光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42 (3): 726, 网络出版: 2022-04-19
东门渡窑古陶瓷化学成分与烧制工艺研究  下载: 589次
下载: 589次
Research on the Chemical Composition and Process Feature of Ancient Porcelain Produced in Dongmendu Kiln
东门渡窑 古陶瓷 化学组成 显微结构 波长色散X射线荧光光谱 Dongmendu Kiln Ancient porcelain Chemical composition Microstructures EDXRF
摘要
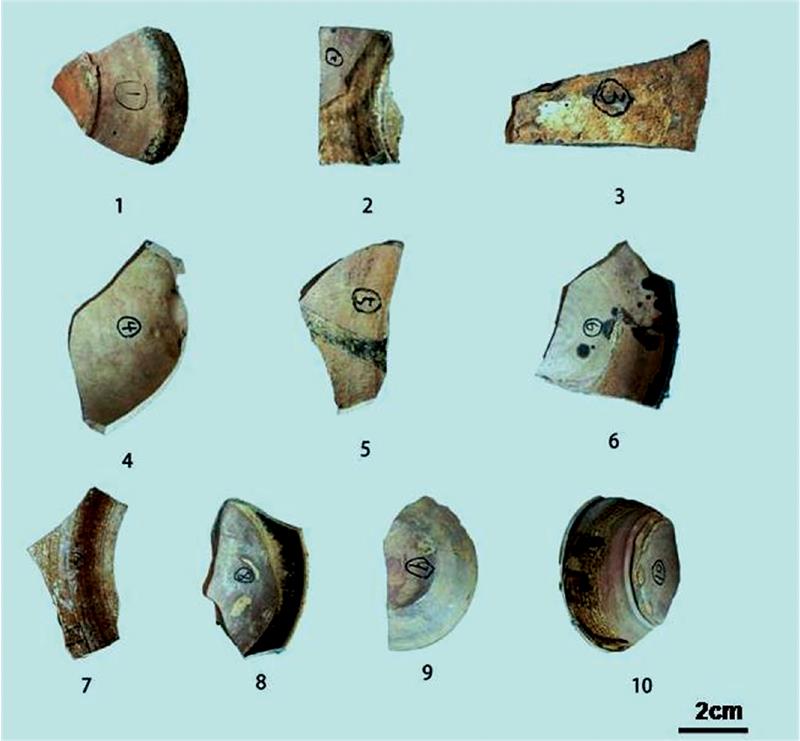
芜湖东门渡窑是古代宣州窑场的早期窑口之一, 属古越窑系青瓷; 该窑口出产的陶瓷产品器型别具一格, 具有鲜明的地域特色。 但长期以来, 对于东门渡窑瓷器仅仅从其外观推测其工艺特征, 对该类瓷器的微观结构特征和配方工艺特点缺乏必要的分析证据。 为系统解析东门渡窑古陶瓷的胎、 釉化学组成和烧制工艺, 运用波长色散X射线荧光光谱法(EDXRF), 结合光学显微分析手段, 对东门渡窑古陶瓷胎、 釉的化学成分和微观结构等进行深入探究; 采用X射线衍射分析、 红外光谱及热重分析等多种光谱技术, 探明了古陶瓷样品胎体的物相组成、 主要化学成分和烧制特点; 同时, 综合不同的分析表征, 对其制瓷工艺特点和该窑口的性质进行了科学的推测。 研究表明, 东门渡窑古陶瓷胎体成分具有显著的高硅、 低铝特征, 属于典型的南方瓷器; 瓷胎的主要制备原料为瓷石, 并可能掺入了当地盛产的高铁含量的赭红色粘土; 瓷器釉料配方采用了南方越窑系的高钙釉制备工艺。 依据瓷器的显微分析结果, 瓷胎和瓷釉内显著的粗颗粒表明, 原料未淘洗或淘洗不精, 加工过程不精细。 胎体化学成分分析显示, 该瓷器样品的烧制温度不高于1 200 ℃, 或高温段保温时间不够。 东门渡窑古陶瓷整体配方工艺和烧制水平不高, 应为唐宋宣州地方以烧造一般民间用品为主的陶瓷窑厂。 研究结果对于客观认识安徽古代制瓷业的工艺水平、 发展特点和规律具有重要的科学价值, 对探究中国古代官窑的内涵、 窑业生产布局、 确立宣州窑在安徽瓷业的发展及南北方瓷业技术的交流中的历史地位具有重要学术意义, 有利于推动安徽省遗址保护规划建设和传承保护地域文化。
Abstract
Dongmendu Kiln was one of the earliest kilns among the ancient Xuanzhou kilns, which belonged to the celadon of Yue Kiln series. The porcelains of Dongmendu Kiln, with its distinctive local characteristics, had a special style. The research on the structural properties in the micro length scale and process features about the porcelains was still superficial for lack of evidence. So far, its process features were only evaluated from the external morphology of implements. Wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) combined with optical microscopic analysis was applied to determine the elemental abundance patterns of the porcelain bodies and glazes excavated from Dongmendu Kiln. Meanwhile, XRD, FT-IR and TG-DSC analysis were used to test the porcelain body’s phases, major ingredients and fire characteristics. Based on the above comprehensive characterizations, the process feathers and attributes were concluded reasonably. Evidence revealed that porcelains produced in Dongmendu Kiln were the typical south porcelains because of high silicon and low aluminum contents. The porcelain body was made up of china stone, which was mixed with some ember clays in the local. The porcelain glazes exhibited the typical properties of Yue Kiln due to the high calcium contents. The presence of big particles in porcelain bodies and glazes indicated that the processing of raw materials was not elaborate. The phases of the porcelain body revealed that the sintering temperature was not high than 1200℃, or the holding time at high temperature was much shorter. Overall, the formulation process and fire level of Dongmendu Kiln were not high. It should be a typical kiln in the Tang and Song Dynasties of Xuanzhou, where civil ceramics were produced. The results had important scientific value on an objective understanding of the process level, characteristics and laws of the ancient porcelain in Anhui. It is of great academic significance to explore the connotation of ancient Chinese imperial kilns, the production layout of kiln industry, and to establish the historical position of Xuanzhou kiln in the development of Anhui porcelain industry and the exchange of porcelain technology between the south and the north. Further, it was also advantageous to promote the conservation and planning construction of Anhui ruins and heritage and protection of the regional culture.
崔名芳, 朱建华, 胡瑞, 陈尚前. 东门渡窑古陶瓷化学成分与烧制工艺研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42(3): 726. Ming-fang CUI, Jian-hua ZHU, Rui HU, Shang-qian CHEN. Research on the Chemical Composition and Process Feature of Ancient Porcelain Produced in Dongmendu Kiln[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(3): 726.