72(9): 1020-1024.
[10] 罗子江, 倪照风, 丁召, 等. InxGa1-xAs/GaAs异质薄膜的临界厚度[J]. 功能材料, 2018, 49(8): 8166-8171.
罗子江, 倪照风, 丁召, 等. InxGa1-xAs/GaAs异质薄膜的临界厚度[J]. 功能材料, 2018, 49(8): 8166-8171.
Luo Z J, Ni Z F, Ding Z, et al. The critical thickness of InxGa1-xAs/GaAs heterofilms[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2018, 49(8): 8166-8171.
Luo Z J, Ni Z F, Ding Z, et al. The critical thickness of InxGa1-xAs/GaAs heterofilms[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2018, 49(8): 8166-8171.
[11] 罗子江, 周勋, 贺业全, 等. RHEED实时监控下MBE生长不同In组分的InGaAs薄膜[J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(11): 2107-2111.
罗子江, 周勋, 贺业全, 等. RHEED实时监控下MBE生长不同In组分的InGaAs薄膜[J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(11): 2107-2111.
Luo Z J, Zhou X, He Y Q, et al. The MBE growth research on different composition of In of InGaAs films under the real-time monitoring of RHEED[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(11): 2107-2111.
Luo Z J, Zhou X, He Y Q, et al. The MBE growth research on different composition of In of InGaAs films under the real-time monitoring of RHEED[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(11): 2107-2111.
[12] 郭祥, 王一, 魏文喆, 等. 不同应力下的InxGa1-xAs薄膜表面形貌[J]. 材料导报, 2015, 29(2): 21-23,37.
郭祥, 王一, 魏文喆, 等. 不同应力下的InxGa1-xAs薄膜表面形貌[J]. 材料导报, 2015, 29(2): 21-23,37.
Guo X, Wang Y, Wei W Z, et al. Study on the surface morphology of InxGa1-xAs film subjected to varying stresses[J]. Materials Review, 2015, 29(2): 21-23, 37.
Guo X, Wang Y, Wei W Z, et al. Study on the surface morphology of InxGa1-xAs film subjected to varying stresses[J]. Materials Review, 2015, 29(2): 21-23, 37.
[13] 刘宝林, 杨树人, 陈伯军, 等. LP: MOCVD研制InGaAs/InP应变量子阱LD[J]. 光子学报, 1996, 25(5): 434-438.
刘宝林, 杨树人, 陈伯军, 等. LP: MOCVD研制InGaAs/InP应变量子阱LD[J]. 光子学报, 1996, 25(5): 434-438.
Liu B L, Yang S R, Chen B J, et al. InGaAs/InP strained quantum well LD by LP-MOCVD[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 1996, 25(5): 434-438.
Liu B L, Yang S R, Chen B J, et al. InGaAs/InP strained quantum well LD by LP-MOCVD[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 1996, 25(5): 434-438.
[14] 刘洋, 李林, 乔忠良, 等. MOCVD生长1.06 μm波段InGaAs/GaAs单量子阱材料的发光特性研究[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(11): 1106001.
刘洋, 李林, 乔忠良, 等. MOCVD生长1.06 μm波段InGaAs/GaAs单量子阱材料的发光特性研究[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(11): 1106001.
Liu Y, Li L, Qiao Z L, et al. Optical characteristics of 1.06 μm InGaAs/GaAs quantum well grown by MOCVD[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(11): 1106001.
Liu Y, Li L, Qiao Z L, et al. Optical characteristics of 1.06 μm InGaAs/GaAs quantum well grown by MOCVD[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(11): 1106001.
[15] 朱龙德, 李晶, 陈德勇, 等. InGaAs/InP体材料和量子阱、超晶格材料的低压MOCVD生长及材料特性的测试分析[J]. 半导体学报, 1993, 14(4): 208-216.
朱龙德, 李晶, 陈德勇, 等. InGaAs/InP体材料和量子阱、超晶格材料的低压MOCVD生长及材料特性的测试分析[J]. 半导体学报, 1993, 14(4): 208-216.
Zhu L D, Li J, Chen D Y, et al. Low pressure MOCVD growth and characterization of InGaAs/InP bulk materials, quantum wells and superlattices[J]. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 1993, 14(4): 208-216.
Zhu L D, Li J, Chen D Y, et al. Low pressure MOCVD growth and characterization of InGaAs/InP bulk materials, quantum wells and superlattices[J]. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 1993, 14(4): 208-216.
[16] 王喜莲, 李浴春, 韩爱珍, 等. 用电共沉积方法制备InGaAs薄膜[J]. 材料研究学报, 2001, 15(4): 451-454.
王喜莲, 李浴春, 韩爱珍, 等. 用电共沉积方法制备InGaAs薄膜[J]. 材料研究学报, 2001, 15(4): 451-454.
Wang X L, Li Y C, Han A Z, et al. Preparation and performance of InGaAs thin film by electrodeposit[J]. Chinese Journal of Material Research, 2001, 15(4): 451-454.
Wang X L, Li Y C, Han A Z, et al. Preparation and performance of InGaAs thin film by electrodeposit[J]. Chinese Journal of Material Research, 2001, 15(4): 451-454.
[17] 罗子江, 周勋, 杨再荣, 等. InGaAs/GaAs异质薄膜的MBE生长研究[J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(5): 846-849.
罗子江, 周勋, 杨再荣, 等. InGaAs/GaAs异质薄膜的MBE生长研究[J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(5): 846-849.
Luo Z J, Zhou X, Yang Z R, et al. The MBE growth research on InGaAs/GaAs heterofilms[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(5): 846-849.
Luo Z J, Zhou X, Yang Z R, et al. The MBE growth research on InGaAs/GaAs heterofilms[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(5): 846-849.
[18] Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R. Ram-Mohan L R. Band parameters for III-V compound semiconductors and their alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(11): 5815-5875.
Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R. Ram-Mohan L R. Band parameters for III-V compound semiconductors and their alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(11): 5815-5875.
[19] Deki R, Sasaki T, Takahasi M. Strain relaxation and compositional separation during growth of InGaAs/GaAs(001)[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 468: 241-244.
Deki R, Sasaki T, Takahasi M. Strain relaxation and compositional separation during growth of InGaAs/GaAs(001)[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 468: 241-244.
[20] Arent D J. Deneffe K,van Hoof C, et al. Strain effects and band offsets in GaAs/InGaAs strained layered quantum structures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1989, 66(4): 1739-1747.
Arent D J. Deneffe K,van Hoof C, et al. Strain effects and band offsets in GaAs/InGaAs strained layered quantum structures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1989, 66(4): 1739-1747.
[21] Nahory R E, Pollack M A. Johnston W D Jr, et al. Band gap versus composition and demonstration of Vegard's law for In1-xGaxAsyP1-y lattice matched to InP[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1978, 33(7): 659-661.
Nahory R E, Pollack M A. Johnston W D Jr, et al. Band gap versus composition and demonstration of Vegard's law for In1-xGaxAsyP1-y lattice matched to InP[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1978, 33(7): 659-661.
[22] Sugiyama Y, Inata T, Fujii T, et al. Conduction band edge discontinuity of In0.52Ga0.48As/In0.52(Ga1-xAlx)0.48As(0≤x≤1) heterostructures[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1986, 25(8): L648-L650.
Sugiyama Y, Inata T, Fujii T, et al. Conduction band edge discontinuity of In0.52Ga0.48As/In0.52(Ga1-xAlx)0.48As(0≤x≤1) heterostructures[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1986, 25(8): L648-L650.
[23] Brodsky M H, Lucovsky G. Infrared reflection spectra of Ga1-xInxAs: a new type of mixed-crystal behavior[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1968, 21(14): 990-993.
Brodsky M H, Lucovsky G. Infrared reflection spectra of Ga1-xInxAs: a new type of mixed-crystal behavior[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1968, 21(14): 990-993.
[24] Pearsall T P, Carles R, Portal J C. Single longitudinal-mode optical phonon scattering in Ga0.47In0.53As[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1983, 42(5): 436-438.
Pearsall T P, Carles R, Portal J C. Single longitudinal-mode optical phonon scattering in Ga0.47In0.53As[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1983, 42(5): 436-438.
[25] Emura S, Gonda S I, Matsui Y, et al. Internal-stress effects on Raman spectra of InxGa1-xAs on InP[J]. Physical Review B, 1988, 38(5): 3280-3286.
Emura S, Gonda S I, Matsui Y, et al. Internal-stress effects on Raman spectra of InxGa1-xAs on InP[J]. Physical Review B, 1988, 38(5): 3280-3286.
[26] Yu S J, Asahi H, Emura S, et al. Raman scattering study of thermal interdiffusion in InGaAs/InP superlattice structures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 70(1): 204-208.
Yu S J, Asahi H, Emura S, et al. Raman scattering study of thermal interdiffusion in InGaAs/InP superlattice structures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 70(1): 204-208.
[27] Estrera J P, Stevens P D, Glosser R, et al. Phonon mode study of near-lattice-matched InxGa1-xAs using micro-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1992, 61(16): 1927-1929.
Estrera J P, Stevens P D, Glosser R, et al. Phonon mode study of near-lattice-matched InxGa1-xAs using micro-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1992, 61(16): 1927-1929.
亢玉彬, 唐吉龙, 张健, 方铉, 房丹, 王登魁, 林逢源, 魏志鹏. 高应变InxGa1-xAs薄膜的结晶质量及光学特性[J]. 中国激光, 2019, 46(2): 0203002. Yubin Kang, Jilong Tang, Jian Zhang, Xuan Fang, Dan Fang, Dengkui Wang, Fengyuan Lin, Zhipeng Wei. Crystallization Quality and Optical Properties of High Strain InxGa1-xAs Film[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(2): 0203002.
 下载: 577次
下载: 577次