Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Leibniz Institute of Surface Engineering (IOM), Permoserstraße 15, 04318 Leipzig, Germany
2 JENOPTIK Optical Systems GmbH, Göschwitzer Straße 25, 07745 Jena, Germany
3 Institute of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, TU Dresden, 01062 Dresden, Germany
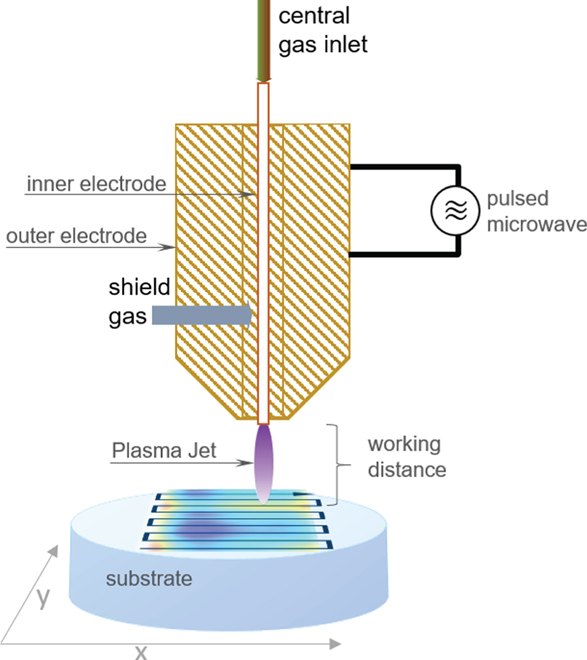
To meet the increasing market demand for optical components, Plasma Jet Machining (PJM) of Borosilicate Crown Glass (BCG), which can be an alternative to Fused Silica, is presented. Surface figure error correction was performed by applying reactive plasma jet etching, where a fluorine-containing microwave driven plasma jet is employed to reduce the figure error in a deterministic dwell-time controlled dry etching process. However, some of the glass constituents of BCG cause the formation of a residual layer during surface treatment which influences the local material removal. By heating the substrate to about TS = 325 °C to 350 °C during processing, the etching behavior can clearly be improved. Geometric conditions of the optical element nevertheless lead to a characteristic temperature distribution on the substrate surface, which requires an adjustment of the local dwell times in order to obtain the required material removal. Furthermore, the resulting local surface roughness is also influenced by the surface temperature distribution. It is shown that figure error can be significantly reduced by taking the local temperature distribution and resulting local etching rates into account. A subsequent polishing step smoothens roughness features occurring during etching to provide optical surface quality.To meet the increasing market demand for optical components, Plasma Jet Machining (PJM) of Borosilicate Crown Glass (BCG), which can be an alternative to Fused Silica, is presented. Surface figure error correction was performed by applying reactive plasma jet etching, where a fluorine-containing microwave driven plasma jet is employed to reduce the figure error in a deterministic dwell-time controlled dry etching process. However, some of the glass constituents of BCG cause the formation of a residual layer during surface treatment which influences the local material removal. By heating the substrate to about TS = 325 °C to 350 °C during processing, the etching behavior can clearly be improved. Geometric conditions of the optical element nevertheless lead to a characteristic temperature distribution on the substrate surface, which requires an adjustment of the local dwell times in order to obtain the required material removal. Furthermore, the resulting local surface roughness is also influenced by the surface temperature distribution. It is shown that figure error can be significantly reduced by taking the local temperature distribution and resulting local etching rates into account. A subsequent polishing step smoothens roughness features occurring during etching to provide optical surface quality.
Plasma Jet Machining Atmospheric Plasma Jet Reactive plasma jet etching Borosilicate Crown Glass Figure error Chemical etching Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2022, 18(1): 2022003
1 东华大学理学院, 上海 201620
2 东华大学磁约束核聚变教育部研究中心, 上海 201620
通过发射光谱对大气压氦等离子体射流三个不同位置进行测量, 并采用光谱拟合获得氮气分子振转温度的方法, 研究了放电电压和气体流量以及离喷口的距离对射流的温度和化学活性的影响。发现大气压等离子体射流的气体温度和振动温度均随着放电电压增加而升高, 随着气体流量的增大而降低, 随着离喷口距离的增加而降低并逐步趋于稳定。通过对等离子体射流中振动温度的变化趋势并结合活性成分氧原子光谱强度的变化证实了等离子体射流的活性亦随着气体流量及离喷口距离的增大而降低, 随着放电电压增加而升高的结论。
大气压等离子体射流 发射光谱 振转温度 Atmospheric plasma jet Optical emission spectroscopy Vibrational and rotational temperature





