基体温度对钛膜表面形貌和力学性能的影响研究
Titanium and its alloys are widely utilized within the military, aerospace, shipping, nuclear energy, and biomedical fields because of the advantages of low density, high strength, good corrosion resistance, and high biocompatibility. Moreover, titanium films are important materials for surface protection due to their high hardness and good compactness. During the preparation of titanium films, the surface morphology and phase structure will be influenced by substrate properties (e.g., surface morphology and temperature), working gas pressure, and other factors. Substrate temperature mainly influences the growth process of thin films, which directly affects the grain structure of the films, and thus changes the corresponding mechanical properties.
This study aims to establish the relationship between substrate temperature and mechanical properties of titanium films.
Firstly, titanium film samples were prepared at a substrate temperature range of 600~750 ℃ by using resistance evaporation coating on the surface of molybdenum substrate. Then, the structural characterization of the film was examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) so as to obtain the preferred orientation of titanium film. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) were employed to identify the surface morphologies of the titanium films, including grain size distribution and surface roughness. Finally, an AFM nano-indentation method was performed to examine the mechanical properties of the titanium films and obtain the elastic modulus of titanium film.
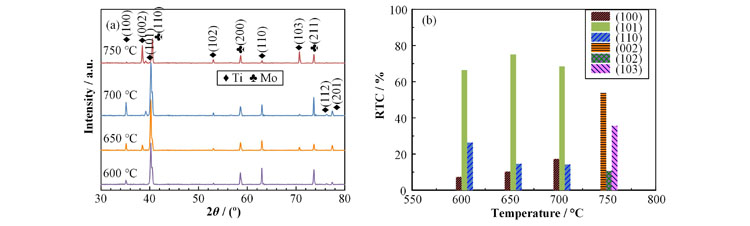
The results demonstrate that the substrate temperature significantly influences the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium films. When the substrate temperature increases from 600 ℃ to 750 ℃, the preferred orientation of titanium films changes from (101) to (002) due to the competition between the minimization of strain energy and surface energy. With the increase of substrate temperature, the mobility of titanium atoms on the substrate increases, resulting in increased average grain size, surface roughness, and elastic modulus of the titanium films. The average grain size increases by 26% as the substrate temperature increased from 600 ℃ to 750 ℃.
The microstructure, surface morphology, and mechanical properties of titanium films are sensitive to substrate temperature. A high substrate temperature in the process of resistance evaporation is more desirable to obtain titanium films with high mechanical properties.
王杏, 马明旺, 万瑞芸, 王磊, 谈效华. 基体温度对钛膜表面形貌和力学性能的影响研究[J]. 核技术, 2023, 46(10): 100202. Xing WANG, Mingwang MA, Ruiyun WAN, Lei WANG, Xiaohua TAN. Effect of substrate temperature on surface morphology and mechanical properties of Ti films[J]. NUCLEAR TECHNIQUES, 2023, 46(10): 100202.