2019, 17(4) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第17卷 第4期
Free-space propagation of autofocusing Airy vortex beams with controllable intensity gradients Download:1301次
Download:1301次
 Download:1301次
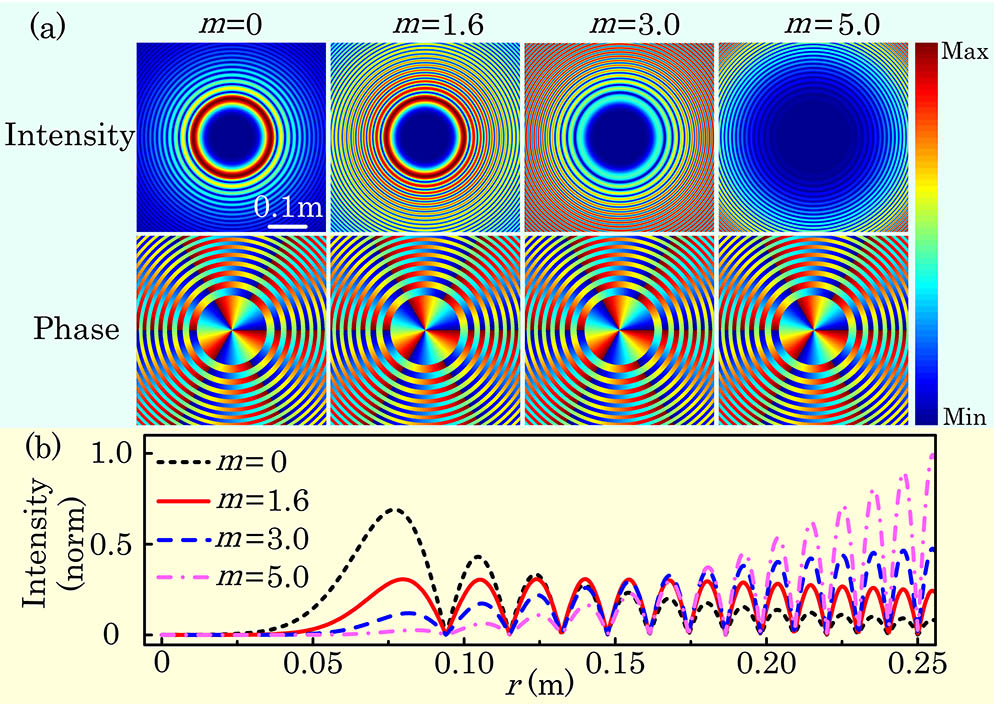
Download:1301次Vortex splitting is one of the main causes of instability in orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes transmission. Recent advances in OAM modes free-space propagation have demonstrated that abruptly autofocusing Airy vortex beams (AAVBs) can potentially mitigate the vortex splitting effect. However, different modes of vortex embedding will affect the intensity gradients of the background beams, leading to changes in the propagation characteristics of vortex beams. This study presents the unification of two common methods of coupling autofocusing Airy beams with vortices by introducing a parameter (m ), which also controls the intensity gradients and focusing properties of the AAVBs. We demonstrate that vortex splitting can be effectively reduced by selecting an appropriate value of the parameter (m ) according to different turbulence conditions. In this manner, the performance of OAM-based free-space optical systems can be improved.
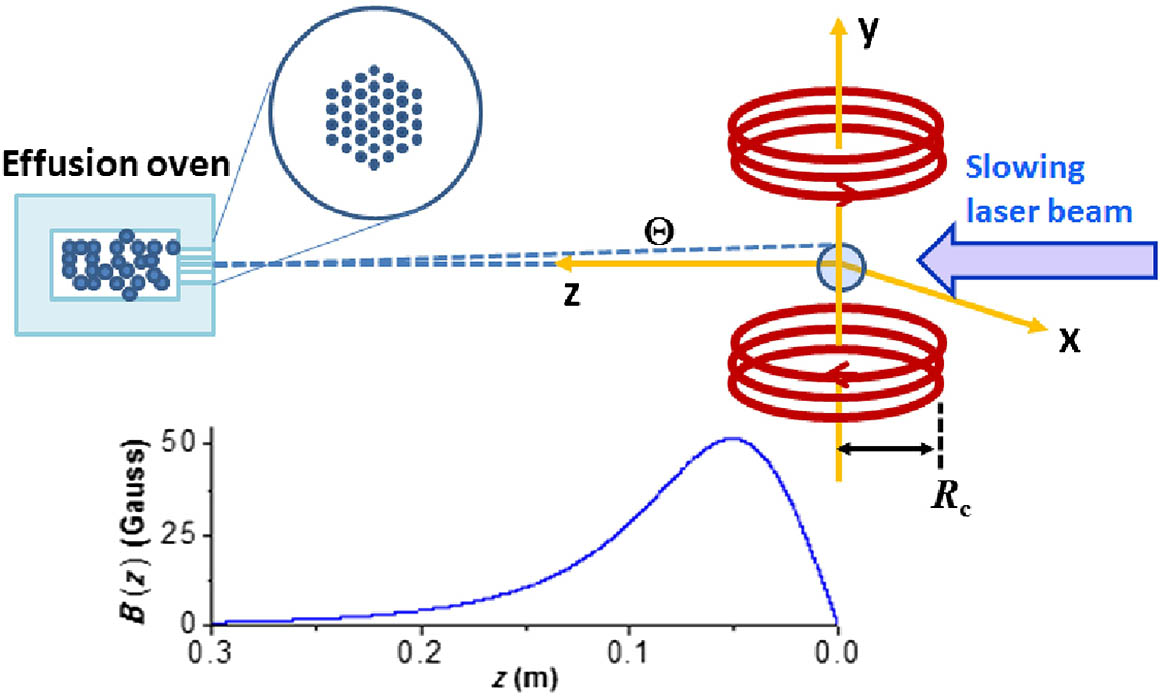
010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation We study a Zeeman slower using the magnetic field generated by a pair of coils for a magneto-optical trap. The efficiency of the Zeeman slower is shown to be dependent on the intensity and frequency detuning of the laser light for slowing the atoms. With the help of numerical analysis, optimal experimental parameters are explored. Experimentally, the optimal frequency detuning and intensity of the slowing beam are explored, and 4 × 107 ytterbium atoms are trapped in the magneto-optical trap.
020.3320 Laser cooling 020.7490 Zeeman effect As the key part of chip-scale atomic clocks (CSACs), the vapor cell directly determines the volume, stability, and power consumption of the CSAC. The reduction of the power consumption and CSAC volumes demands the manufacture of corresponding vapor cells. This overview presents the research development of vapor cells of the past few years and analyzes the shortages of the current preparation technology. By comparing several different vapor cell preparation methods, we successfully realized the micro-fabrication of vapor cells using anodic bonding and deep silicon etching. This cell fabrication method is simple and effective in avoiding weak bonding strengths caused by alkali metal volatilization during anodic bonding under high temperatures. Finally, the vapor cell D2 line was characterized via optical-absorption resonance. According to the results, the proposed method is suitable for CSAC.
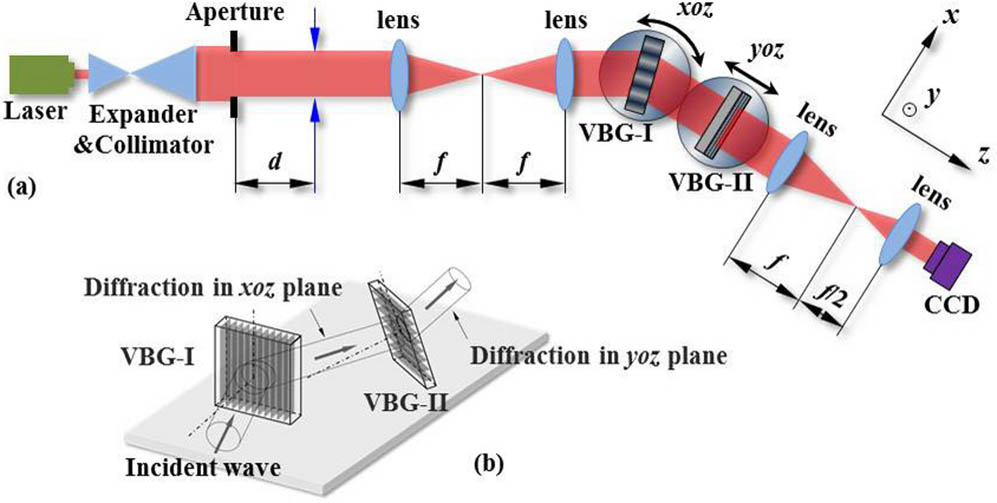
020.1335 Atom optics 020.1670 Coherent optical effects 110.3960 Microlithography Angular filtering by volume Bragg grating in photothermorefractive glass for nanosecond laser pulse Download:970次
Download:970次
 Download:970次
Download:970次The two-dimensional angular filter based on volume Bragg gratings in photothermorefractive glass for a nanosecond (ns) laser pulse is demonstrated. The experimental results show that the near-field beam quality of the laser pulse was effectively improved. The near-field modulation and contrast ratio were improved by 1.75 and 4.48 times, respectively. The power spectral density curves showed that the spatial frequencies more than 0.9 mm 1 in the x direction and 1.2 mm 1 in the y direction were effectively suppressed.
050.7330 Volume gratings A tutorial on laser-based lighting and visible light communications: device and technology [Invited] Download:927次
Download:927次
 Download:927次
Download:927次This tutorial focuses on devices and technologies that are part of laser-based visible light communication (VLC) systems. Laser-based VLC systems have advantages over their light-emitting-diode-based counterparts, including having high transmission speed and long transmission distance. We summarize terminologies related to laser-based solid-state lighting and VLC, and further review the advances in device design and performance. The high-speed modulation characteristics of laser diodes and superluminescent diodes and the on-chip integration of optoelectronic components in the visible color regime, such as the high-speed integrated photodetector, are introduced. The modulation technology for laser-based white light communication systems and the challenges for future development are then discussed.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 230.0230 Optical devices Impact of optical–electrical conversion responsivity in sub-sampled photonic analog-to-digital converter Download:650次
Download:650次
 Download:650次
Download:650次This Letter investigates the impact of the photodiode (PD) saturation in a sub-sampled photonic analog-to-digital converter (PADC) with two individual pulse lasers. It is essentially proved that when the optical power to the saturated PD increases, the optical–electrical conversion (OEC) responsivity and digitized output power of the PADC decrease. If femtosecond pulses are employed for the PADC sampling clock, the time-stretching process in a dispersive medium is necessary to decrease the impact of the PD saturation. In contrast, when the sampling clock with picosecond pulses is utilized, the PD saturation is more tolerable, and thus, the OEC responsivity can be improved by an increase of the optical power to the PD no matter if the time-stretching process is employed.
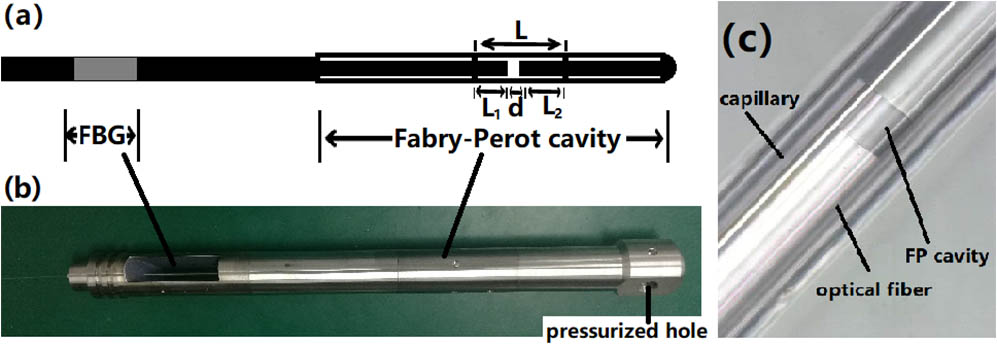
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 230.0250 Optoelectronics A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity cascaded fiber sensing system was manufactured for temperature and pressure sensing. Temperature sensing as high as 175°C was performed by an FBG for the linear variation of an FBG wavelength with temperature. After the temperature was sensed, the demodulation system can find the original FP cavity length and its pressure and cavity length correlation coefficient; thus, the ambient pressure would be calculated. The sensing pressure can be as high as 100 MPa with a repeatability of 1/10,000 and high stability. This kind of fiber sensor has been used in the Shengli Oil Field.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 050.2230 Fabry-Perot Optical frequency combs, which are generated by the cascade of a phase modulator and a Mach–Zehnder intensity modulator, are used as a polychromatic signal source in the terahertz imaging system to improve imaging quality. The interference effect caused by the monochromatic wave has been greatly suppressed. The required optical power in the presented system is as low as ~ 30 %
110.6795 Terahertz imaging This study introduced the research and development of a portable and miniaturized system for the measurement of the refractive index of sub-microliter liquid based on a microfluidic chip. A technical method of double-beam interference, was proposed for use in the measurement. Based on this, by using a laser diode as a light source, changes in the refractive index were calculated by utilizing a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor to detect the movement of interference fringes of the liquid. Firstly, this study simulated the effects of influencing factors on the interference infringes of two Gaussian beams, such as their spot sizes, distance between two beam spots, and detection range. Secondly, this research introduced the system design and construction of the double-beam interference method and analyzed the results of refractive index tests on sub-microliter aqueous glucose solutions with different concentrations. The measurement accuracy reached 10 4 refractive index units. This system has a compact structure and is rendered portable by using batteries for its power supply. The entire system is designed to be a double Z-shaped structure with a length of about 15 cm, a width of 5 cm, and a height of about 10 cm. It can be used to measure changes in the refractive index of sub-microliter to nanoliter liquids based on the use of a microfluidic chip.
120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation Integrated optoelectronic chip pair for transmitting and receiving optical signals simultaneously Download:679次
Download:679次
 Download:679次
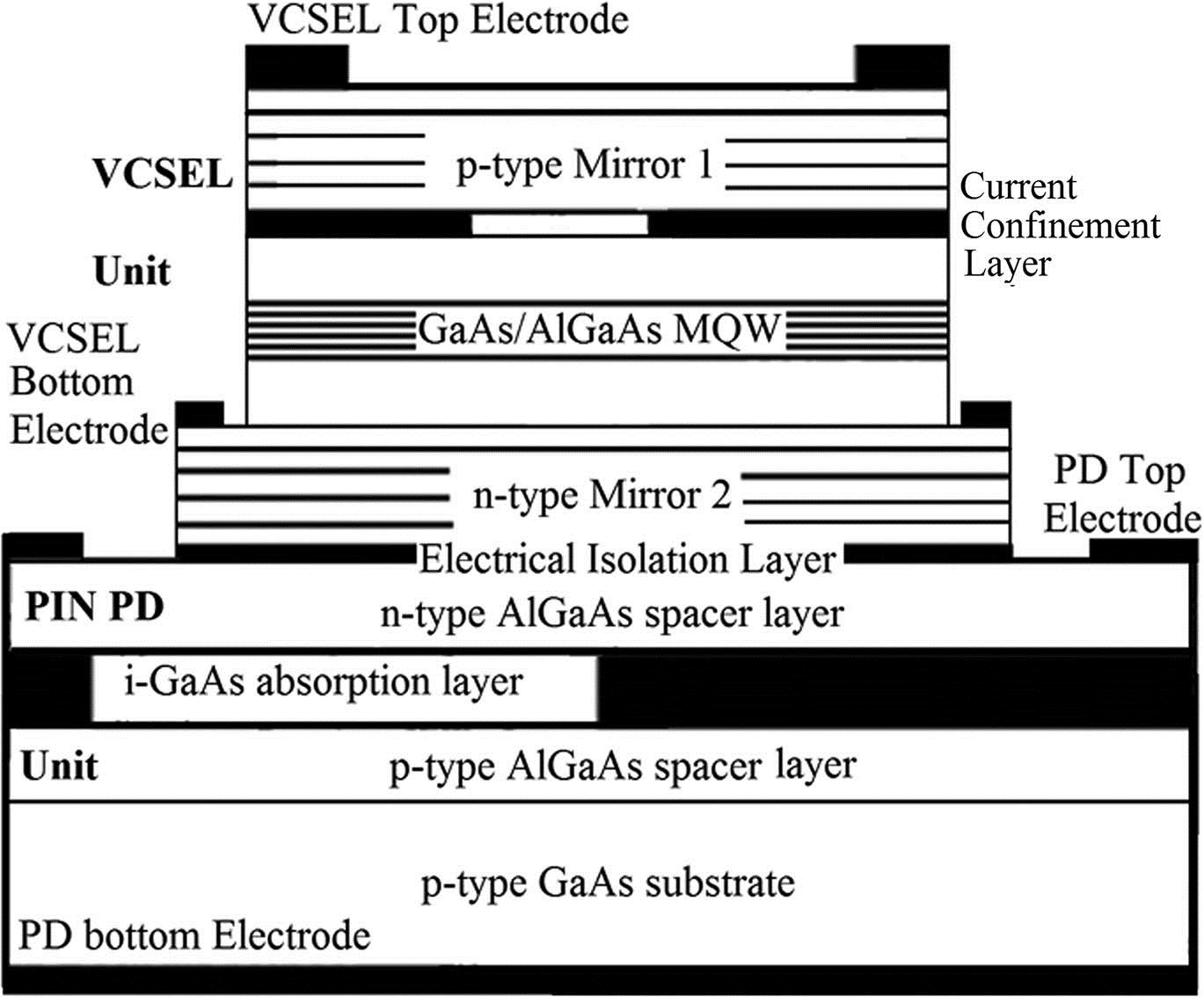
Download:679次An integrated optoelectronic chip pair, which can transmit and receive optical signals simultaneously, is proposed in this Letter. The design and optimization of its key structure, the vertical cavity surface emitting laser’s distributed Bragg reflector, are presented. Analysis is also done for its influence on the integrated chip’s performance. Moreover, the chip pair’s performance under dynamic conditions is analyzed. Their 3 dB modulation bandwidths are higher than 10 GHz, and their 3 dB photo-response bandwidths are around 23 GHz. Their applications will further improve the performances of the optical interconnects.
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.0250 Optoelectronics 250.7260 Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers Gold nanorods (GNRs) with two different aspect ratios were successfully utilized as saturable absorbers (SAs) in a passively Q -switched neodymium-doped lutetium lithium fluoride (Nd:LLF) laser emitting at 1.34 μm. Based on the GNRs with an aspect ratio of five, a maximum output power of 1.432 W was achieved, and the narrowest pulse width was 328 ns with a repetition rate of 200 kHz. But, in the case of the GNRs with the aspect ratio of eight, a maximum output power of 1.247 W was achieved, and the narrowest pulse width was 271 ns with a repetition rate of 218 kHz. Our experimental results reveal that the aspect ratios of GNRs have different saturable absorption effects at a specific wavelength. In other words, for passively Q -switched lasers at a given wavelength, we are able to select the most suitable GNRs as an SA by changing their aspect ratio.
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers We demonstrate a 0.95 GHz repetition rate fully stabilized Yb:fiber frequency comb without optical amplification. Benefitting from the high mode power and high coherence, this comb achieved 35 to 42 dB signal to noise ratio on the direct heterodyne beat signals with at least six continuous wave lasers (at 580, 679, 698, 707, 813, and 922 nm) while keeping >40 dB carrier envelope frequency signal. It can be used for the direct measurement of optical frequencies at visible and near-infrared wavelengths and has great potential on simultaneous comparison of multiple optical frequencies.
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers We demonstrate a coherent synthesis system based on femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser technology. The output pulse of the amplification system is divided into two replicas and seeded into photonic crystal fibers of two parallel branches for nonlinear pulse compression. Because of the different nonlinear dynamics in the photonic crystal fibers, the compressed pulses show different spectra, which can be spliced to form a broad coherent spectrum. The integrated timing jitter between the pulses of two branches is less than one tenth of an optical cycle. By coherently synthesizing pulses from these two branches, 8 fs few-cycle pulses are produced.
140.3490 Lasers, distributed-feedback 060.2420 Fibers, polarization-maintaining 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings Hybrid femtosecond laser system based on a Yb:KGW regenerative amplifier for NP polarization Download:523次
Download:523次
 Download:523次
Download:523次We report a hybrid femtosecond laser system based on a femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser and a Yb-doped potassium gadolinium tungstate (Yb:KGW) regenerative amplifier. To match the central wavelength of the seed source, a Yb:KGW crystal is used in the regenerative amplifier for N p 21 μ J
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.3615 Lasers, ytterbium Fractional density of states (FDOS) hinders the accurate measuring of the overall spontaneous emission (SE) control ability of a three-dimensional (3D) photonic crystal (PC) with the current widely used SE decay lifetime measurement systems. Based on analyzing the FDOS property of a 3D PC from theory and simulation, the excitation focal spot position averaged FDOS with a distribution broadening parameter was proposed to accurately reflect the overall SE control ability of the 3D PC. Experimental work was done to confirm that our proposal is effective, which can contribute to comprehensively characterizing the SE control performance of photonic devices with quantified parameters.
160.5298 Photonic crystals This Letter presents a double-layer structure combining a cracked cross meta-surface and grating surface to realize arbitrary incident linear terahertz (THz) wave polarization conversion. The arbitrary incident linear polarization THz wave will be induced with the same resonant modes in the unit cell, which results in polarization conversion insensitive to the linear polarization angle. Moreover, the zigzag-shaped resonant surface current leads to a strong magnetic resonance between the meta-surface and gratings, which enhances the conversion efficiency. The experimental results show that a more than 70% conversion rate can be achieved under arbitrary linear polarization within a wide frequency band. Moreover, around 0.89 THz nearly perfect polarization conversion is realized.
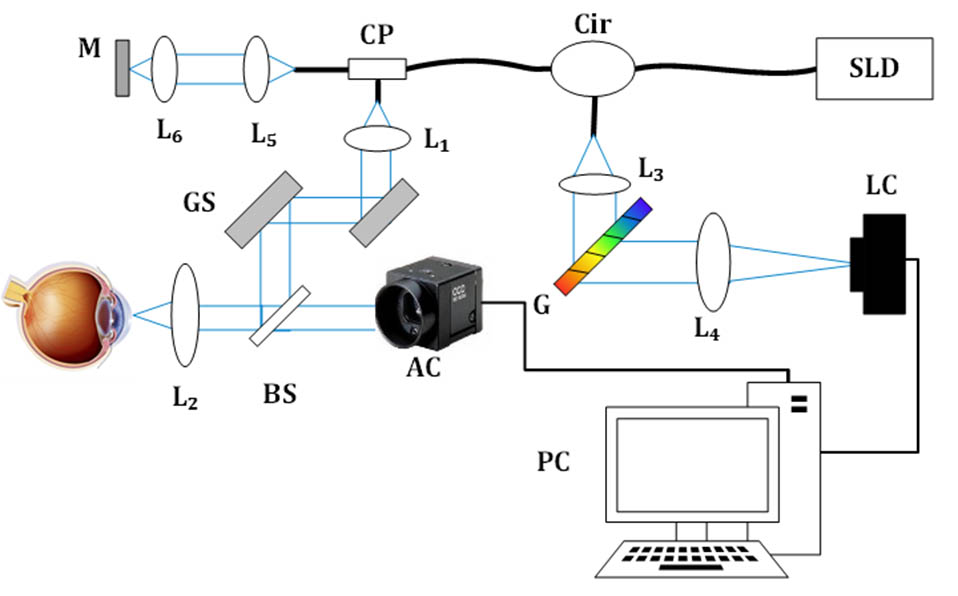
160.3918 Metamaterials 050.2230 Fabry-Perot 260.5430 Polarization We demonstrated a method for measurement of central corneal thickness (CCT) with a sub-micrometer sensitivity using a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system without needing a super broad bandwidth light source. By combining the frequency and phase components of Fourier transform, the method is capable of measurement of a large dynamic range with a high sensitivity. Absolute phases are retrieved by comparing the correlations between the detected and simulated interference fringes. The phase unwrapping ability of the present method was quantitatively tested by measuring the displacement of a piezo linear stage. The human CCTs of six volunteers were measured to verify its clinical application. It provides a potential tool for clinical diagnosis and research applications in ophthalmology.
170.4500 Optical coherence tomography 170.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices Sensing of ultrasonic fields based on polarization parametric indirect microscopic imaging Download:623次
Download:623次
 Download:623次
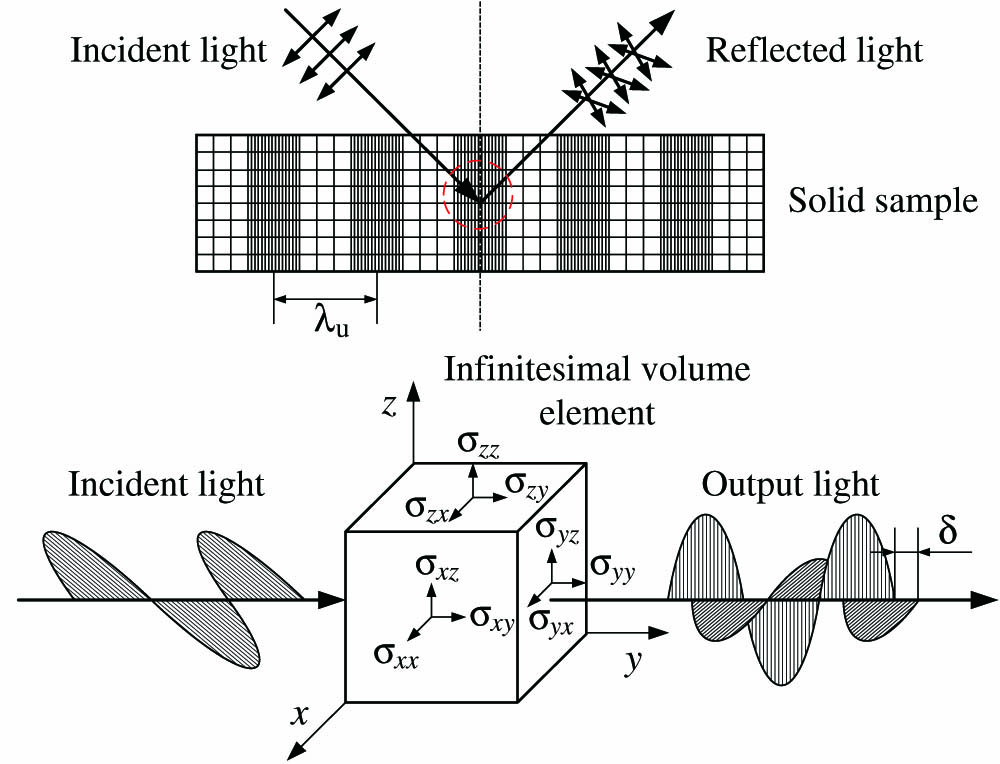
Download:623次This Letter tackles the issue of non-contact detection of ultrasonic fields by utilizing a novel optical method based on the parametric indirect microscopic imaging (PIMI) technique. A general theoretical model describing the three-dimensional anisotropic photoelastic effect in solid was developed. The mechanism of polarization status variations of light passing through the stress and strain fields was analyzed. Non-contact measurements of the ultrasonic field propagating in an isotropic quartz glass have been fulfilled by the PIMI technique under different ultrasonic excitation conditions. PIMI parameters such as sin δ
170.7170 Ultrasound 260.5430 Polarization 260.1440 Birefringence Echinococcosis—a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus or Echinococcus multilocularis larvae—occurs in many regions in the world. This disease can pose a serious threat to public health and thus requires a convenient and cost-effective method for early detection. So, we developed a novel method based on visual saliency and scale-invariant features that detects the tapeworm parasites. This method improves upon existing bottom-up computational saliency models by introducing a visual attention mechanism. The results indicated that the proposed method offers a higher level of both accuracy and computational efficiency when detecting Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces, which in turn could improve early detection of echinococcosis.
170.3880 Medical and biological imaging Theoretical study on negative permittivity of the material producing sharp surface plasmon resonance dips Download:704次
Download:704次
 Download:704次
Download:704次Using theoretical simulations for optical fiber surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors and prism-based SPR sensors coated with negative permittivity material (NPM), we investigated the effect of the permittivity of NPM on the transmitted spectrum of optical fiber SPR sensors and the reflected spectrum of prism-based SPR sensors and then obtained optimum permittivity of the NPM, which can excite the sharpest SPR spectrum in the white light region (400–900 nm).
280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 240.6680 Surface plasmons 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦