激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61 (3): 0314004, 网络出版: 2024-03-07
激光粉末床熔融ECY768合金冶金缺陷、显微组织、力学性能研究(特邀)创刊六十周年特邀
Metallurgical Defects, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of ECY768 Alloy Processed via Laser Powder Bed Fusion (Invited)
激光粉末床熔融 ECY768钴基高温合金 冶金缺陷 显微组织 力学性能 laser powder bed fusion ECY768 cobalt-based superalloy metallurgical defects microstructure mechanical properties
摘要
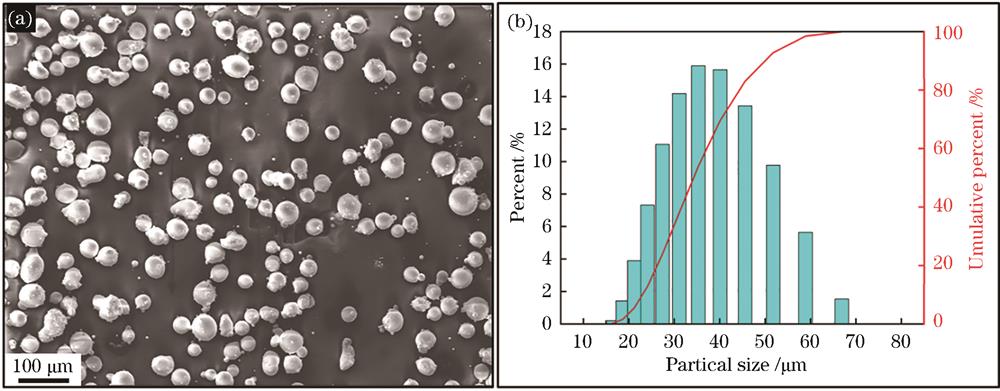
激光粉末床熔融(LPBF)是钴基高温合金复杂构件整体制造的理想方法。ECY768是一种性能优异的新型钴基高温合金,但目前LPBF成形ECY768合金的研究还十分匮乏。研究了LPBF成形ECY768钴基高温合金的冶金缺陷、显微组织和基础力学性能。结果表明:LPBF成形ECY768合金的冶金缺陷主要为气孔、未熔合和热裂纹;通过调整激光体能量密度等工艺参数,可实现无裂纹、高致密(孔隙率<0.5%)ECY768合金成形。LPBF成形ECY768合金的显微组织为以柱状晶为主的“柱状晶+等轴晶”混合组织,总体上呈一定的“〈0 0 1〉/构建方向”择优取向;晶粒内部具有细密的胞状亚晶结构,胞晶边界不仅分布有胞状位错网络,还分布有球状MC型和条带状M23C6型两类纳米级碳化物析出相。在优选工艺参数下,LPBF成形ECY768合金的屈服强度为1002 MPa(构建方向)/1267 MPa(垂直构建方向),远高于铸造或LPBF成形的其他主要钴基高温合金;延伸率为10.5%(构建方向)/13.3%(垂直构建方向),与铸造或LPBF成形的其他主要钴基高温合金基本相当。优良的致密度、细密的胞状亚晶结构、纳米碳化物的大量析出及其与位错网络的相互作用是LPBF成形ECY768合金具有优异力学性能的关键。
Abstract
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is an ideal technique for the comprehensive fabrication of intricate components using cobalt-based superalloys. Despite the outstanding performance of ECY768, a novel cobalt-based superalloy, there exists a research gap concerning the LPBF processing of this alloy. This study delves into the metallurgical defects, microstructure, and fundamental mechanical properties of the ECY768 cobalt-based superalloy when subjected to LPBF. The findings reveal that the predominant metallurgical defects in ECY768 alloy processed by LPBF are gas pores, lack-of-fusion, and hot cracks. Adjusting processing parameters, such as laser energy density, facilitates the production of ECY768 specimens devoid of cracks and exhibiting high density (porosity <0.5%). The LPBF-processed ECY768 alloy exhibits a mixed grain structure comprising predominantly columnar grains with some equiaxed grains. A〈0 0 1〉preferred orientation, nearly parallel to the build direction, is evident. Within the solidification grains, a cellular dendritic microstructure is observable. Sub-grain boundaries concentrate both a dislocation network and two types of nano-scale carbides-ball-shaped MC-type carbides and band-shaped M23C6-type carbides. Under optimized processing parameters, the yield strength of ECY768 specimens reaches 1002 MPa (parallel to build direction) and 1268 MPa (perpendicular to build direction), surpassing that of other main cobalt-based superalloys formed by casting or LPBF. Simultaneously, the elongation of ECY768 specimens is 10.5% (parallel to build direction) and 13.3% (perpendicular to build direction), aligning closely with the performance of other main cobalt-based superalloys produced through casting or LPBF. The exceptional mechanical properties of LPBF-processed ECY768 alloy are attributed to satisfactory relative density, a refined cellular dendritic microstructure, substantial nanocarbide precipitation, and their interaction with the dislocation network.
刘浩博, 魏恺文, 钟桥, 弓健强, 李祥友, 曾晓雁. 激光粉末床熔融ECY768合金冶金缺陷、显微组织、力学性能研究(特邀)[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(3): 0314004. Haobo Liu, Kaiwen Wei, Qiao Zhong, Jianqiang Gong, Xiangyou Li, Xiaoyan Zeng. Metallurgical Defects, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of ECY768 Alloy Processed via Laser Powder Bed Fusion (Invited)[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(3): 0314004.