
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Precision Instruments, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 School of Physics, University of the Witwatersrand, Wits, South Africa
Spatial light modulators, as dynamic flat-panel optical devices, have witnessed rapid development over the past two decades, concomitant with the advancements in micro- and opto-electronic integration technology. In particular, liquid-crystal spatial light modulator (LC-SLM) technologies have been regarded as versatile tools for generating arbitrary optical fields and tailoring all degrees of freedom beyond just phase and amplitude. These devices have gained significant interest in the nascent field of structured light in space and time, facilitated by their ease of use and real-time light manipulation, fueling both fundamental research and practical applications. Here we provide an overview of the key working principles of LC-SLMs and review the significant progress made to date in their deployment for various applications, covering topics as diverse as beam shaping and steering, holography, optical trapping and tweezers, measurement, wavefront coding, optical vortex, and quantum optics. Finally, we conclude with an outlook on the potential opportunities and technical challenges in this rapidly developing field.
liquid crystal spatial light modulators liquid crystal devices structured light holography applications Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(8): 230026
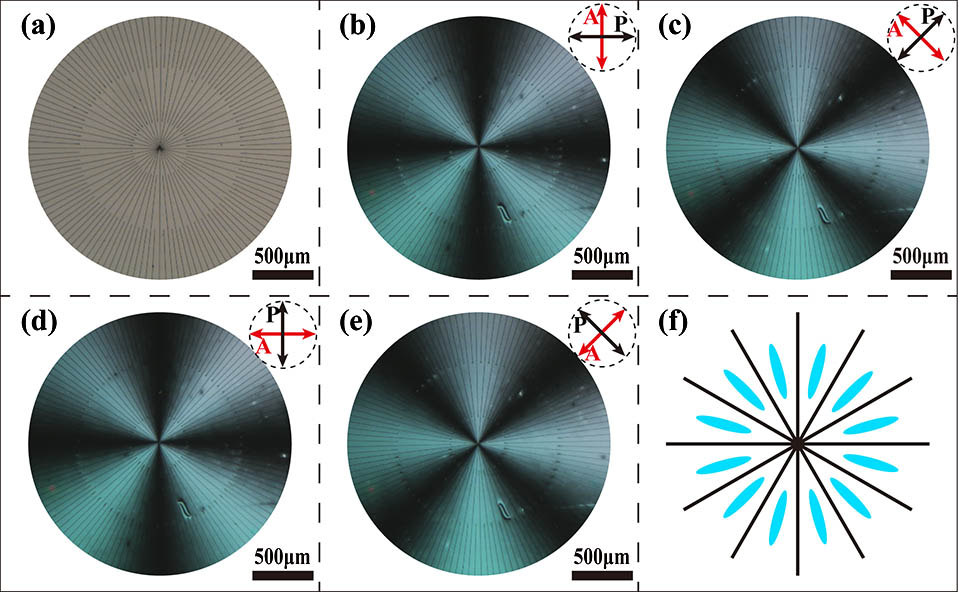
本文提出了一种基于空间光调制器的可实现任意图案设计的单步曝光光配向方法。通过像素级精确控制输出光的偏振方向, 可完成对局部区域液晶指向矢的自由取向, 从而实现具有任意图案设计的Pancharatnam-Berry(PB)相液晶器件的制作。这种非干涉曝光投影光配向法不仅简单、高效, 并且能大幅降低环境扰动的影响。基于该方法, 采用两种光取向材料制备了多种PB相液晶器件: 光栅、透镜、全息图和q-plate等。实验表明, 本文制作的PB相液晶器件可实现连续的相位分布和较高的衍射效率。基于这些PB相器件, 本文进一步提出了应用于增强现实显示领域的抬头显示和头戴式显示系统。
液晶器件 光配向 空间光调制器 几何相位 PB相 liquid crystal devices photoalignment spatial light modulator geometric phase Pancharatnam-Berry phase
为实现自然、舒适的增强现实显示, 需要解决传统增强现实显示中调焦和辐辏冲突的问题。多平面显示通过在空间中构建二维切片画面来实现三维显示, 由于每层画面都显示在不同深度, 因此可以准确地表达三维显示的深度信息, 有效地缓解调焦和辐辏冲突的问题。本文主要介绍基于液晶散射膜的多平面增强现实显示系统, 包括基于正型聚合物稳定向列相液晶、反型聚合物稳定向列相液晶、聚合物稳定胆甾相液晶的多平面增强现实显示。聚合物稳定向列相液晶的响应速度可以达到0.65 ms, 聚合物稳定胆甾相液晶的响应速度也在3 ms以内, 因此可以通过时分复用的方式实现多平面增强现实显示。最后讨论了基于液晶散射膜多平面增强现实显示有待解决的问题以及未来的发展趋势。
多平面显示 液晶器件 增强现实 聚合物稳定液晶 multi-plane display liquid crystal devices augmented reality PSLC
1 南开大学现代光学研究所, 天津 300350
2 天津光电子传感器与传感网络技术重点实验室, 天津 300350
3 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所应用光学国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
介绍了不同液晶材料在太赫兹(THz)波段的光学各向异性和外场调制特性。在此基础上,综述了几种基于液晶与人工电磁微结构相结合的THz功能器件,该器件可实现对THz波的调谐滤波、电磁诱导透明、相位调制以及偏振控制功能等;系统地分析了液晶与人工电磁微结构的相互作用机理、THz波长尺度下液晶的外场调控规律与表面相互作用。此外,还对THz液晶光子器件的研究发展趋势进行了展望。
太赫兹技术 石墨烯 光子晶体 超材料 液晶器件

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
2 Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
In this Letter, we present an electrically tunable holographic waveguide display (HWD) based on two slanted holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (HPDLC) gratings. Experimental results show that a see-through effect is obtained in the HWD that both the display light from HWD and the ambient light can be clearly seen simultaneously. By applying an external electric field, the output intensity of the display light can be modulated, which is attributed to the field-induced rotation of the liquid crystal molecules in the two HPDLC gratings. We also show that this electrically tunable performance enables the HWD to adapt to different ambient light conditions. This study provides some ideas towards the development of HWD and its application in augmented reality.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 050.1950 Diffraction gratings Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(1): 012301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Special Display Technology, Ministry of Education, National Engineering Laboratory of Special Display Technology, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Display Technology, Academy of Opto-Electronic Technology, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
2 Key Laboratory of Advanced Functional Materials and Devices of Anhui Province, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
3 School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
4 Aston Institute of Photonic Technologies, Aston University, Birmingham B4 7ET, UK
A band-gap-tailored random laser with a wide tunable range and low threshold through infrared radiation is demonstrated. When fluorescent dyes are doped into the liquid crystal and heavily doped chiral agent system, we demonstrate a wavelength tuning random laser instead of a side-band laser, which is caused by the combined effect of multi-scattering of liquid crystal (LC) and band-gap control. Through rotating the infrared absorbing material on the side of the LC cell, an adjustable range for random lasing of 80 nm by infrared light irradiation was observed.
Liquid-crystal devices Lasers, tunable Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000390

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Physics Department, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China
2 ECE Department, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong 999077, China
3 College of Information Science and Technology, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
4 E-mail: amwtam@ust.hk
A liquid crystal Pancharatnam–Berry (PB) axilens is proposed and fabricated via a digital micro-mirror-device-based photo-patterning system. The polarization-dependent device behaves as an axilens for a left-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring is focused with a long focal depth in the transverse direction at the output, and an anti-axilens for a right-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring gradually expands at the output. The modification of the size and the sharpness of the diffracted ring beam is demonstrated by encoding a positive (negative) PB lens term into the director expression of a PB (anti-)axicon.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 050.1965 Diffractive lenses 230.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(6): 062301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The MOE Key Laboratory of Weak-Light Nonlinear Photonics, and TEDA Institute of Applied Physics and School of Physics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300457, China
2 Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University of Ljubljana and Department of Complex Matter, J. Stefan Institute, Ljubljana SI1000, Slovenia
3 Faculty of Physics, Vienna University, Wien A-1090, Austria
4 Synergetic Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tianjin 300071, China
We develop a new method for smooth and continuous space-variant alignment of the liquid crystal medium in micro-patterned structures, which is based on a radial micro-structured pattern of polymeric ribbons exhibiting out-of-plane orientation with respect to the ITO-coated glass plates. Thanks to the broad range of electrical tunability of the optical retardation for the micro-patterned liquid crystal structures, transformation of the fundamental Gaussian beam into different types of specific beams, including generalized cylindrical vector beams, vortex beams, and vectorial vortex beams, is efficiently demonstrated.
050.4865 Optical vortices 230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 220.0220 Optical design and fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(7): 070501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Electronics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
3 Research Institute of Electronic Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
4 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Space Microwave, Xi’an 710100, China
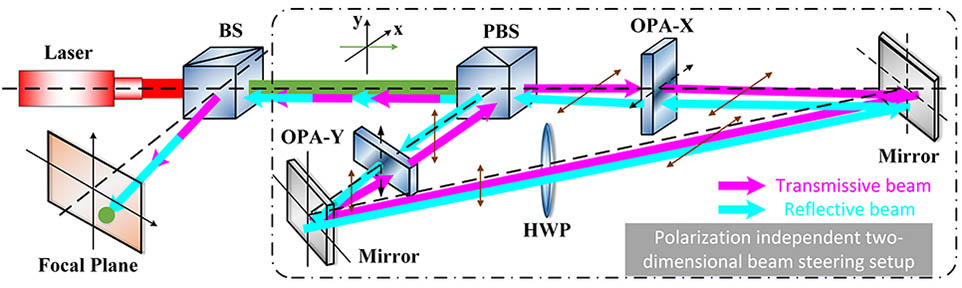
A polarization-independent nonmechanical laser beam steering scheme is proposed to realize continuous two-dimensional (2D) scanning with high efficiency, where the core components are two polarization-dependent devices, which are called liquid crystal optical phased arrays (LC-OPAs). These two one-dimensional (1D) devices are orthogonally cascaded to work on the state of azimuthal and elevation steering, respectively. Properties of polarization independence as well as 2D beam steering are mathematically and experimentally verified with a good agreement. Based on the experimental setup, linearly polarized beams with different polarization angles are steered with high accuracy. The measured angular deviations are less than 5 μrad, which is on the same order of the accuracy of the measurement system. This polarization-independent 2D laser beam steering scheme has potential application for nonmechanical laser communication, lidar, and other LC-based systems.
160.3710 Liquid crystals 120.4820 Optical systems 230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 101601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Microelectronics and Optoelectronics, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw 00-665, Poland
2 Institute of Applied Physics, Military University of Technology, Warsaw 00-908, Poland
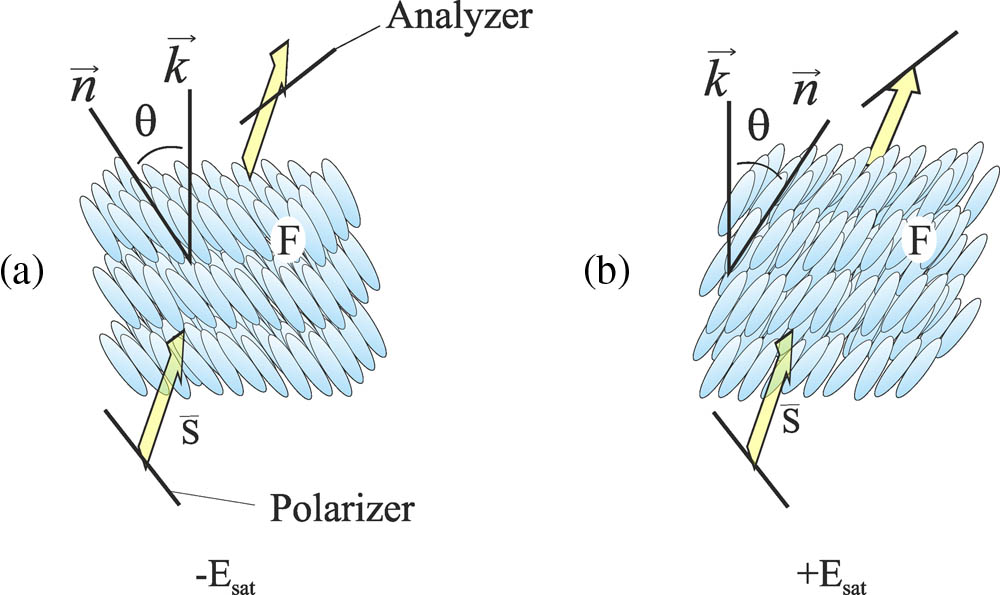
Surface stabilized (anti) ferroelectric liquid crystal cells can be used as an optically addressed media for optical data processing. The structure of the cell has to contain a photo sensible agent, i.e., an absorbing dye-doped orienting layer. The all-optical generation of the diffractive grating can be done due to the switching parameters of the smectic slab within cells with a sensitive layer. This Letter considers a study of the optically induced charge generation into the dye-doped layer, and the explanation of the phenomena of the selective molecular director reorientation, while cell driving what leads to the induction of phase grating.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 102302





