Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang Lab, Research Center for Humanoid Sensing, Hangzhou, China
2 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, State Key Laboratory of Extreme Photonics and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
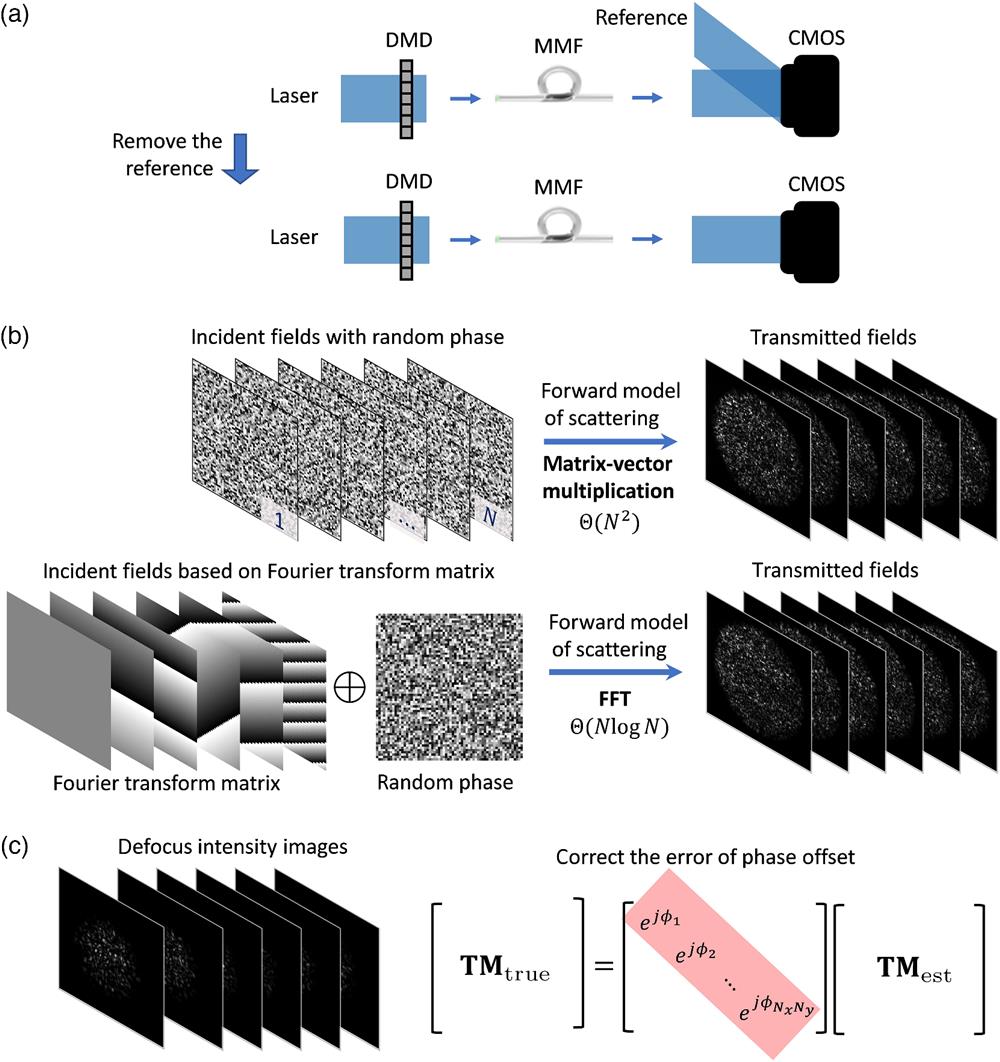
Imaging through multimode fiber (MMF) provides high-resolution imaging through a fiber with cross section down to tens of micrometers. It requires interferometry to measure the full transmission matrix (TM), leading to the drawbacks of complicated experimental setup and phase instability. Reference-less TM retrieval is a promising robust solution that avoids interferometry, since it recovers the TM from intensity-only measurements. However, the long computational time and failure of 3D focusing still limit its application in MMF imaging. We propose an efficient reference-less TM retrieval method by developing a nonlinear optimization algorithm based on fast Fourier transform (FFT). Furthermore, we develop an algorithm to correct the phase offset error of retrieved TM using defocused intensity images and hence achieve 3D focusing. The proposed method is validated by both simulations and experiments. The FFT-based TM retrieval algorithm achieves orders of magnitude of speedup in computational time and recovers 2286 × 8192 TM of a 0.22 NA and 50 μm diameter MMF with 112.9 s by a computer of 32 CPU cores. With the advantages of efficiency and correction of phase offset, our method paves the way for the application of reference-less TM retrieval in not only MMF imaging but also broader applications requiring TM calibration.
transmission matrix retrieval multimode fiber imaging through scattering Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Applied Optics, University of Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9, Stuttgart 70569, Germany
2 Institut für Lasertechnologien in der Medizin und Messtechnik, Helmholtzstrasse 12, Ulm 89081, Germany
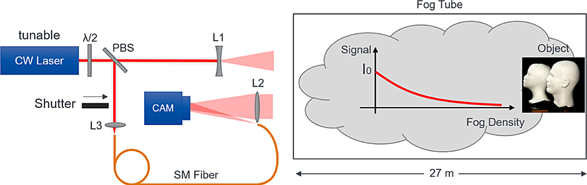
Interferometric detection enables the acquisition of the amplitude and phase of the optical field. By making use of the synthetic wavelength as a computational construct arising from digital processing of two off-axis digital holograms, it is possible to identify the shape of an object obscured by fog and further increase the imaging range due to the increased sensitivity in coherent detection. Experiments have been conducted inside a 27 m long fog tube filled with ultrasonically generated fog. We show the improved capabilities of synthetic phase imaging through fog and compare this technique with conventional active laser illumination imaging.
Digital holography Phase imaging Imaging through scattering media Two-wavelength holography 3D shape measurement Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2023024
红外与激光工程
2023, 52(2): 20220318
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所 量子光学重点实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学 材料与光电研究中心,北京 100049
透过散射介质的光学成像是人们长期追求但一直未能真正解决的问题。研究人员提出并发展了各种各样的方法和技术,从最早只利用弹道光的时间门和空间门技术,到后来利用了散射光的波前整形、散射矩阵测量和散斑自相关成像,再到近年热门的深度学习方法。尽管这些方法和技术都经过了毛玻璃、氧化锌薄膜、生物组织切片等薄散射介质的原理性验证,但随着介质厚度增加,所有方法和技术都迅速失效。厚度一直是难以克服的瓶颈。这篇评论归纳对比了散射成像的主要方法和技术,重新审视了经过散射介质波前被完全随机化等主流观点,分析了现有方法和技术无法透过厚散射介质成像的原因,并提出了未来有望真正解决问题的研究方向。
透过散射介质成像 弹道光 散射光 波前整形 散斑自相关成像 深度学习 imaging through scattering media ballistic photons scattered photons wavefront shaping speckle autocorrelation imaging deep learning 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(8): 20220261
南京航空航天大学党政办公室, 江苏 南京 210016
基于记忆效应的散斑解卷积法是近几年提出的一种可以实现透过散射介质层成像的方法。可用于散斑解卷积法的算法有很多,但具体的对比分析工作却鲜有报道。设计并搭建了基于记忆效应的透过散射层成像的光学系统,对探测到的散斑进行解卷积计算,并重建出对象图像。在重建过程中,分别使用互相关解卷积算法、维纳滤波算法、正则化解卷积算法以及Lucy-Richardson算法进行解卷积计算。对不同算法重建的图像进行了多个图像质量评价指标的计算。综合图像质量和计算时间,发现互相关解卷积算法在透过散射层成像的应用中具有最大优势,并从原理上进行了简要的解释。
成像系统 解卷积 散斑 透过散射介质层成像 算法 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(22): 221104
南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院, 江苏 南京 210094
由于散射介质的强散射作用,传统光学成像系统无法对散射介质后的物体进行成像与运动追踪。针对这一问题,提出了一种透过散射介质对运动物体进行追踪与重建的方法。基于散射介质的光学记忆效应理论,通过先验信息解算散射成像系统的点扩展函数,利用点扩展函数的轴向缩放关系确定轴向位移,利用重建物体的互相关确定横向偏移。基于此方法搭建的实验系统也很好地实现了散射介质后物体的快速重建与运动追踪。所提方法仅需采集移位物体的连续散斑图像即可追踪物体位移,无需特定装置且效果优异,有利于透过散射介质成像在生物医学领域的应用。
成像系统 透过散射介质成像 运动目标追踪 反卷积 点扩展函数 光学学报
2020, 40(12): 1211001
1 中山大学物理学院, 广东 广州 510275
2 汕头大学理学院物理系, 广东 汕头 515063
散射光学成像恢复是光学成像领域最重要的研究课题之一。科学家已经提出各种技术实现不同散射环境下的成像恢复。其中,散斑相关性的解卷积技术具有成像质量高、恢复速度快和易于集成等优点。简要综述了散斑相关成像的进展,从光学记忆效应和解卷积原理出发,介绍点扩展函数新物理特性及其在成像恢复中的应用,总结点扩展函数的间接获取方法,最后提出光场全要素(plenoptics)的概念。光场的全要素探索有望在更复杂散射环境中提供更全面的信息,使散射光学成像技术在生物、医疗、海洋、**和日常生活等场景中更具应用前景。
成像系统 散斑相关成像 散射介质成像 散射
天津大学 精密仪器与光电子工程学院 光电信息技术教育部重点实验室, 天津 300072
在水下环境中, 悬浮的散射颗粒对光场的散射和吸收作用导致成像清晰度显著下降。基于偏振成像的水下图像复原技术是实现水下清晰成像的有效方法之一。该技术利用散射光的偏振特性, 分离场景光和散射光, 估计散射光强和透射系数, 实现成像清晰化。近年来, 偏振成像技术已广泛、高效地应用于水下图像复原和水下目标识别等诸多领域。水下偏振图像复原技术作为光学成像技术和图像处理技术的交叉领域, 引起了广泛的关注并取得了大量优秀的研究成果。文中主要介绍了基于偏振成像的水下复原技术的基本原理、偏振信息处理方法和最新发展现状, 综述了近年来偏振水下图像复原技术代表性的改进型方法。
偏振成像 水下图像复原 散射介质成像 polarimetric imaging underwater image restoration imaging in scattering media 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(6): 0603006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Shanghai, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Center for Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, Beijing, China
The problem of imaging through thick scattering media is encountered in many disciplines of science, ranging from mesoscopic physics to astronomy. Photons become diffusive after propagating through a scattering medium with an optical thickness of over 10 times the scattering mean free path. As a result, no image but only noise-like patterns can be directly formed. We propose a hybrid neural network for computational imaging through such thick scattering media, demonstrating the reconstruction of image information from various targets hidden behind a white polystyrene slab of 3 mm in thickness or 13.4 times the scattering mean free path. We also demonstrate that the target image can be retrieved with acceptable quality from a very small fraction of its scattered pattern, suggesting that the speckle pattern produced in this way is highly redundant. This leads to a profound question of how the information of the target being encoded into the speckle is to be addressed in future studies.
imaging through scattering media deep learning neural network computational imaging Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(3): 036002
1 中国工程物理研究院应用电子学研究所,四川 绵阳 621900
2 电子科技大学 光电信息学院,四川 成都 610054
在利用散射成像法测量激光强度分布中,CCD像面与散射屏平面存在较大角度时,光斑形状和强度分布都会产生严重畸变,给强度分布测量带来较大影响。分析了畸变产生的原因,给出了畸变坐标和理想坐标的数学模型,提出一种结合CCD像素合并的网格法来校正这种畸变。“网格法”利用自制标准网格成像,通过识别网格像边界来确定标准网格和畸变网格的对应关系,利用此对应关系在输出图像时恢复光斑;利用均匀光源成像来校正系统光强分布畸变。结果表明,该方法能够较好地校正光斑的形状畸变;能够实时恢复光斑的真实光强分布,单元强度畸变恢复误差小于1%。该校正方法在激光强度分布散射成像测量中非常实用。
光学测量 畸变校正 网格法 激光强度分布 散射成像 漫反射





