Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Radiology Technology, College of Health and Medical Technology, Middle Technical University (MTU), Baghdad, Iraq
2 Department of Physics, College of Education for Pure Science (Ibn-AL-Haitham), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
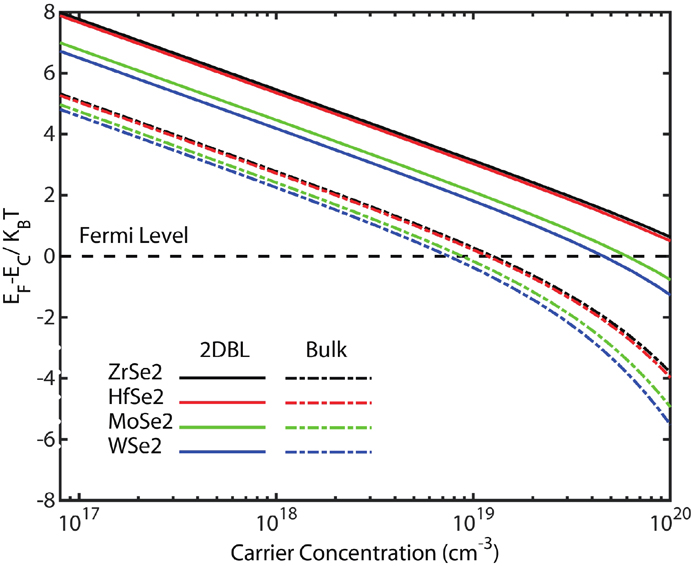
Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.
ZT thermoelectric property 2D-bilayer Boltzmann-transport equation TE power factor Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(3): 032001
武汉理工大学 材料复合新技术国家重点实验室, 武汉 430070
固溶结合掺杂是优化材料热电性能的有效途径。本研究采用固相反应结合等离子体活化烧结成功合成了一系列单相的Mo1-xWxSeTe(0≤x≤0.5)固溶体及其Nb掺杂产物。热电输运研究表明, W固溶结合Nb掺杂显著提高了Nb2yMo0.5-yW0.5-ySeTe固溶体的载流子浓度、载流子迁移率、电导率和功率因子, 适当降低了样品的晶格热导率, 进而显著提高了材料的热电优值ZT。随着Nb掺杂量的增加, 掺杂引入的离散能级转变为连续的杂质能带, 同步提升了载流子浓度和载流子迁移率。取向性研究发现, 由于在平行方向晶格热导率较低, Nb2yMo0.5-yW0.5-ySeTe固溶体在平行烧结压力方向的ZT略优。最优组分Nb0.03Mo0.485W0.485SeTe在垂直于烧结压力和平行于烧结压力方向获得了最高ZT, 分别达到0.31和0.36(@823 K), 是目前MoSe2基热电材料获得的最好结果之一。后续通过优化掺杂元素来改善Seebeck系数和功率因子, 将有望进一步提升MoSe2基化合物的ZT。
Mo1-xWxSeTe固溶体 Nb掺杂 晶格热导率 热电优值ZT Mo1-xWxSeTe solid solutions Nb doping lattice thermal conductivity thermoelectric figure of merit ZT 




