光子学报
2021, 50(10): 1006002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Optical delay lines (ODLs) are one of the key enabling components in photonic integrated circuits and systems. They are widely used in time-division multiplexing, optical signal synchronization and buffering, microwave signal processing, beam forming and steering, etc. The development of integrated photonics pushes forward the miniaturization of ODLs, offering improved performances in terms of stability, tuning speed, and power consumption. The integrated ODLs can be implemented using various structures, such as single or coupled resonators, gratings, photonic crystals, multi-path switchable structures, and recirculating loop structures. The delay tuning in ODLs is enabled by either changing the group refractive index of the waveguide or changing the length of the optical path. This paper reviews the recent development of integrated ODLs with a focus on their abundant applications and flexible implementations. The challenges and potentials of each type of ODLs are pointed out.
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 230.5750 Resonators 130.4815 Optical switching devices 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(10): 101301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
A polarization-maintained coupled optoelectronic oscillator (COEO) with its performance significantly improved by a short-length unpumped erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is reported and experimentally investigated. A 10 GHz optical pulse train with a supermode suppression ratio of 61.8 dB and a 10 GHz radio frequency signal with a sidemode suppression ratio of 94 dB and a phase noise of 121.9 dBc/Hz at 10 kHz offset are simultaneously generated. Thanks to saturable absorption of the 1 m unpumped EDF, which introduces relatively large cavity loss to the undesired modes and noise, the supermode suppression ratio and the phase noise are improved by 9.4 and 7.9 dB, respectively.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 010604
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 430074, Wuhan, China
All-optical integrators are key devices for the realization of ultra-fast passive photonic networks, and, despite their broad applicability range (e.g., photonic bit counting, optical memory units, analogue computing, etc.), their realization in an integrated form is still a challenge. In this work, an all-optical integrator based on a silicon photonic phase-shifted Bragg grating is proposed and experimentally demonstrated, which shows a wide operation bandwidth of 750 GHz and integration time window of 9 ps. The integral operation for single pulse, in-phase pulses, and π-shifted pulses with different delays has been successfully achieved.
Integrated optics devices Wavelength filtering devices Analog optical signal processing All-optical devices Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000182

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 CETC Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Applications, Shijiazhuang 050081, China
3 The 54th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation, Shijiazhuang 050081 China
A full-band direct-conversion receiver using a microwave photonic in-phase and quadrature (I/Q) mixer is proposed and experimentally evaluated in terms of radio frequency (RF) range, port isolation, phase imbalance, conversion gain, noise figure, spurious-free dynamic range, and error vector magnitude. The proposed microwave photonic I/Q mixer shows significant advantages in local oscillator leakage and I/Q phase imbalance over entire RF bands, which are recognized as major drawbacks of conventional direct-conversion receivers.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 250.4110 Modulators Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010014
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We review the recent progress of photonic generation of millimeter wave (MMW)-ultra-wideband (UWB) signals. To fully satisfy the standard defined by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the baseband signal (background signal) and the residual local oscillator (LO) signal should be well controlled. We discuss several schemes in this work for generating background-free MMW-UWB signals that are fully compliant with the FCC requirement.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010007

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Electrical Engineering Department, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran 113658639, Iran
The common and traditional method for optical dispersion compensation is concatenating the transmitting optical fiber by a compensating optical fiber having a high-negative dispersion coefficient. In this Letter, we take the opposite direction and show how an optical fiber with a high-positive dispersion coefficient is used for dispersion compensation. Our optical dispersion compensating structure is the optical implementation of an iterative algorithm in signal processing. The proposed dispersion compensating system is constructed by cascading a number of compensating sub-systems, and its compensation capability is improved by increasing the number of embedded sub-systems. We also show that the compensation capability is a trade-off between the transmission length and bandwidth. We use the simulation results to validate the performance of the introduced dispersion compensating module. Photonic crystal fibers with high-positive dispersion coefficients can be used for constructing the proposed optical dispersion compensating module.
060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(3): 030601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Isfahan, Isfahan, Iran
In this Letter, a method based on the effects of imperfect oscillators in lasers is proposed to distinguish targets in continuous wave tracking lidar. This technique is based on the fact that each lidar signal source has a specific influence on the phase noise that makes real targets from the false ones. A simulated signal is produced by complex circuits, modulators, memory, and signal oscillators. For example, a deception laser beam has an unequal and variable phase noise from a real target. Thus, the phase noise of transmitted and received signals does not have the same power levels and patterns. To consider the performance of the suggested method, the probability of detection (PD) is shown for various signal-to-noise ratios and signal-to-jammer ratios based on experimental outcomes.
030.5630 Radiometry 050.5080 Phase shift 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 100302

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We present a theoretical analysis, systematic simulation, and experimental measurements for the phase noise, timing jitter, and frequency stability in the frequency distribution of millimeter waves over distant optical fiber links. The conception that the dissemination of a higher frequency reference instead of a lower one can achieve a better frequency stability is discussed and verified. We find that the system’s noise floor, including thermal noise, shot noise, and any other noise from electronic components, is considered to be a fundamental limitation for a frequency reference transmission system. Benefiting from the high-precision time delay variation discrimination and accurate locking control operation, a highly stabilized reference is distributed to a remote end over a 60 km spooled fiber, achieving a frequency stability of 4×10 17 at an average time 1000 s, corresponding to 23 fs of RMS timing jitter (0.01 Hz–1 MHz).
120.5050 Phase measurement 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120006
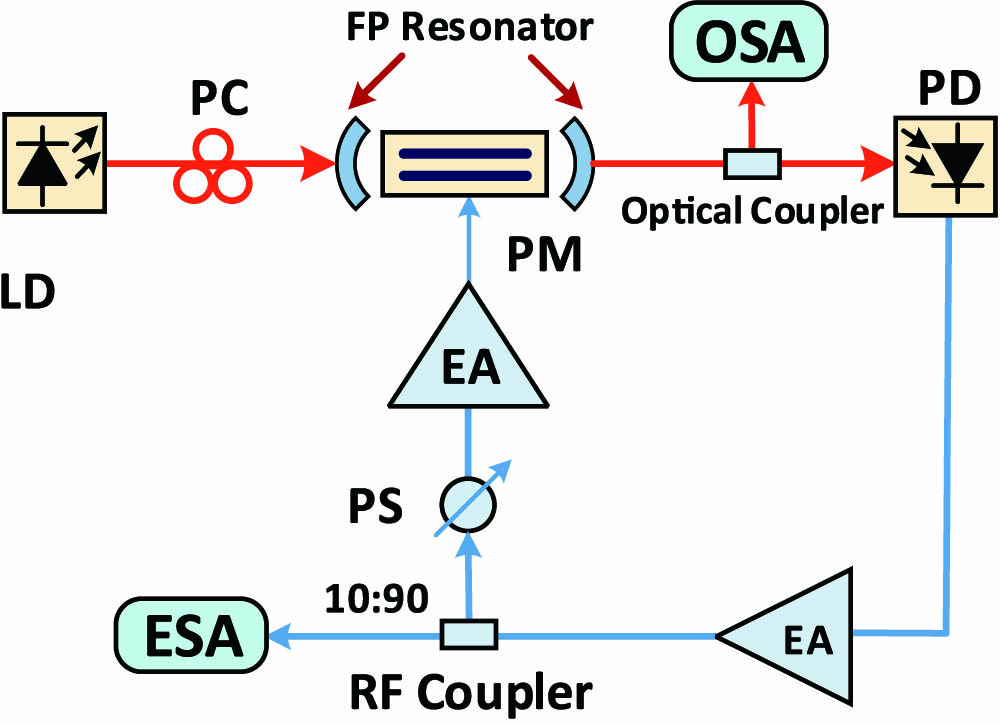
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
3 School of Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
A novel compact optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) employing a Fabry–Perot (FP) resonant electro-optic (EO) modulator is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The resonant modulator is used as the optical storage element as well as the mode selection element, which can greatly reduce the system complexity and make the system more portable. Moreover, the optical resonance and electrical transmission response for the FP resonant EO modulator are theoretically and experimentally studied. The proposed OEO oscillates at 10 and 20 GHz in the proof-of-concept experiment, and the corresponding single-sideband phase noise can reach below 118 and 108 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset frequency, respectively.
070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 070.5753 Resonators Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 110701





