光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41 (7): 2245, 网络出版: 2021-09-08
“加瓷”处理绿松石的成分及谱学特征研究  下载: 571次
下载: 571次
Study on Composition and Spectral Characteristics of Turquoise Treated by “Porcelain-Added”
“加瓷”绿松石 红外吸收光谱 化学成分 紫外吸收光谱 宝石学特征 “Porcelain-added” treatment of turquoise Infrared absorption spectrum Chemical composition Ultraviolet absorption spectrum Gemmological characteristic
摘要
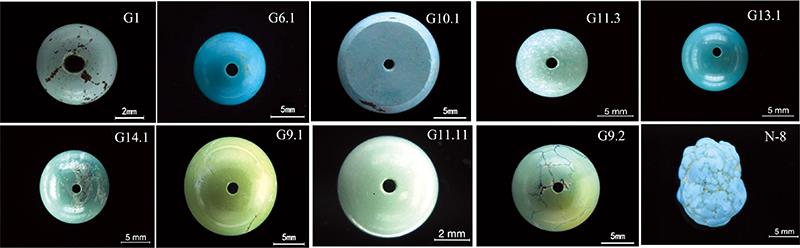
近年来, 市场上出现了一类利用新型无机结合剂处理的绿松石, 经此类方法处理的绿松石与天然绿松石极为相似, 普遍表现为结构细腻、 呈现玻璃-蜡状光泽, 行业上称之为“加瓷”处理绿松石(简称“加瓷”绿松石)。 采取常规宝石学仪器、 红外吸收光谱仪、 紫外-可见分光光度计以及能谱色散型X射线荧光光谱仪对“加瓷”绿松石的宝石学性质、 振动光谱特征以及化学成分组成特征进行了系统的研究和分析。 研究结果显示: “加瓷”绿松石样品的密度大都小于2.200 g·cm-3, 与处理前密度有关, 故用于“加瓷”处理的样品以密度较低的绿松石为主; “加瓷”绿松石均表现为典型的低密度、 较细腻的结构外观和蜡状-玻璃光泽的组合特征, 与品质相当的天然绿松石特征不一致, 可作为“加瓷”绿松石重要的辅助性鉴别特征。 “加瓷”绿松石在长、 短波紫外荧光下的发光性与天然绿松石近于一致; 显微观察下铁线、 裂隙凹陷处常出现白色融出物, 孔道内可见毛发状结晶体。 “加瓷”绿松石的主要化学成分与天然类似, 以CuO, Al2O3和P2O5为主, 并含有一定量的FeOT(铁的氧化物), ZnO、 SiO2, K2O和CaO。 其中, “加瓷”处理绿松石样品中SiO2含量基本在6.40%以上, 均高于天然绿松石中的SiO2含量(1.96%~6.25%), 而Al2O3和P2O5含量都较天然绿松石偏低, 磷铝比例基本与天然绿松石一致, 为1.10左右。 利用“加瓷”绿松石较高的SiO2含量和表面特征可将其与天然绿松石进行有效鉴别。 “加瓷”绿松石与天然绿松石的红外吸收光谱特征基本一致。 “加瓷”绿松石的UV-Vis光谱表现为620~750 nm处的吸收峰以及425 nm附近处较为锐利的吸收峰, 因颜色不同峰位稍有偏移, 但总体与天然绿松石的UV-Vis光谱特征趋于一致。
Abstract
In recent years, a kind of turquoise treated with a new type of inorganic binder has appeared on the market. The turquoise treated by this method is very similar to the natural turquoise, which is generally characterized by a fine structure, glassy luster or greasy luster. It is called “porcelain-added” turquoise in markets. Conventional gemological testing instruments, infrared absorption spectrometers, UV-Vis spectrometers and energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometers were used to systematically study and analyze the gemological properties, vibration spectrum characteristics and chemical composition characteristics of “porcelain-added” turquoise. The results show that the density of turquoise samples treated with “porcelain” is mostly less than 2.2 g·cm-3, and its density is related to the density of turquoise before treatment. The samples treated with “porcelain” are mainly turquoise with a lower density. The turquoise treated by “porcelain” is characterized by typical low density, delicate structural appearance and strong wax-glass luster combination, which is inconsistent with the characteristics of natural turquoise and can be used as an important auxiliary identification feature of turquoise treated by “porcelain”. The luminescence of turquoise treated by “porcelain” under long-wave and short-wave UV fluorescence is nearly consistent with natural turquoise. Under microscopic observation, the white melting matter often appears in the iron wire and crevasses, and hair-like crystals can be seen in the pores. The main chemical composition of “porcelain-added” turquoise is similar to the natural turquoise, with CuO, Al2O3 and P2O5 as the main components, and containing a certain amount of FeOT, ZnO, SiO2, K2O and CaO. Among them, the SiO2 content of the “porcelain-added” turquoise sample is basically above 6.40%, which is higher than that of the natural turquoise (1.96%~6.25%), and its Al2O3 and P2O5 contents are lower than those of the natural turquoise, and the proportion of phosphorus and aluminum is basically the same as that of the natural turquoise, about 1.10. The high content of SiO2 and surface feature in turquoise can be effectively distinguished from natural turquoise by “adding porcelain”. The infrared absorption spectrum of turquoise treated by “adding porcelain” is basically the same as that of natural turquoise, which is difficult to distinguish. The Ultraviolet absorption spectrum of turquoise treated by “porcelain addition” shows the absorption peak at 620~750 nm and the relatively sharp absorption peak near 425 nm. The peak positions are slightly shifted due to different colors, but the overall UV absorption spectrum characteristics are consistent with those of natural turquoise.
黄莉莹, 陈全莉, 高欣欣, 杜阳, 徐丰舜. “加瓷”处理绿松石的成分及谱学特征研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(7): 2245. Li-ying HUANG, Quan-li CHEN, Xin-xin GAO, Yang DU, Feng-shun XU. Study on Composition and Spectral Characteristics of Turquoise Treated by “Porcelain-Added”[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(7): 2245.