1 中国科学院物理研究所北京凝聚态物理国家研究中心,北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学物理科学学院,北京 100049
3 松山湖材料实验室,广东 东莞 523808
4 上海交通大学IFSA协同创新中心,上海 200240
基于超快超强激光的强场太赫兹辐射源通常具有较低的重复频率,此类辐射源的表征和应用对太赫兹时域波形和频谱测量技术提出了新要求。介绍了中国科学院物理研究所光物理重点实验室发展的几种针对太赫兹脉冲时域波形和频谱的单发测量系统,重点讨论了每种方案的设计原理和特点。这些单发探测方案适用于低重复频率的强场太赫兹脉冲源,有助于准确表征太赫兹辐射性质、深入理解太赫兹产生机制、拓展强场太赫兹应用范围。
测量 太赫兹辐射 电光采样 自相关测量 中国激光
2023, 50(17): 1714001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for GeoMechanics and Deep Underground Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
2 School of Science, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing 100089, China
3 Institute Key Laboratory of Optic Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
4 Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory, Dongguan 523808, China
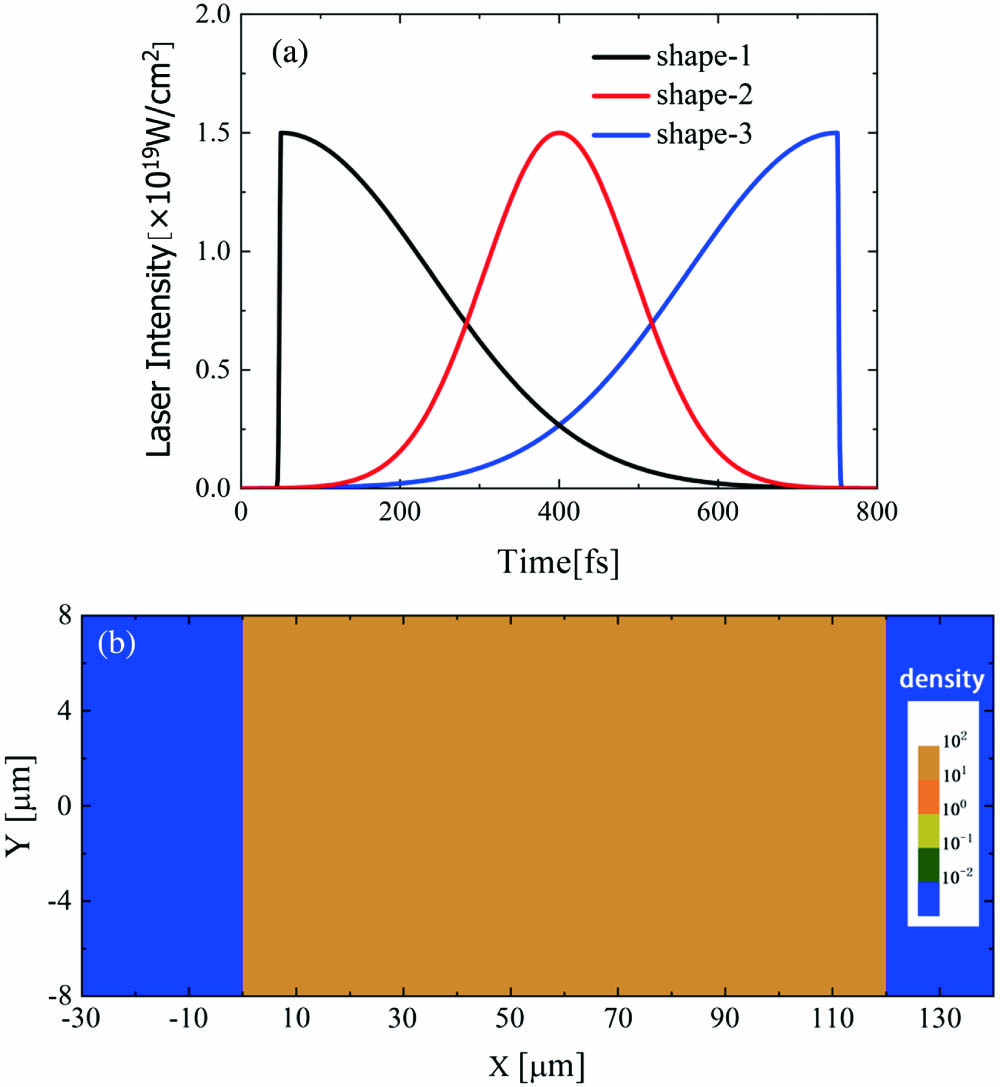
In the scheme of fast ignition of inertial confinement fusion, the fuel temperature mainly relies on fast electrons, which act as an energy carrier, transferring the laser energy to the fuel. Both conversion efficiency from the laser to the fast electron and the energy spectrum of the fast electron are essentially important to achieve highly effective heating. In this study, a two-dimensional particle in cell simulation is applied to study the generation of fast electrons from solid-density plasmas with different laser waveforms. The results have shown that the slope of the rising edge has a significant effect on fast electron generation and energy absorption. For the negative skew pulse with a relatively slow rising edge, the mechanism can most effectively accelerate the electrons. The overall absorption efficiency of the laser energy is optimized, and the fast electron yield in the middle- and low-energy range is also improved.
laser waveform fast electrons particle-in-cell simulations plasmas Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(6): 063801
1 中国科学院物理研究所北京凝聚态物理国家实验室, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学物理学院, 北京 100049
3 北京航空航天大学电子信息工程学院, 北京 100191
4 德州仪器(中国)有限公司北京办事处, 北京 100190
5 松山湖材料实验室, 广东 东莞 523808
报道了一种基于发光二极管(LED)的强脉冲场太赫兹相机,其工作原理是皮秒脉宽的强场太赫兹辐照到LED之后,当太赫兹电场强度大于50 kV/cm时,由于碰撞电离效应,LED两端会产生纳秒脉宽的光伏信号。利用此效应成功制备了扫描式和阵列式的LED太赫兹相机,并捕捉到了由铌酸锂倾斜波前技术产生的强场太赫兹焦斑。该相机有成本低、信号强、响应快、成像面积大等特点,并会为发展基于强场非线性效应的太赫兹成像技术提供新思路。
成像系统 发光二极管 强脉冲场太赫兹 倾斜波前 太赫兹成像 光学学报
2021, 41(24): 2411002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
2 School of Physical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4 Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory, Dongguan 523808, China
5 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Shanghai 201800, China
We propose a spatial diffraction diagnostic method via inserting a millimeter-gap double slit into the collimated terahertz beam to monitor the minute variation of the terahertz beam in strong-field terahertz sources, which is difficult to be resolved in conventional terahertz imaging systems. To verify the method, we intentionally fabricate tiny variations of the terahertz beam through tuning the iris for the infrared pumping beam before the tilted-pulse-front pumping setups. The phenomena can be well explained by the theory based on the tilted-pulse-front technique and terahertz diffraction.
spatial diffraction diagnostic method strong-field terahertz sources tilted-pulse-front pumping terahertz diffraction Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(5): 051901
1 北京航空航天大学电子信息工程学院, 北京 100083
2 北京航空航天大学微波感知与安防应用北京市重点实验室, 北京 100191
3 中国科学院物理研究所北京凝聚态物理国家实验室(筹), 北京 100190
4 中国科学院大学物理科学学院, 北京 100049
5 松山湖材料实验室, 广东 东莞 523808
国家自然科学基金、中国科学院战略重点研究计划、北京航空航天大学卓越和青年拔尖人才支持计划;
太赫兹技术 强太赫兹辐射脉冲源 铌酸锂 倾斜波前技术 飞秒激光

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3 School of Automation Science and Electrical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4 School of Physical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We systematically study the optimization of highly efficient terahertz (THz) generation in lithium niobate (LN) crystal pumped by 800 nm laser pulses with 30 fs pulse duration. At room temperature, we obtain a record optical-to-THz energy conversion efficiency of 0.43% by chirping the pump laser pulses. Our method provides a new technique for producing millijoule THz radiation in LN via optical rectification driven by joule-level Ti:sapphire laser systems, which deliver sub-50-fs pulse durations.
190.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics 040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 041901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing National Laboratory of Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Beijing 100190, China
2 Department of Physics, Heze University, Heze 274015, China
3 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
In our work, a high-quality broadband femtosecond optical vortex is obtained by use of a continuous spiral phase plate (SPP) to modulate an ultrashort femtosecond (fs) laser with a broadband spectrum. The experimental results demonstrate that the continuous SPP is of good quality and that it can be used to efficiently produce a high-power fs optical vortex.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S22602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 中国科学院光学天文重点实验室(国家天文台), 北京100012
2 中国科学院大学, 北京100049
3 北京师范大学天文系, 北京100875
4 中国科学院物理研究所, 北京100190
5 大阪大学激光工程研究所, 大阪565-0871, 日本
6 中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所, 上海201800
7 上海交通大学物理学院, 上海200240
8 高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海201800
9 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 绵阳621900
Magnetic reconnection (MR) is a universal physical process in plasma, in which the stored magnetic energy is converted into high-velocity flows and energetic particles. It is believed that MR plays an important role in many plasma phenomena such as solar fare, gamma-ray burst, fusion plasma instabilities, etc.. The process of MR has been studied in detail by dedicated magnetic-driven experiments. Here, we report the measurements of magnetic reconnection driven by Shenguang II lasers and Gekko XVII lasers. A collimated plasma jet is observed along the direction perpendicular to the reconnection plane with the optical probing. The present jet is very different from traditional magnetic reconnection outflows as known in the two-dimensional reconnection plane. In our experiment, by changing the delay of optical probing beam, we measure the temporal evolution of jet from 0.5 ns to 2.5 ns and its velocity around 400 km/s is deduced. Highcollimated jet is also confirmed by its strong X-ray radiation recorded by an X-ray pinhole camera. With the help of optical interferograms we calculate the jet configuration and its density distribution by using Abel inverting technique. A magnetic spectrometer with an energy range from hundred eV up to one MeV is installed in front of the jet, in the direction perpendicular to the reconnection plane, to measure the accelerated electrons. Two cases are considered for checking the acceleration of electrons. The results show that more accelerated electrons can be found in the reconnection case than in the case without reconnection. We propose that the formation and collimation of the plasma jet, and the electron energy spectrum may be possible directly influenced by the reconnection electric field, which is very important for understanding the energy conversion in the process of MR and establishment of the theoretical model. Finally the electron energy spectra of three different materials Al, Ta and Au are also shown in our work. The results indicate that the higher atomic number material can obtain a better signal-noise ratio, which provides some helpful references for our future work.
磁重联 电子加速 magnetic reconnection electron acceleration Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): 165201
1 中国科学院 物理研究所, 北京凝聚态物理国家实验室, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院 国家天文台, 北京 100012
3 上海交通大学 物理系, 激光等离子体教育部重点实验室, 上海 200240
4 高功率激光物理国家实验室, 上海 201800
利用“神光Ⅱ”激光装置的两束激光烧蚀半圆柱壳层靶产生了高速等离子体喷流。喷流的参数由光学和X射线诊断测量。喷流是准直的,在真空中传播。一维流体力学模拟被用来间接地计算喷流的速度。喷流的准直可能来源于高Z等离子体的辐射冷却。由于和年轻恒星喷流具有某些几何相似性,实验室喷流对于在实验室中模拟年轻恒星喷流具有潜在应用。
实验室天体物理 等离子体喷流 喷流准直 高功率激光 laboratory astrophysics plasma jet jet collimation high power laser 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032035
1 鲁东大学物理与光电工程学院, 山东 烟台 264205
2 中国科学院物理研究所光物理重点实验室, 北京 100190
3 中国科学技术大学中国科学院基础等离子体物理重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230026
4 中国科学院国家天文台光学天文重点实验室, 北京 100012
5 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
6 中国科学院高功率激光物理重点实验室, 上海 201800
7 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100094
8 浙江大学物理系聚变科学理论与模拟研究所, 浙江 杭州 310027
9 鲁尔大学理论物理研究所, 德国 波鸿 D-44780
10 马里兰大学帕克分校物理系, 美国 马里兰 University Park 20742
11 上海交通大学物理系教育部激光等离子体物理研究重点实验室, 上海 200240
激光等离子体磁重联实验再现了卫星观测到的日地磁场活动特征。一方面,实验再现了太阳冕区物质抛射及耀斑结构,包括明亮的尖屋顶状环、具有微细结构的磁化等离子体团以及二者之间因为磁场拉扯而产生的二阶电流片。另一方面,实验发现存在三个电子扩散区(EDR),这与欧洲空间局Cluster卫星先后在2003年和2005年发现的分别处于地磁尾重联区中间部位及两侧分形线位置的两类EDR结构相似。所不同的是,在激光等离子体磁重联实验中,两类EDR在一次重联过程中产生,但中心EDR出现时间晚于两侧EDR,且其发展速度更快,喷流速度接近或者超过迎流Alfven速度。通过对太阳耀斑附近、地磁尾重联区以及激光等离子体自生磁场重联区位置等离子体的参数比较,显示三者在一定程度上具有Euler-Alfven相似性,这表明可以通过激光等离子体自生磁场的重联过程来研究其他两种等离子体中的磁重联现象。
实验室天体物理 太阳冕区物质抛射 太阳耀斑 磁重联 电子扩散区 激光与光电子学进展
2013, 50(8): 080013





