Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 CAS Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
4 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
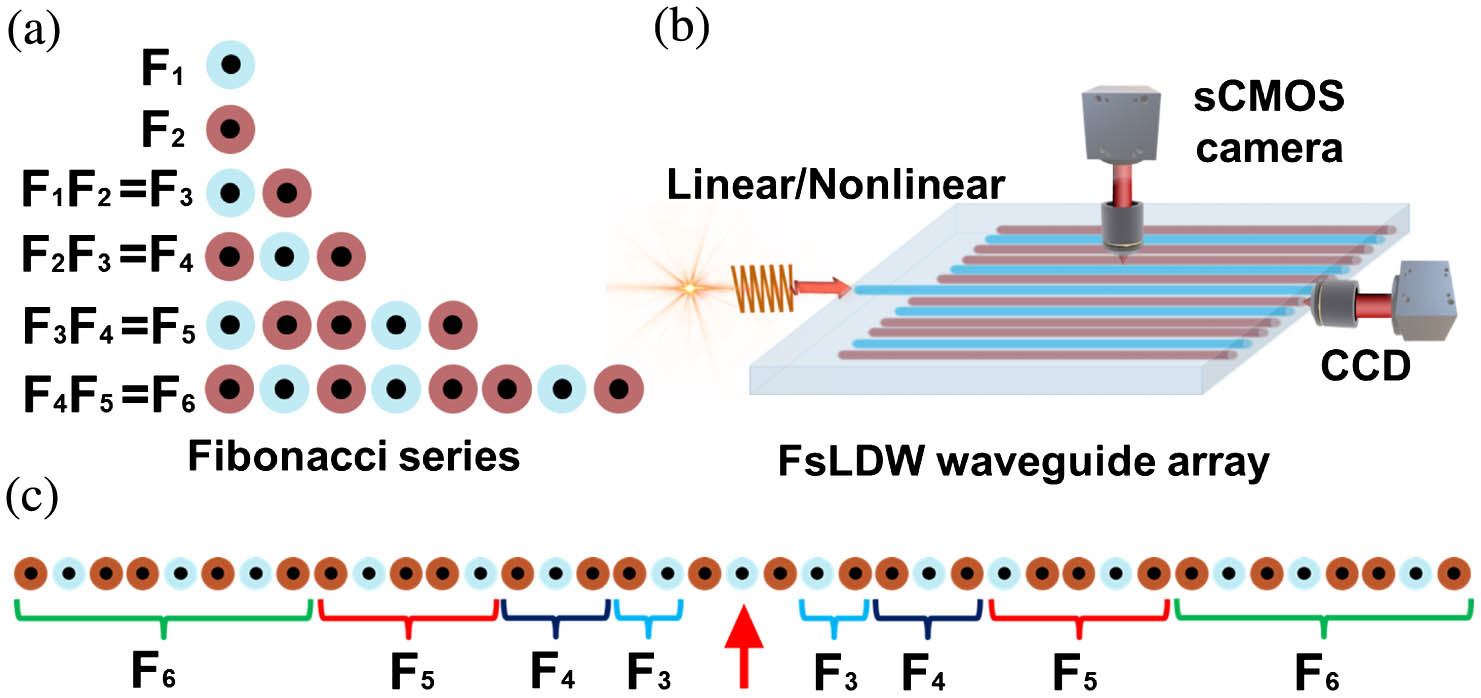
Based on the one-dimensional periodic and Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays, we experimentally investigate localized quantum walks (QWs), both in the linear and nonlinear regimes. Unlike the ballistic transport behavior in conventional random QWs, localization of QWs is obtained in the Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays both theoretically and experimentally. Moreover, we verify the enhancement of the localization through nonlinearity-induced effect. Our work provides a valid way to study localization enhancement in QWs, which might broaden the understanding of nonlinearity-induced behaviors in quasi-periodic systems.
Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays nonlinearity-induced effect localization enhancement Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 101301
重庆邮电大学 光通信与网络重点实验室, 重庆 400065
为降低卫星激光通信系统中的硬件资源,结合斐波那契数列的性质,基于矩阵扩展的方法提出了一种码率兼容低密度奇偶校验(RateCompatible LowDensity ParityCheck,RCLDPC)码的构造方法。用该方法所构造的RCLDPC码围长为6且具有准循环特性,所需存储元素少,降低了计算复杂度,利于硬件实现,更适合在卫星激光系统中传输。仿真结果表明:利用该方法构造的RCLDPC码在较大码率范围内均具有良好的译码性能,且在相同条件下,当误码率(BER)为10-6时,所构造的RCLDPC码与同码率、同码长的其他码型相比较,其净编码增益均有一定提高。
卫星激光通信 码率兼容低密度奇偶校验码 斐波那契数列 矩阵扩展 低复杂度 satellite laser communications RCLDPC codes Fibonacci sequence matrix extension low complexity
齐齐哈尔大学 计算机与控制工程学院, 黑龙江 齐齐哈尔 161006
用共参数的两种混沌系统生成可置换传统双随机相位编码系统中随机相位模板的新模板.将明文图像编码为相位信息, 克服原双随机相位编码系统对第一块相位模板不敏感的缺陷; 构建可产生均匀非相关随机序列的广义Fibonacci混沌系统, 生成均匀分布的相位模板进行图像加密, 提高密钥传输效率及系统对密钥的敏感性; 对一次加密得到的复值图像, 采用提取其振幅及相位的替代操作进行再加密, 解决其像素值不能通过按位“异或”进行替代的问题,使密文图像分布更均匀, 信息熵达到7.995 8, 能有效抵御统计分析攻击.在二次加密中, 将产生加密模板的混沌初值与一次加密得到的密文联系, 像素数改变率达到0.995 239, 更接近理想期望值, 增强了系统对明文的敏感性, 有效抵御选择明文攻击.仿真实验表明,该方法有效增加了密钥空间和密钥敏感性, 提高了加密系统加密效率和安全性.
信息光学 图像加密 虚拟光学加密 混合混沌 广义Fibonacci混沌 Information optics Image encryption Virtual optical encryption Hybrid chaotic Generalized Fibonacci chaos
1 中南大学物理与电子学院, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 长江大学物理与光电工程学院, 湖北 荆州 434023
3 中南大学超微结构与超快过程湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
斐波那契波带片(FiZP)在焦平面上有两个不同的主焦点且具有独特的自恢复特性,因此FiZP光束能够在不同平面同时捕获微粒,同时对微粒实现焦平面上的自由移动。仿真分析了FiZP的构成与轴向强度,利用液晶空间光调制器、倒置光学显微镜以及光学元件组合搭建实验平台,对微粒进行三维捕获。实验验证了FiZP光束具有三维光学捕获特性,并可用于构建三维光镊,实现复杂的捕获功能。
光电子学 三维光镊 斐波那契波带片(FiZP) 自恢复特性 双焦点 光学学报
2017, 37(10): 1035001
湖南理工学院 信息与通信工程学院, 湖南 岳阳 414000
利用常规材料构造了Fibonacci序列准周期结构, 运用传输矩阵法研究了该结构的空间传输特性, 并基于该结构优良的空间传输特性设计了小角度低通空间滤波器.数值模拟结果表明, 该小角度空间滤波器的角域带宽可通过改变序列的结构类型和序列数来调谐, 其调谐规律为: 随着Fibonacci 序列F(m,1)中m值的增加, 对应空间滤波器的角域带宽减小; 随着序列数的增大, 对应角域带宽也减小.在调谐的基础上, 还可通过改变构成准周期结构的介质折射率参量来精确调节其角域带宽.相比于基于超材料的小角度空间滤波器而言, 基于Fibonacci序列的小角度空间滤波器制备更简单, 且有望应用于新一代的高功率激光系统中.
信息光学 空间滤波器 传输矩阵法 Fibonacci 序列 准周期结构 小角域带宽 透射谱 Information optics Spatial filter Transfer matrix method Fibonacci sequence Quasi-periodic structure Small angle-domain bandwidth Transmittance spectra
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
We propose a new algorithm to extend the standard Fibonacci photon sieve to the phase-only gen-eralized Fibonacci photon sieve (GFi PS) and find that the focusing properties of the phase-only GFi PS are only relevant to the characteristic roots of the recursion relation of the generalized Fibonacci sequences. By switching the transparent and opaque zones on the basis of the generalized Fibonacci sequences, we not only realize adjustable bifocal lengths, but also give their corresponding analytic expressions. Besides, we investigate a special phase-only GFi PS, a spiral-phase GFi PS, which can present twin vortices along the axial coordinate. Compared with the single focusing system, bifocal system can be exploited to enhance the processing speed, and offer a broad range of applications, such as direct laser writing, optical tweezers or atom trapping and paralleled fluorescence microscope.
Diffractive lenses Generalized Fibonacci sequence Photon sieve Spiral phase X-ray optics Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2016, 14(1): 34
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A kind of diffractive optical elements (DOE) with star-ring topological structure is proposed and their focusing and imaging properties are studied in detail. The so-called star-ring topological structure denotes that a large number of pinholes distributed in many specific zone orbits. In two dimensional plane, this structure can be constructed by two constrains, one is a mapping function, which yields total potential zone orbits, corresponding to the optical path difference (OPD); the other is a switching sequence based on the given encoded seed elements and recursion relation to operate the valid zone orbits. The focusing and imaging properties of DOE with star-ring topological structure are only determined by the aperiodic sequence, and not relevant to the concrete geometry structure. In this way, we can not only complete the traditional symmetrical DOE, such as circular Dammam grating, Fresnel zone plates, photon sieves, and their derivatives, but also construct asymmetrical elements with anisotropic diffraction pattern. Similarly, free-form surface or three dimensional DOE with star-ring topological structure can be constructed by the same method proposed. In consequence of smaller size, lighter weight, more flexible design, these elements may allow for some new applications in micro and nanphotonics.
diffractive optics star-ring topology mapping function switching sequence Fibonacci Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): 962403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
A new photon sieve with Fibonacci sequence is proposed and a focusing and imaging model of the Fibonacci photon sieve (FiPS) is presented based on the Huygens-Fresnel principle.The results show that the FiPS presents two longitudinal foci with the ratio of golden mean.When the diameters of pinholes are equal to 1.165 times the width of corresponding orbits,the intensity of the two foci is almost the same.Compared with the resolution of Fibonacci zone plate (FiZP),FiPS has higher transverse resolution.Finally,higher transverse resolution on the two focal planes is improved by applying Gaussian apodized technology to the numbers of pinholes of FiPS.In consequence of smaller size,lighter weight,more flexible design and bifocal property,the FiPS can be applied to optical switches,nanometer lithography,bionic eyes,multi-focus imaging and ranging,even some new applications such as ranging from X-ray microscopy and THz imaging.
光学器件 光子筛 衍射积分 斐波那契 高斯切趾技术 optical devices photon sieve diffraction integral Fibonacci Gaussian apodized technology Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): 0923001
1 武汉理工大学 光纤传感技术国家工程实验室, 武汉 430070
2 武汉理工大学 光纤传感技术与信息处理教育部重点实验室, 武汉 430070
提出一种基于Fibonacci与最小均方差联合解调光纤法布里-珀罗传感器腔长的算法.利用Fibonacci搜索方法, 在一系列估计值中快速搜索到对应的最小均方差的数值, 并作为腔长解调结果.仿真分析了算法迭代次数与解调准确度之间的关系并进行温度测量实验.结果表明, 该算法的理论平均解调误差小于2×10-5 pm, 与实际腔长的拟合度优于0.9999, 解调动态范围可达2.5 mm;实验中, 该算法腔长解调分辨率为0.15 nm, 对应的温度分辨率达0.03℃, 解调时间少于0.03 s, 具有解调准确度高和运算速度快等优点.
光纤法布里-珀罗传感器 解调 均方差 Fibonacci搜索方法 分辨率 误差 快速度 Fabry-Perot interferometers Demodulation Mean square error Fibonacci search technique Resolution Error analysis High speed





