2015, 13(11) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第13卷 第11期
Space-adjustable dark magneto-optical trap for efficient production of heteronuclear molecules Download:993次
Download:993次
 Download:993次
Download:993次We present a simple, robust, space-adjustable dark magneto-optical trap (MOT) for the efficient production of heteronuclear molecules. Double-mixed beams made up of repumping beams and depumping beams propagate in nearly opposite directions in the dark MOT. This optical arrangement can easily adjust the spatial positions of two clouds by changing the power ratio of the two repumping beams, and ensure a good overlap, which is very necessary for the production of heteronuclear molecules. The imaging of cold atoms by camera and the collision-induced loss rate obtained by recording the loading curve of the cold atoms show that we obtain a perfect overlap of atom clouds. The number of RbCs molecules with the double-mixed beams is improved by 70%, which is higher than the one with the single-mixed beam.
020.3320 Laser cooling 020.7010 Laser trapping 300.6360 Spectroscopy, laser 300.6390 Spectroscopy, molecular Concave grating miniature spectrometer with an expanded spectral band by using two entrance slits Download:927次
Download:927次
 Download:927次
Download:927次A new miniature spectrometer with two entrance slits is proposed to expand the spectral band. The proposed spectrometer is designed such that the two entrance slits share the same concave grating and detector array. The two slits are located at different positions such that the spectral range of the same light source incident on the detector array varies greatly between the two slits. Only one of the two slits is illuminated at a given time; as such, the two spectral ranges are sequentially measured. Theoretical calculation and experimentation are conducted to verify the proposed design.
050.1950 Diffraction gratings 220.4830 Systems design 300.6190 Spectrometers In an experiment on the round-trip fiber transfer of joint frequency and time signals based on wavelength-division multiplexing technology, a specific bidirectional erbium-doped fiber amplifier (Bi-EDFA) with low noise and high symmetry simultaneously is designed and applied to compensate for the loss of the link. The Allan deviation (ADEV) deterioration of the 1 GHz frequency signal induced by the Bi-EDFA is only 8 × 10 15 9 × 10 18 10 4 s 1.7 × 10 14 1.2 × 10 17 10 4 s 10 3 s 7.3 × 10 14 2.5 × 10 17 10 4 s 1
060.2320 Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators 060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems An adaptive digital backward propagation (ADBP) algorithm is proposed and experimentally demonstrated based on the variance of the intensity noise. The proposed algorithm can self-determine the unknown nonlinear coefficient γ ξ
060.2300 Fiber measurements 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers This Letter proposes to apply full-color computer-generated holograms to the virtual image projection system so that the viewers can comfortably view floating images. Regarding the spatial division and distribution operation, a modified Gerchberg–Saxton algorithm is used for acquiring the phase infographics, which are input into the spatial light modulator for the reconstructed projection. Such a virtual image projection system could reach the vertical angle of view of 15°–75° and the horizontal angle of view 360°, and the mixed-light modulating proportion contains a 3 mW red light laser, a 2 mW green light laser, and a 2.6 mW blue light laser to achieve the full-color mixed-light proportion with a speckle contrast of 6.65%. The relative diffraction efficiency and root mean square error of the reconstructed image are 95.3% and 0.0524, respectively.
090.1760 Computer holography 090.0090 Holography 090.2870 Holographic display The exoplanet search is one of the most exciting research fields in astrophysics. The Antarctic Bright Star Survey Telescope (BSST), capable of continuous exoplanet observation on polar nights, is a Ritchey–Chretien telescope with a three-lens field corrector, and has a 300 mm aperture, 2.76 focal ratio, and a wavelength coverage ranging from 0.36 to 1.014 μm. Equipped with a 4 k × 4 k 12 μm / pixel
110.0110 Imaging systems 220.0220 Optical design and fabrication 230.0230 Optical devices A CO 2 CO 2 CO 2
120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation 300.6260 Spectroscopy, diode lasers 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Due to the excellent electro-optic properties of lead lanthanum zirconium titanate (( Pb , La ) ( Zr , Ti ) O 3 1 × 2 1 × 4 1 × 2 1 × 2 20.5 dB 1 × 4 20.5 dB 15 mm × 6 mm
060.4510 Optical communications 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.3130 Integrated optics materials 130.4815 Optical switching devices Highly sensitive and homogeneous SERS substrate fabricated by a femtosecond laser combined with dewetting Download:809次
Download:809次
 Download:809次
Download:809次We report a simple, cost-effective and repeatable method for fabricating a large area and uniform substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). The silicon, micromachined by a femtosecond laser, is coated with gold film and then treated through the dewetting process. The morphology shows a higher electric field enhancement due to light trapping. The enhancement factor of the SERS substrate is 9.2 × 10 7
240.6695 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers An efficient two-stage KTiOAO 4 M 2
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes A diode-end-pumped tunable twisted-mode cavity Tm, Ho:YAG laser with single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) operation is demonstrated in this Letter. The maximal SLM output power is 106 mW with a slope efficiency of 4.86%. The wavelength can be changed from 2090.38 to 2097.32 nm by tuning the angle of an etalon.
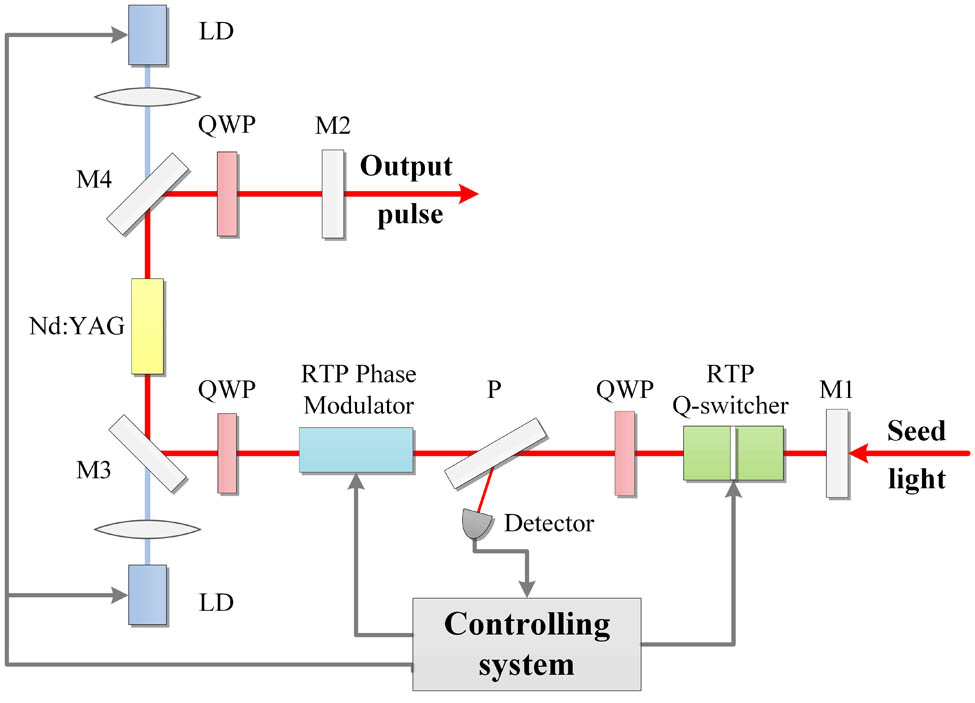
140.3570 Lasers, single-mode 140.3600 Lasers, tunable 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state A stable, single-longitudinal-mode, nanosecond-pulsed Nd:YAG laser with a laser-diode dual-end pumping arrangement is constructed. Injection seeding is performed successfully by utilizing a Rb TiOPO 4 M 2
140.3570 Lasers, single-mode 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched We report experimental progress in weakening the frequency difference lock-in phenomenon in a Y-shaped cavity dual-frequency laser. A cube coil pair is chosen to provide a uniform magnetic field for tunability and uniformity of magnetic field strength. When the transverse magnetic field intensity is 9 mT, the frequency difference lock-in phenomenon is evidently weakened and the frequency difference can be continuously tuned in the range of 0.12 MHz to 1.15 GHz. Moreover, the relationship between the minimal frequency difference and magnetic field intensity are investigated and discussed. Then a Y-shaped cavity dual-frequency laser is expected to be utilized as an optimum light source for heterodyne interferometric sensing and precise laser measurement.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 140.1340 Atomic gas lasers 140.3460 Lasers A sideband-controllable soliton mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser is successfully demonstrated utilizing the nonlinear polarization rotation technique. The sidebands can be produced or suppressed by performing simple polarization light tuning with a polarization controller. It is believed that the elimination of the sidebands is due to the dispersive waves that are filtered out by the polarization-dependent isolator in the resonator. With the elimination of the Kelly sidebands, the obtained 3 dB bandwidth is 10.6 nm and the attainable pulse duration is 0.86 ps. In this experiment, it is proven that the existence of Kelly sidebands limits the attainable pulse duration.
140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Early detection and timely treatment of nerve injury is crucial for the repair of nerve function. One week following a crush injury, heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) is over-expressed along the entire length of the sciatic nerve. Herein, we present an approach to detect injured nerves by photoacoustic microscopy after labeling the injured nerve with HSP27 antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles. The studies reveal that nanoprobe administration enabled the detection of injured nerves by photoacoustic microscopy, especially during the early stages within 3–7 days post injury. In conclusion, photoacoustic microscopy combined with antibody-conjugated nanoparticles holds potential for the early detection of nerve injury.
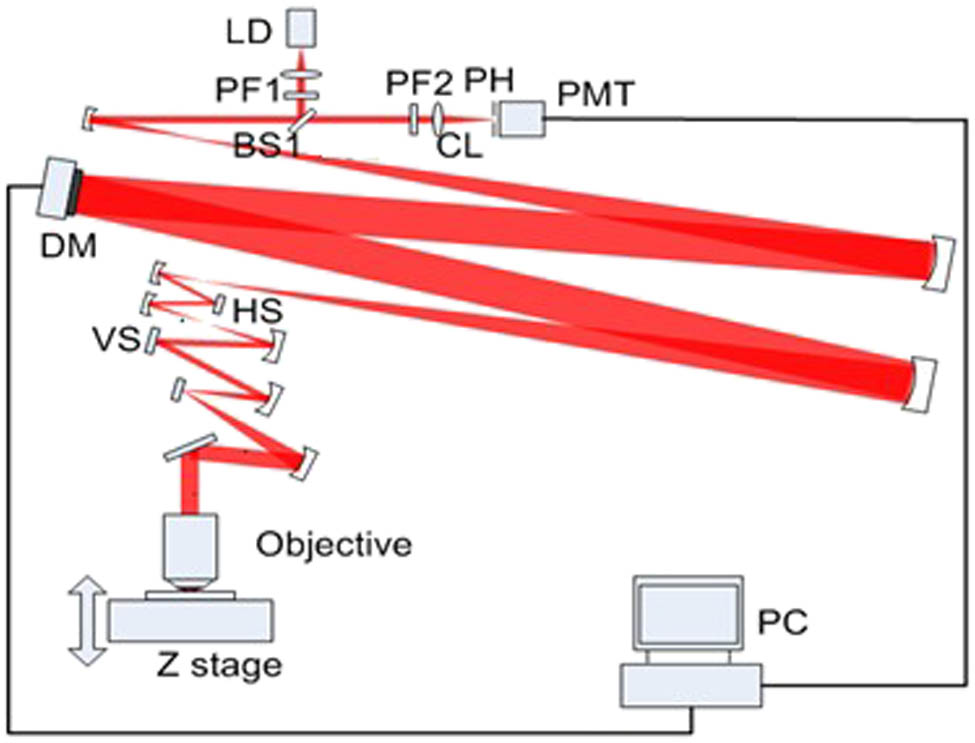
170.0170 Medical optics and biotechnology 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Facilitated with stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm for wavefront sensorless correcting aberrations, an adaptive optics (AO) confocal fluorescence microscopy is developed and used to record fluorescent signals in vivo . Vessels of mice auricle at 80, 100 and 120 μm depth are obtained, and image contrast and fluorescence intensity are significantly improved with AO correction. The typical 10%–90% rise-time of the metric value measured is 5.0 s for a measured close-loop bandwidth of 0.2 Hz. Therefore, the AO confocal microscopy implemented with SPGD algorithm for robust AO corrections will be a powerful tool for study of vascular dynamics in future.
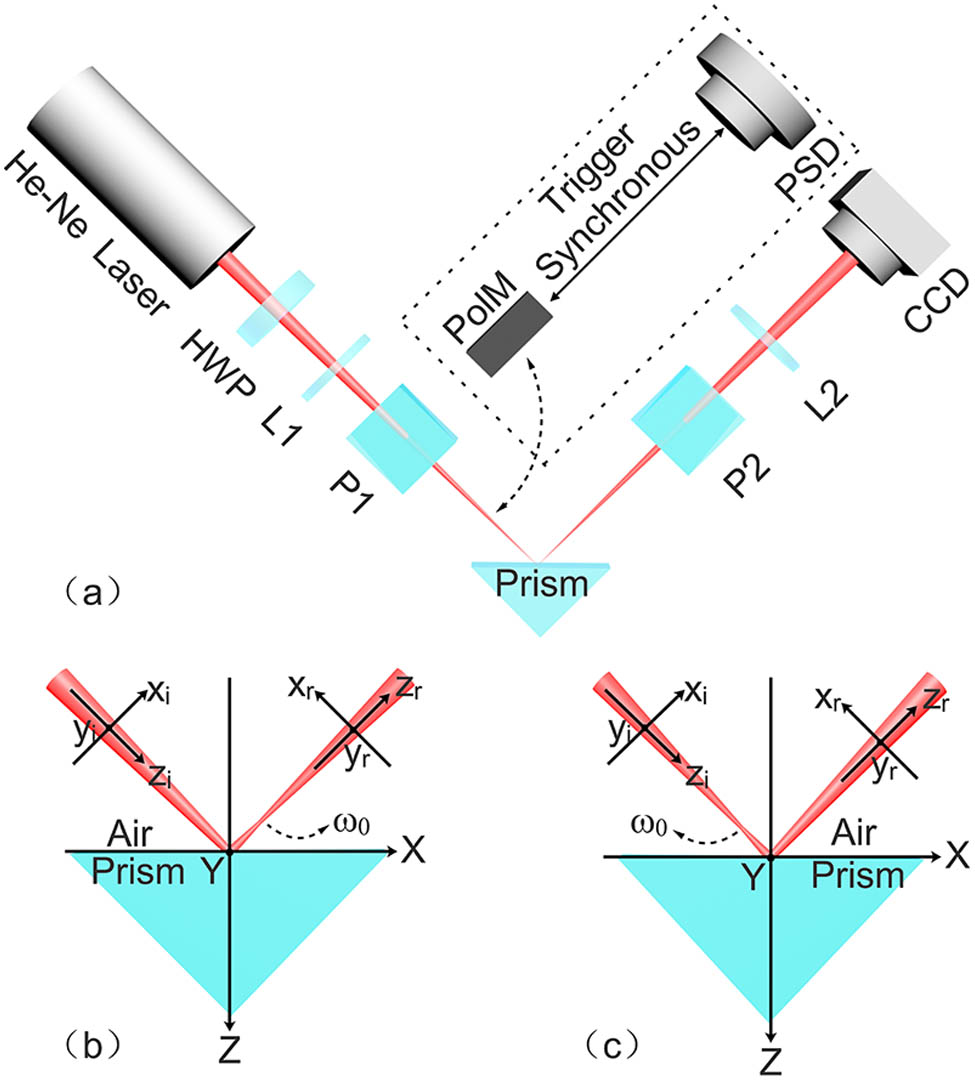
110.0110 Imaging systems 170.0170 Medical optics and biotechnology 170.1790 Confocal microscopy 170.0180 Microscopy In this Letter, a method for detecting the focused beam waist of lasers is proposed by using weak measurements based on the so-called weak-value amplification. We establish a propagation model to describe the quantitative relation between the beam waist and the amplified shift of the spin Hall effect of light (SHEL), which is sensitive to the variation of the beam waist. We experimentally measure the amplified shift corresponding to a different beam waist and the experimental data agrees well with theoretical calculation. These results confirm the rationality and feasibility of our method.
240.3695 Linear and nonlinear light scattering from surfaces 260.5430 Polarization 140.3295 Laser beam characterization The spectral properties of entangled photon pairs generated via quasi-phased matching in spontaneous parametric down-conversion are proposed and demonstrated experimentally. A general mathematical model for evaluating the spectral properties is developed to obtain the spectrum shape and range of down-converted photons. The model takes into account the effects of phase mismatching due to non-ideal pumping and the relationship between crystal periodic modulation function and the incidence angle of the pump beam. The spectrum curve shape is determined by the discrete Fourier transform of a Gaussian pump beam and the integration of parametric down-conversion generated by an individual plane wave. An experiment is carried out with a PPLN non-linear crystal and dispersing optics, which shows a good consistency in their spectral ranges and shapes with our model predictions within the spectrum of 600–633 nm. This therefore illustrates that both the simulation model and the experimental process are reasonable. This novel method has potential applications in high-accuracy calibration in the wide spectrum using correlated photons.
190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes 120.3940 Metrology 300.6410 Spectroscopy, multiphoton 040.5250 Photomultipliers Long plasma channels and high-voltage discharges induced by strong picosecond laser pulses Download:1138次
Download:1138次
 Download:1138次
Download:1138次The formation of long plasma channels and laser-induced high-voltage discharges are demonstrated by focusing infrared picosecond laser pulses in air. Based on measurements of the channel conductivity, the maximum electron density in excess of 10 14 cm 3
320.5390 Picosecond phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 140.3440 Laser-induced breakdown 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦