Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
A novel see-through virtual retina display (VRD) system is proposed in this Letter. An optical fiber projector is used as the thin-light-beam source, which is modified from a laser scan projector by separating the laser sources and the scan mechanical structure. A synthetic aperture method is proposed for simple, low-cost fabrication of a volume holographic lens with large numerical aperture. These two key performance-enhanced elements are integrated into a lightweight and ordinary-glasses-like optical see-through VRD system. The proposed VRD system achieves a weight of 30 g and a diagonal field of view of 60°.
090.2820 Heads-up displays 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 170.5755 Retina scanning 110.2350 Fiber optics imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(9): 090901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonics Research Center, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
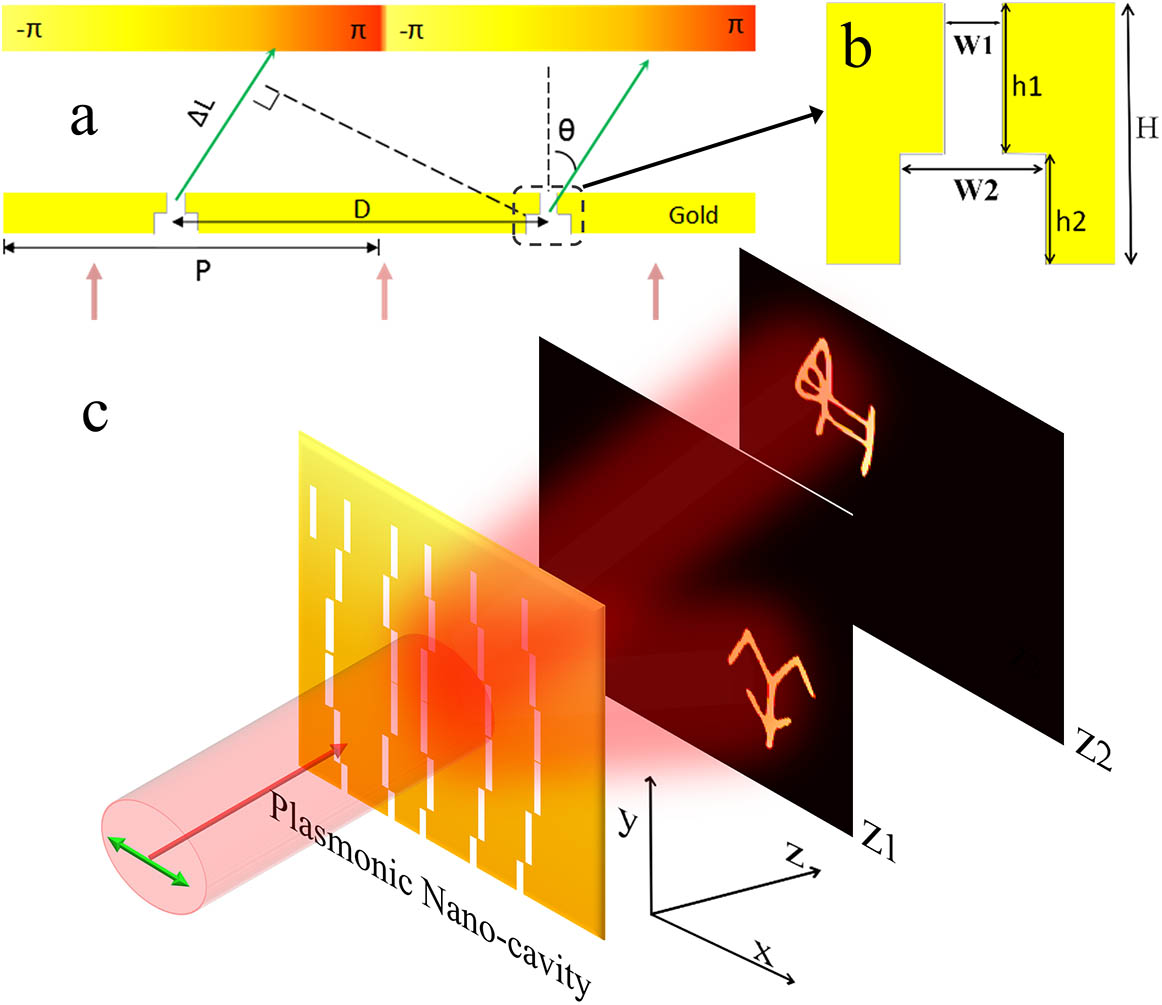
Controlling both amplitude and phase of light in the subwavelength scale is a challenge for traditional optical devices. Here, we propose and numerically investigate a novel plasmonic meta-hologram, demonstrating broadband manipulation of both phase and amplitude in the subwavelength scale. In the meta-hologram, phase modulation is achieved by the detour phase distribution of unit cells, and amplitude is continuously modulated by a T-shaped nano-cavity with tunable plasmonic resonance. Compared to phase-only holograms, such a meta-hologram could reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) images with higher signal-to-noise ratio and better image quality, thus offering great potential in applications such as 3D displays, optical communications, and beam shaping.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.3918 Metamaterials 090.2890 Holographic optical elements Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 062402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
3 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies of Jiangsu Province and Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Technologies of Ministry of Education, Suzhou 215006, China
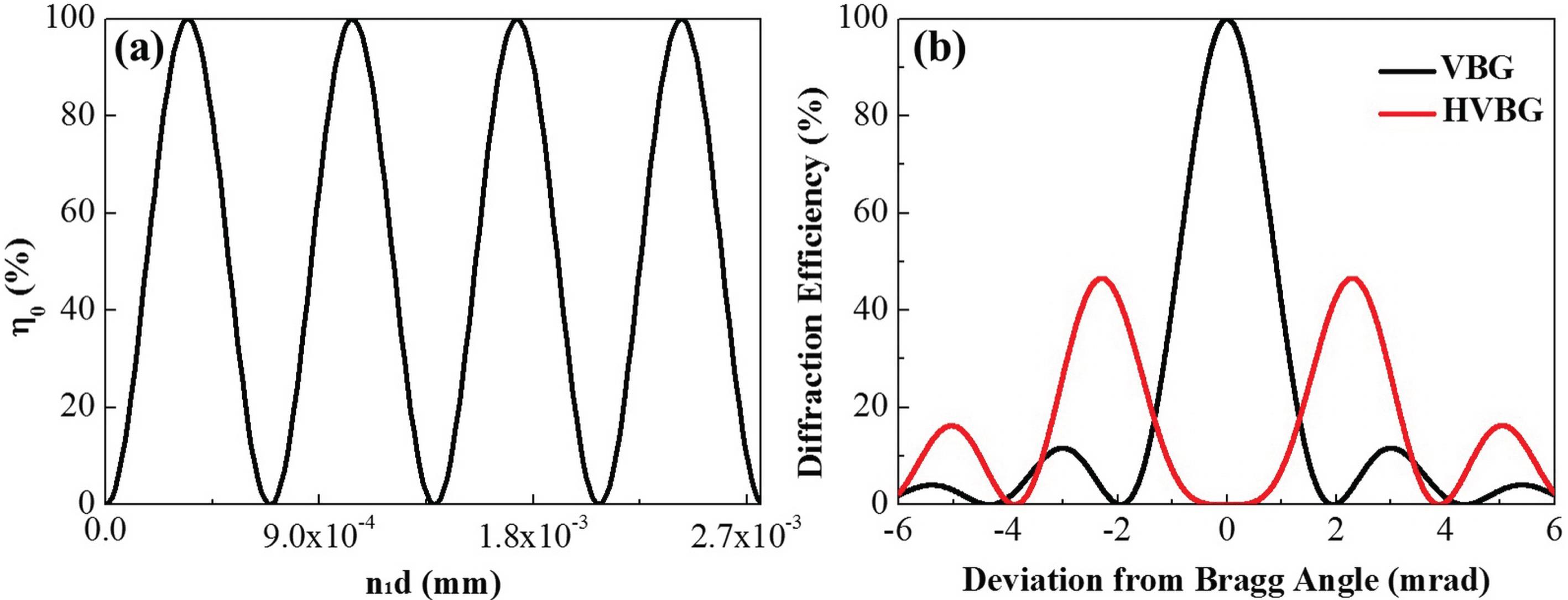
A band-stop angular filter (BSF) based on hump volume Bragg gratings (HVBGs) is proposed. Band-stop filtering in a two-stage amplifier laser system is discussed and simulated. Simulation results show that small-scale self-focusing effects in the laser system can be effectively suppressed with the BSF due to the control of fast nonlinear growth in a specific range of spatial frequencies in the laser beam. Near-field modulation of the output beam from the laser system was decreased from 2.69 to 1.37 by controlling the fast nonlinear growth of spatial frequencies ranging from $0.6~\text{mm}^{-1}$ to $1.2~\text{mm}^{-1}$ with the BSF. In addition, the BSF can be used in a plug-and-play scheme and has potential applications in high-power laser systems.
holographic optical elements self-focusing spatial filtering volume gratings High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(2): 02000e29

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Signal Processing and Transmission, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, China
2 Key Lab of Broadband Wireless Communication and Sensor Network Technology, Ministry of Education, Nanjing, China
It is shown that orbital angular momentum (OAM) is a promising new resource in future classical and quantum communications. However, the separation of OAM modes is still a big challenge. In this paper, we propose a simple and efficient separation method with a radial varying phase. In the method, specific radial varying phases are designed and modulated for different OAM modes. The resultant beam is focused to the spots with different horizontal and vertical positions after a convex lens, when the coordinate transformation, including two optical elements with coordinate transformation phase and correct phase, operates on the received beam. The horizontal position of the spot is determined by the vortex phases, and the vertical position of the spot is dependent on the radial varying phases. The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method is feasible both for separation of two OAM modes and separation of three OAM modes. The proposed separation method is available in principle for any neighboring OAM modes because the radial varying phase is controlled. Additionally, no extra instruments are introduced, and there is no diffraction and narrowing process limitation for the separation.
Optical vortices Spatial discrimination Holographic optical elements Photonics Research
2017, 5(4): 04000267
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Electroholography Group, Brigham Young University, 459 Clyde Building, Provo, Utah 84602, USA
2 MIT Media Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Mass. Ave, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, USA
This paper presents progress on the characterization of guided-wave light modulators for use in a low-cost holographic video monitor based on the MIT scanned-aperture architecture. A custom-built characterization apparatus was used to study device bandwidth, RGB operation, and linearity in an effort to identify optimal parameters for high bandwidth, GPU-driven, full-color holographic display.
090.1705 Color holography 090.1970 Diffractive optics 090.2870 Holographic display 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 090.5694 Real-time holography Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(1): 010003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Microelectronics and Optoelectronics, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw 00-665, Poland
2 Institute of Applied Physics, Military University of Technology, Warsaw 00-908, Poland
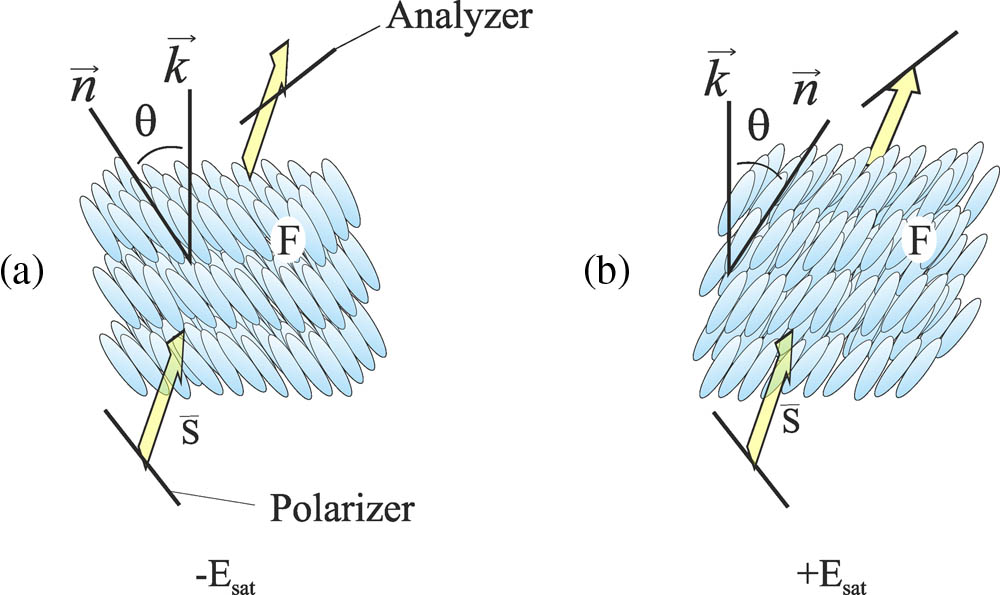
Surface stabilized (anti) ferroelectric liquid crystal cells can be used as an optically addressed media for optical data processing. The structure of the cell has to contain a photo sensible agent, i.e., an absorbing dye-doped orienting layer. The all-optical generation of the diffractive grating can be done due to the switching parameters of the smectic slab within cells with a sensitive layer. This Letter considers a study of the optically induced charge generation into the dye-doped layer, and the explanation of the phenomena of the selective molecular director reorientation, while cell driving what leads to the induction of phase grating.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 102302

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
2 Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Institute of Micro & Nano Optics, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, .China
We propose and demonstrate free-space optical data links based on coaxial sidelobe-modified optical vortices (CSMOVs). In contrast to the optical communication systems based on amplitude, frequency, or phase detection, the proposed scheme uses the radii ratio between the principle ring and the first sidelobe of the CSMOV. Therefore, the demand of stringent alignment and/or accurate phase matching is released. We design and optimize a composite computer-generated hologram to generate a CSMOV with four topological charges (TCs). Extracted from the images captured by a CCD camera, the radii ratio between the principle ring and the first sidelobe of different TCs are consistent with the theoretical values.
050.4865 Optical vortices 060.4510 Optical communications 090.2890 Holographic optical elements Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 100502
1 浙江工业大学 理学院应用物理系, 浙江 杭州 310023
2 杭州博源光电科技有限公司, 浙江 杭州 310023
基于全息光学理论分析了全息光学元件的高斯成像性质, 包括光焦度、成像位置、衍射效率以及作为光纤光谱仪光栅元件的可行性, 并以全息光栅的成像理论以及光谱仪工作原理为基础, 设计了光谱仪器光学系统的各个参数, 通过Zemax软件的仿真、像质评价及优化, 得出最终的参数和模拟结果。所使用的全息光栅记录波长为575 nm, 记录光束之间的夹角为10°, 一束为平面波, 一束为球面波, 焦距40 mm,使用+1级衍射光, 光栅孔径为10 mm。光谱仪的工作波长范围为400 nm~800 nm, 体积140 mm*30 mm*40 mm, 谱面展宽29.1 mm。通过在光学平台上搭建光路, 利用已研发完成的电路系统及光谱仪软件, 针对汞灯光谱进行了试验, 光谱分辨率优于8 nm, 测量得到的汞灯光谱与标准汞灯光谱一致, 表明了所设计的基于全息元件的光纤光谱仪光学系统是可行的。
全息光学元件 光纤光谱仪 Zemax仿真 光学设计 holographic optical elements fiber spectrometer Zemax simulation optical design
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Physics, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
A novel scheme is proposed, in which the aberrations in the off-axis holographic lenses used as demultiplexers are reduced to a low enough level for relatively small channel spacing. The scheme includes optimizing the recording and reconstruction geometries and collimating the reconstruction wave with a gradient-index lens. A demultiplexer operated in the 1 550-nm band with 5-nm channel spacing and ?\infty-dB crosstalk is obtained using the scheme. The channel spacing can be decreased to 2 nm by etching the cladding of the output fibers to a smaller size.
解复用器 全息透镜 离轴 单色像差 060.1810 Buffers, couplers, routers,switches, and multiplexers 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 090.1000 Aberration compensation Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(9): 090603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optics and Electron Information Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, Pennsylvania State University, PA 16802, USA
An electrically controlled optical chopper based on switchable holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (H-PDLC) gratings is demonstrated through a programmable, adjustable, and periodic external driving source. Compared with traditional mechanical optical choppers, the H-PDLC chopper exhibits many advantages, including faster response time, less waveform deformation, as well as easier integration, control, and fabrication, to name a few. Its excellent performance makes the device potentially useful in frequency modulation optical systems, such as frequency division multiplexed microscopy system.
聚合物分散液晶光栅 光斩波器 占空比 230.2090 Electro-optical devices 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 050.1950 Diffraction gratings 230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(12): 1167





