
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information and Navigation College, Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710077, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 College of Computer and Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4 Teaching and Research Support Center, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
Remarkable progress has been made in satellite-based quantum key distribution (QKD), which can effectively provide QKD service even at the intercontinental scale and construct an ultralong-distance global quantum network. But there are still some places where terrestrial fiber and ground stations cannot be constructed, like harsh mountainous areas and air space above the sea. So the airborne platform is expected to replace the ground station and provide flexible and relay links for the large-scale integrated communication network. However, the photon transmission rate would be randomly reduced, owing to the randomly distributed boundary layer that surrounds the surface of the aircraft when the flight speed is larger than 0.3 Ma. Previous research of airborne QKD with boundary layer effects is mainly under the air-to-ground scenario in which the aircraft is a transmitter, while the satellite-to-aircraft scenario is rarely reported. In this article, we propose a performance evaluation scheme of satellite-to-aircraft QKD with boundary layer effects in which the aircraft is the receiver. With common experimental settings, the boundary layer would introduce a loss to the transmitted photons, decrease of the quantum communication time, and decrease of the secure key rate, which shows that the aero-optical effects caused by the boundary layer cannot be ignored. Our study can be performed in future airborne quantum communication designs.
satellite-to-aircraft quantum key distribution boundary layer aero-optical effects Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(4): 042702
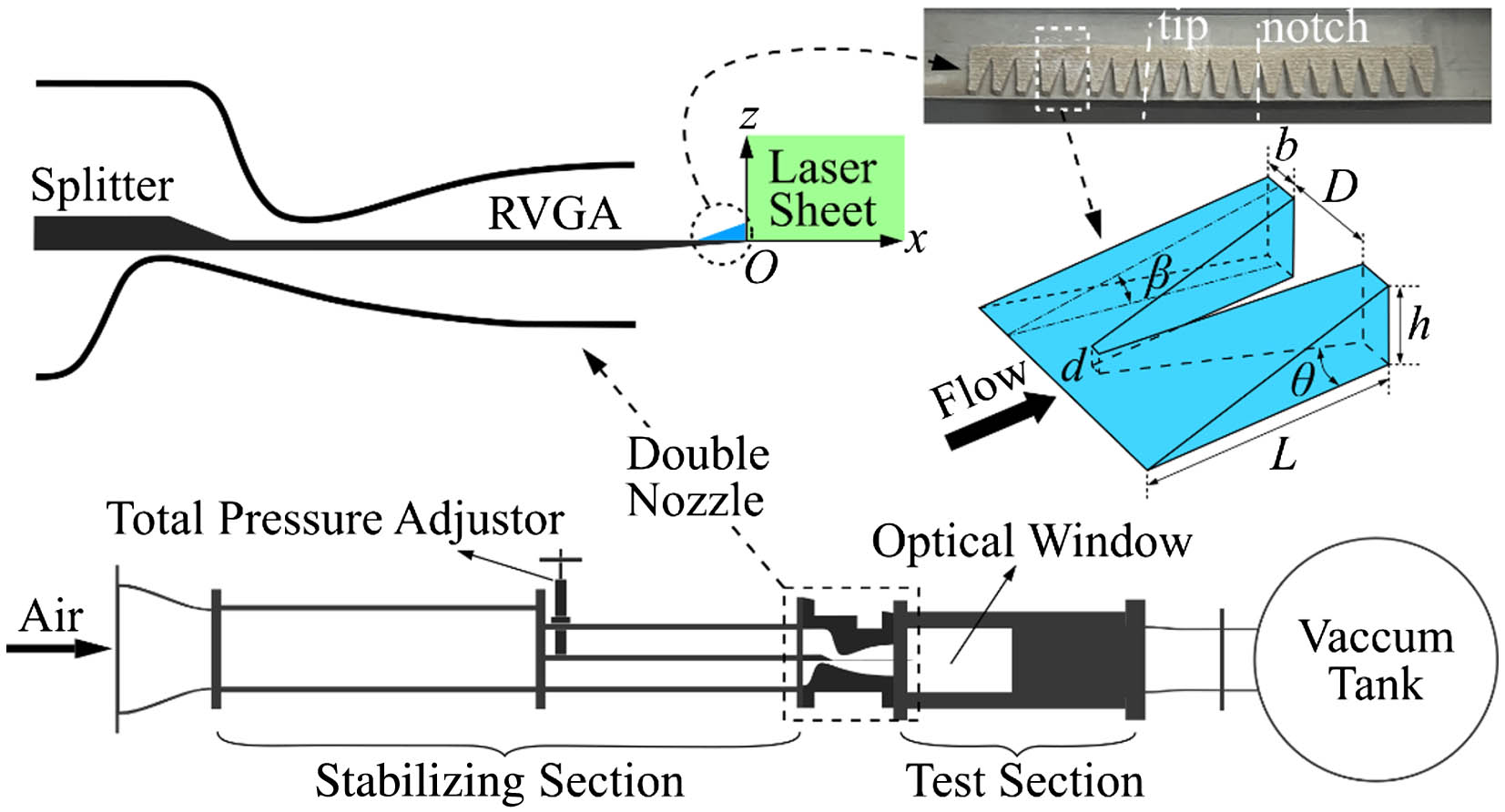
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Aerospace Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
The infrared imaging windows of the hyper/supersonic optical dome are encountering severe aero-optical effects (AOEs), so a flow control device, the ramp vortex generator array (RVGA) is proposed based on the ramp vortex generator to inhibit the supersonic mixing layers’ AOE, which is done by the nanotracer-based planar laser scattering technique and ray-tracing method. The experiments prove that under different pressure conditions, RVGA can reduce the mean and standard deviation of the root mean square of the optical path difference () and reduce the supersonic mixing layers’ thickness and mixture a great deal. The AOE of the pressure-matched mixing layer is the weakest. Higher RVGA results in better optical performance. RVGA has the potential to be applied to supersonic film cooling to reduce aero-optical aberrations.
aero-optical effects supersonic mixing layer RVGA OPDrms flow control Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(3): 030102
红外与激光工程
2022, 51(12): 20220713
扬州大学 机械工程学院, 江苏 扬州 225127
利用大涡模拟方法对受周期性控制的超声速混合层进行数值模拟, 揭示出受控涡结构的特性; 使用光线追踪方法计算光束穿越受控混合层流场产生的气动光学波前畸变。通过对受控涡结构特性的分析, 提出了一种气动光学效应校正方法, 并以不同控制周期下的超声速混合层为例, 对设计的校正方法进行检验。结果表明: 对于受周期性控制的超声速混合层, 按照校正方法获取的波前补偿信号能够使气动光学波前畸变的幅值降低50%以上; 指出混合层流场中涡结构的规整程度是影响畸变波前校正效果的关键因素。
周期控制 气动光学效应 超声速混合层 波前校正 periodic control aero-optical effects supersonic mixing layer wave front correction 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(8): 0809001
超音速飞行条件下红外成像探测系统受到气动光学效应影响, 其图像畸变和模糊退化问题十分严重, 严重影响了红外制导系统的制导精度。常规的气动光学效应模拟仿真研究存在大数据量计算和非连续仿真问题, 不能满足地面仿真的实时性需要。提出了基于高速湍流统计模型的快速仿真算法, 用于气动退化图像实时复原方法和算法研究。根据本文提出的算法仿真得到的退化图像与实际的气动退化图像相似度较高, 并且模型实现简单, 能够满足地面实时仿真的需要。
红外退化图像 气动光学效应 高速湍流 统计模型 实时仿真 infrared degradation image aero optical effects high speed turbulence statistical model real time simulation
1 北京理工大学 光电学院, 北京 100081
2 北京理工大学 光电学院, 北京 100081,
3 中国科学技术馆, 北京 100012
超高声速飞行器在大气中飞行时, 由于气动热和气动力的作用, 光学窗口会产生严重的气动光学效应, 使目标图像发生像偏移、抖动、模糊和能量衰减。利用有限元分析方法对光学窗口的热光效应、弹光效应和窗口热变形进行研究, 计算了由热光学效应、光学窗口热变形引起的点扩散函数峰值大小及峰值位置(像偏移)随时间的变化趋势。根据对温度场的分布分析, 计算了温度梯度对透过率的影响以及透过率与窗口热辐射随时间变化的趋势, 可为光学窗口的设计、材料的选择及后期的图像处理提供依据。
气动光学效应 光学窗口 热辐射 透过率 aero-optical effects optical window thermal radiation transmissivity
1 华中科技大学,图像识别与人工智能研究所,图像信息处理与智能控制教育部重点实验室,湖北,武汉,430074
2 华中科技大学,光电子工程系,电子科学与技术博士后流动站,湖北,武汉,430074
3 武汉工程大学,计算机图形图像处理研究室,湖北,武汉,430074
从时间序列退化图像中依次连续取两帧图像来估计湍流瞬态点扩展函数,将约束优化原理应用在气动光学效应退化图像的复原过程中.针对气动光学效应湍流点扩展函数复杂多峰、随机多变等特性,在点扩展函数的估计过程中,采用保凸峰等优化策略,将点扩展函数离散值的计算转化为基于松弛迭代的最优化估计,通过极小化准则函数估计点扩展函数值,进而恢复退化图像.实验结果表明,本文方法复原效果好,速度较快.
图像复原 气动光学效应 退化图像 优化估计 Image restoration Aero-optical effects Degraded image Optimization estimation
1 华中科技大学,图像识别与人工智能研究所,湖北,武汉,430074
2 中国航天科工集团公司,北京,100854
高速飞行器在大气层中高速飞行时,其头罩表面受大气气流的影响产生严重的气动光学效应.头罩周围湍流流场的高频变化,将影响来自目标的红外辐射光线的传输,使导引头成像器中目标图像产生模糊、抖动、偏移和能量衰减,给红外成像末制导带来不利影响,降低导引头对目标的探测、跟踪与识别能力,进而影响末制导精度.以红外成像制导技术在高速拦截器上的应用需求为背景,进行了高速湍流流场光学传输效应理论计算基本方法的分析,介绍了建立的数学模型和仿真软件,最后给出了典型状态下的计算结果.
气动光学效应 红外导引头 湍流流场 数字仿真 点扩散函数 Aero-optical effects Infrared seeker Turbulence field Numerical simulation Point spread function
高速流场光学传输效应是影响红外成像末制导技术在高速导弹上应用的关键.研究了气动光学传输效应中层流流场光学传输分量的计算方法,应用光线追迹法和物理光学方法研究层流流场引起的像偏移和低程度的像模糊,结合典型状态下的流场数据,进行了高速层流流场光学传输效应的数学仿真,得到了仿真计算结果.采用实际计算出的流场数据,得出的计算结果与工程计算的结果相比较,证明所建立的气动光学高速流场光学传输效应理论模型基本正确,可以用来进行仿真计算.
气动光学效应 层流流场 数值模拟 点扩散函数 Aero-optical effects Laminar flow field Numerical simulation Point spread function (PSF)
中国航天科工集团,第二研究院二部,北京,100854
采用红外成像寻的精确制导体制的高速飞行器在大气中以高超音速飞行时,头罩周围的高温激波流场将产生气动光学效应,这种效应严重影响了导引头对目标的探测、识别与跟踪,必须对此采取措施进行校正.文中介绍了气动光学效应的光电校正方法,包括基于波前检测与基于像清晰化校正以及高频微型光电子校正等自适应光学校正、图像帧频与帧积分时间自适应变化校正和光学与图像处理综合校正等方法,并对各种方法进行了比较分析.
气动光学效应 光电校正方法 自适应光学 相位差异 校正 Aero-optical effects Photoelectric correction methods Adaptive optics Phase diversity Correction





