Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for GeoMechanics and Deep Underground Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
2 School of Science, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing 100089, China
3 Institute Key Laboratory of Optic Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
4 Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory, Dongguan 523808, China
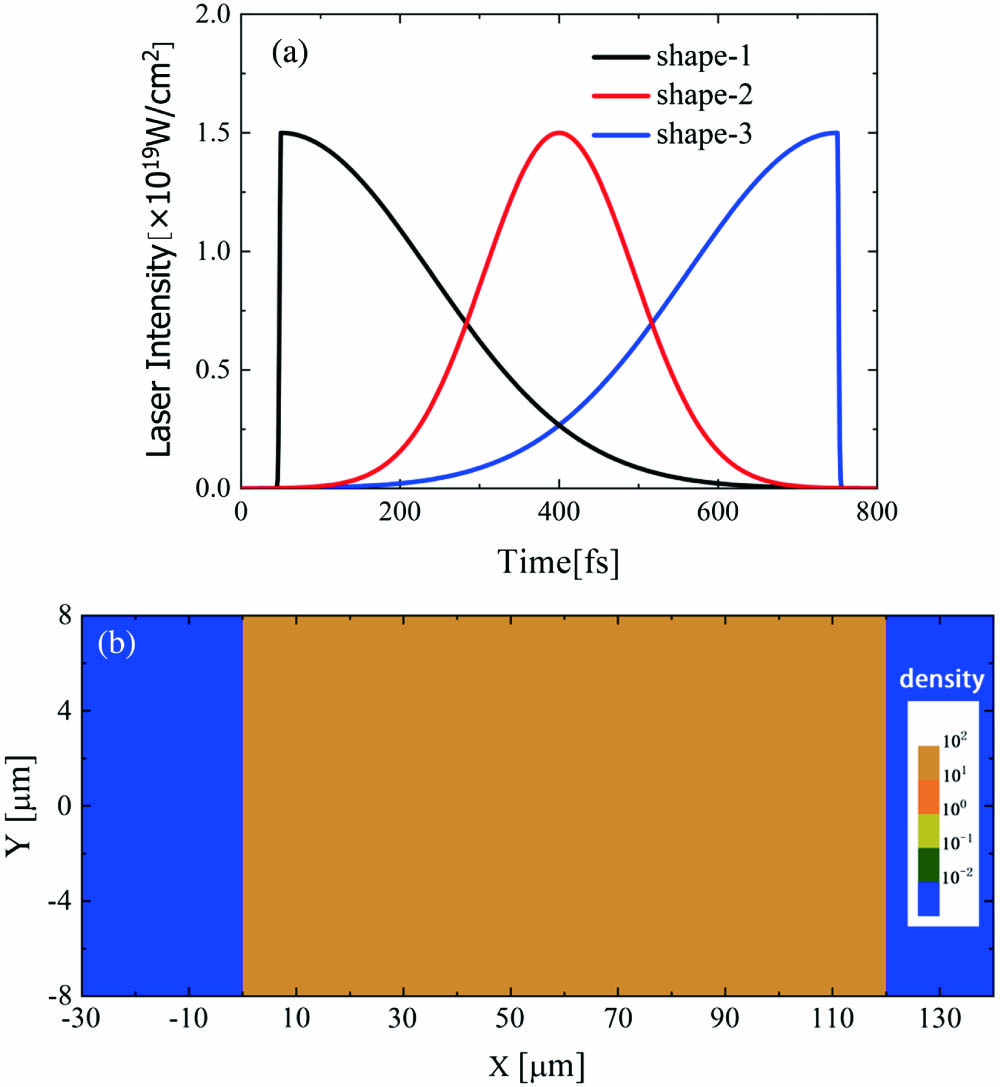
In the scheme of fast ignition of inertial confinement fusion, the fuel temperature mainly relies on fast electrons, which act as an energy carrier, transferring the laser energy to the fuel. Both conversion efficiency from the laser to the fast electron and the energy spectrum of the fast electron are essentially important to achieve highly effective heating. In this study, a two-dimensional particle in cell simulation is applied to study the generation of fast electrons from solid-density plasmas with different laser waveforms. The results have shown that the slope of the rising edge has a significant effect on fast electron generation and energy absorption. For the negative skew pulse with a relatively slow rising edge, the mechanism can most effectively accelerate the electrons. The overall absorption efficiency of the laser energy is optimized, and the fast electron yield in the middle- and low-energy range is also improved.
laser waveform fast electrons particle-in-cell simulations plasmas Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(6): 063801
在激光等离子体相互作用中,各种不同的物理机制将会激发产生强度高达100 T量级的自生磁场。针对前人开展的纳秒激光与等离子体相互作用中自生磁场的质子成像诊断实验,通过分析实验结果并提取磁流体力学模拟中所呈现出的磁场基本特征,对磁场形式进行了假设,并应用蒙特卡罗粒子输运程序FLUKA对质子成像过程进行了大量模拟,得到了与实验结果吻合度较高的磁场分布。通过比较发现:FLUKA模拟得到的磁场的峰值强度以及峰值强度随时间的演化规律与前人LASNEX模拟结果基本吻合,而磁场分布范围大于LASNEX模拟中的结果,这可能是由于磁扩散的影响和欠稠密等离子体的存在。
中国激光
2022, 49(24): 2401001
1 中国科学院物理研究所北京凝聚态物理国家实验室, 北京, 100080
2 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学技术国家重点实验室, 西安, 710068
在超短超强激光与固体薄膜靶相互作用研究中, 实验上首次观测到了沿靶面方向发射的高能超热电子束。该电子束只有在等离子体电子密度标长较短的条件下才会出现。理论模拟表明, 靶表面电磁场的约束作用是产生此电子束的主要原因。这一结果有助于加深对激光惯性约束聚变快点火实验中的锥靶物理过程的理解, 并有潜在的应用前景。
超短超强激光等离子体相互作用 超热电子





