
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics and Applied Optics Beijing Area Major Laboratory, Center for Advanced Quantum Studies, , Beijing 100875, China
2 College of Textiles & Clothing, , Qingdao 266071, China
3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Energy Conversion and Storage Materials, College of Chemistry, , Beijing 100875, China
The aggregation and photoinduced excited state dynamics of organic -conjugated molecules play a vital role in solar energy conversion and applications. This work investigates how solvent polarity affects the aggregation behavior and the photophysical process of perylene diimide dimer (PDI-II). The results show that the conjugations between PDI intramolecular chromophores are more likely to generate excimer, and the conjugations between PDI intermolecular chromophores are more likely to experience symmetry-breaking charge separation. Our study can provide a reference for the design of high-efficiency solar energy conversion materials.
excimer perylene diimide dimer solvent effect transient absorption spectroscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(10): 100009
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (IESL), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), Herakleio 70013, Greece
2 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Hellenic Mediterranean University, Herakleio 71004, Greece
3 Department of Materials Science and Technology, University of Crete, Herakleio 70013, Greece
4 Department of Physics, University of Crete, Herakleio 70013, Greece
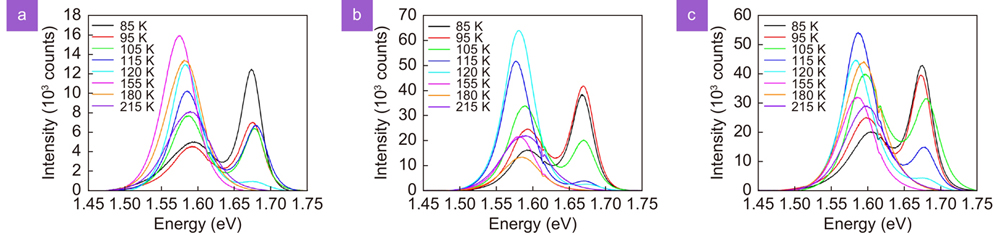
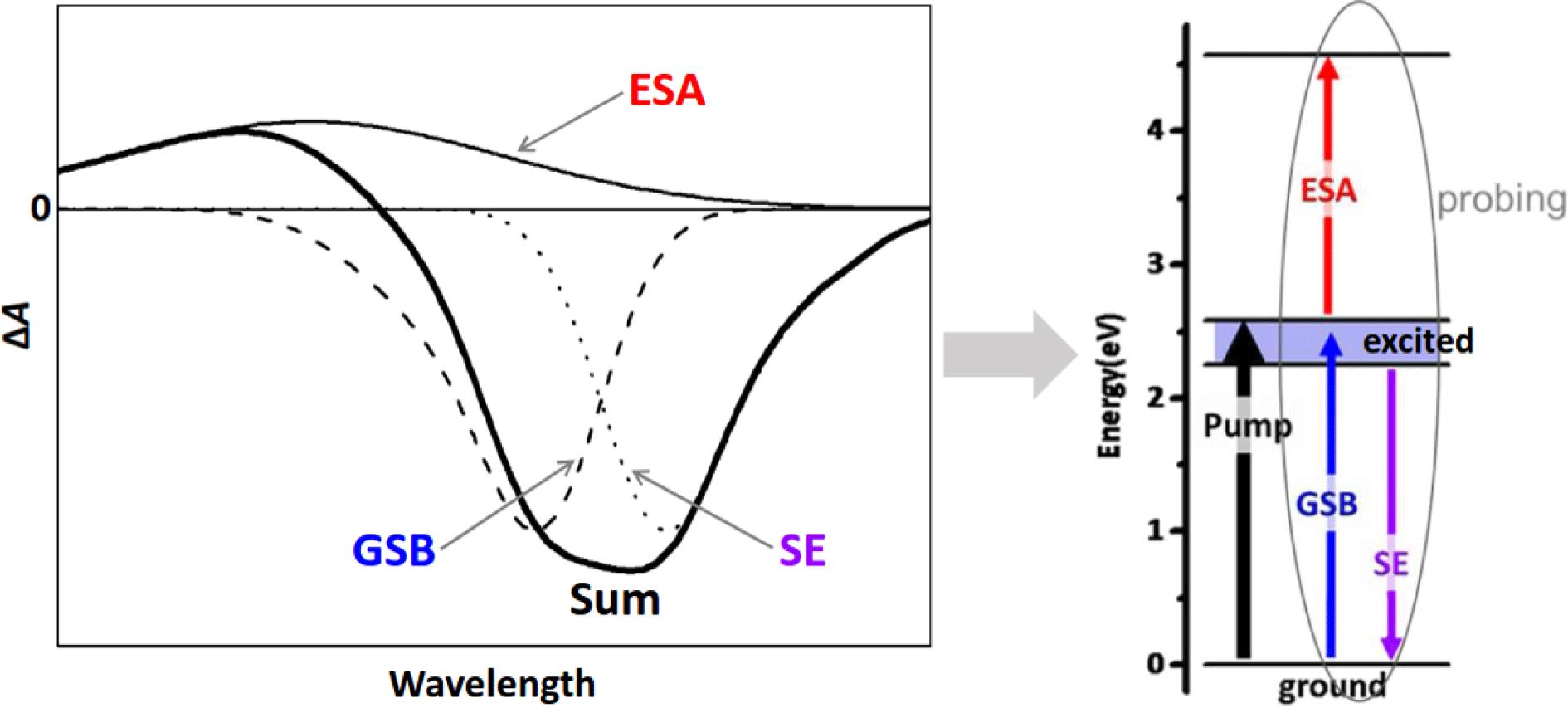
Despite that organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites have attracted enormous scientific attention for energy conversion applications over the recent years, the influence of temperature and the type of the employed hole transport layer (HTL) on the charge carrier dynamics and recombination processes in perovskite photovoltaic devices is still largely unexplored. In particular, significant knowledge is missing on how these crucial parameters for radiative and non-radiative recombinations, as well as for efficient charge extraction vary among different perovskite crystalline phases that are induced by temperature variation. Herein, we perform micro photoluminescence (μPL) and ultrafast time resolved transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) in Glass/Perovskite and two different Glass/ITO/HTL/Perovskite configurations at temperatures below room temperature, in order to probe the charge carrier dynamics of different perovskite crystalline phases, while considering also the effect of the employed HTL polymer. Namely, CH3NH3PbI3 films were deposited on Glass, PEDOT:PSS and PTAA polymers, and the developed Glass/CH3NH3PbI3 and Glass/ITO/HTL/CH3NH3PbI3 architectures were studied from 85 K up to 215 K in order to explore the charge extraction dynamics of the CH3NH3PbI3 orthorhombic and tetragonal crystalline phases. It is observed an unusual blueshift of the bandgap with temperature and the dual emission at temperature below of 100 K and also, that the charge carrier dynamics, as expressed by hole injection times and free carrier recombination rates, are strongly depended on the actual pervoskite crystal phase, as well as, from the selected hole transport material.Despite that organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites have attracted enormous scientific attention for energy conversion applications over the recent years, the influence of temperature and the type of the employed hole transport layer (HTL) on the charge carrier dynamics and recombination processes in perovskite photovoltaic devices is still largely unexplored. In particular, significant knowledge is missing on how these crucial parameters for radiative and non-radiative recombinations, as well as for efficient charge extraction vary among different perovskite crystalline phases that are induced by temperature variation. Herein, we perform micro photoluminescence (μPL) and ultrafast time resolved transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) in Glass/Perovskite and two different Glass/ITO/HTL/Perovskite configurations at temperatures below room temperature, in order to probe the charge carrier dynamics of different perovskite crystalline phases, while considering also the effect of the employed HTL polymer. Namely, CH3NH3PbI3 films were deposited on Glass, PEDOT:PSS and PTAA polymers, and the developed Glass/CH3NH3PbI3 and Glass/ITO/HTL/CH3NH3PbI3 architectures were studied from 85 K up to 215 K in order to explore the charge extraction dynamics of the CH3NH3PbI3 orthorhombic and tetragonal crystalline phases. It is observed an unusual blueshift of the bandgap with temperature and the dual emission at temperature below of 100 K and also, that the charge carrier dynamics, as expressed by hole injection times and free carrier recombination rates, are strongly depended on the actual pervoskite crystal phase, as well as, from the selected hole transport material.
transient absorption spectroscopy μ-photoluminescence variable temperature perovskite crystalline phases hole transport layer charge carrier dynamics Opto-Electronic Science
2022, 1(4): 210005
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室和超强激光科学卓越中心, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
阿秒瞬态吸收(Attosecond Transient Absorption, ATA)谱是一种非常有用的研究原子分子中亚飞秒时间尺度超快动力学的技术。通过数值求解含时薛定谔方程,模拟了氢分子离子( H2+)在近红外(NIR)和深紫外(XUV)强复合激光场中的演化,对比了 H2+在核动和不动两种情形下ATA谱的异同。研究结果显示,当核不动时,所得的ATA谱与原子下的结构类似;当核动时,ATA谱呈现出丰富的周期调制的吸收线结构,而且其调制周期恰好等于NIR光周期的一半。通过分析 H2+的电离解离特性,证实了该半周期调制是源于 H2+基态和激发态的不同量子跃迁路径间的干涉。对比两种情形下的ATA谱,可以看出核运动对分子ATA谱的显著影响。
超快光学 瞬态吸收谱 阿秒脉冲 含时薛定谔方程 半周期调制
利用带间激发的超快瞬态吸收光谱,研究了导电(n型)氮(N)掺杂和半绝缘(SI)钒(V)掺杂6H-SiC晶片的超快载流子复合动力学过程。N杂质和/或固有缺陷的间接复合主导了n型6H-SiC的载流子弛豫,其寿命超过了10 ns。与n型6H-SiC相比,V掺杂对SI-6H-SiC的瞬态吸收具有显著的调制作用,这源于由V深能级的载流子俘获引起的一个额外的载流复合过程。载流子俘获(寿命约为160 ps)比间接复合快2个数量级以上。通过简化能级模型并进行全局分析,研究了6H-SiC的载流子复合机制,准确地获得了6H-SiC的载流子寿命。
超快光学 载流子动力学 瞬态吸收光谱 n型SiC 半绝缘SiC 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(6): 063201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, Department of Chemical Physics, and Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information & Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, PR China
Over the past decade the integration of ultrafast spectroscopy with nanoscience has greatly propelled the development of nanoscience, as the key information gleaned from the mechanistic studies with the assistance of ultrafast spectroscopy enables a deeper understanding of the structure–function interplay and various interactions involved in the nanosystems. This mini-review presents an overview of the recent advances achieved in our ultrafast spectroscopy laboratory that address the ultrafast dynamics and related mechanisms in several representative nanomaterial complex systems by means of femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy.We attempt to convey instructive, consistent information regarding the important processes, pathways, dynamics, and interactions involved in the nanomaterial complex systems, most of which exhibit excellent performance in photocatalysis.
nanomaterials nanomaterials time-resolved femtosecond pump–probe time-resolved femtosecond pump–probe transient absorption spectroscopy transient absorption spectroscopy ultrafast dynamics ultrafast dynamics High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(3): 03000e22





