
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hefei, China
2 Hefei University of Technology, School of Physics, Department of Optical Engineering, Hefei, China
3 Hefei Normal University, Department of Chemical and Chemical Engineering, Hefei, China
4 University of Science and Technology of China, Science Island Branch of Graduate School, Hefei, China
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging has emerged as a prominent technique for reconstructing obscured objects from images that undergo multiple diffuse reflections. This imaging method has garnered significant attention in diverse domains, including remote sensing, rescue operations, and intelligent driving, due to its wide-ranging potential applications. Nevertheless, accurately modeling the incident light direction, which carries energy and is captured by the detector amidst random diffuse reflection directions, poses a considerable challenge. This challenge hinders the acquisition of precise forward and inverse physical models for NLOS imaging, which are crucial for achieving high-quality reconstructions. In this study, we propose a point spread function (PSF) model for the NLOS imaging system utilizing ray tracing with random angles. Furthermore, we introduce a reconstruction method, termed the physics-constrained inverse network (PCIN), which establishes an accurate PSF model and inverse physical model by leveraging the interplay between PSF constraints and the optimization of a convolutional neural network. The PCIN approach initializes the parameters randomly, guided by the constraints of the forward PSF model, thereby obviating the need for extensive training data sets, as required by traditional deep-learning methods. Through alternating iteration and gradient descent algorithms, we iteratively optimize the diffuse reflection angles in the PSF model and the neural network parameters. The results demonstrate that PCIN achieves efficient data utilization by not necessitating a large number of actual ground data groups. Moreover, the experimental findings confirm that the proposed method effectively restores the hidden object features with high accuracy.
non-line-of-sight imaging point spread function model deep learning Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(2): 026010
1 南昌大学信息工程学院,江西 南昌 330031
2 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所,陕西 西安 710119
在非视域成像场景中,有效的回波光子大量减少,泊松噪声对非视域成像的质量影响较大。传统图像泊松降噪算法存在迭代时间长、模式固定和手动设置参数等问题。为提高非视域成像质量,设计一种基于深度学习的单光子非视域成像泊松降噪方法。为解决训练样本不足的问题,利用几何光学近似和蒙特卡罗方法对非视域场景下的光子运动轨迹进行追踪建模,对非视域成像过程进行仿真,利用仿真数据重建的泊松噪声图像制作数据集。设计基于注意力机制的特征增强降噪网络(AEF-Net),利用仿真数据对网络进行优化训练。最后,搭建一套非视域成像系统对网络的泊松降噪性能进行验证。实验结果表明所提AEF-Net去除非视域场景下的泊松噪声效果优于传统降噪算法。
非视域成像 仿真分析 深度学习 泊松降噪 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(20): 2011003
1 国防科技大学 电子对抗学院, 安徽 合肥 230037
2 国防科技大学 脉冲功率国家重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230037
3 国防科技大学 电子制约技术安徽省重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230037
4 中国人民解放军77126部队, 云南 开远 661600
非视域(Non-Line-of-Sight, NLoS)成像是近年来发展起来的一项新兴技术,其通过分析成像场景中的中介面信息来重建隐藏场景,实现了“拐弯成像”的效果,在多个领域有巨大的应用价值。本文主要针对NLoS成像重建算法进行综述性研究。考虑到目前NLoS成像分类存在交叉和非独立现象,本文基于物理成像模式和算法模型的不同特点,对其进行了独立的重新分类。根据提出的分类标准分别对传统和基于深度学习的NLoS成像重建算法进行了归纳总结,对代表性算法的发展现状进行了概述,推导了典型方法的实现原理,并对比了传统重建方法和基于深度学习的NLoS成像重建算法的重建应用结果。总结了NLoS成像目前存在的挑战和未来的发展方向。该研究对不同类型的NLoS成像进行了较为全面的梳理,对NLoS成像重建算法在内的一系列研究的进一步发展有着一定的支撑和推动作用。
非视域成像 重建算法 成像模式 深度学习 non-line-of-sight imaging reconstruction algorithm imaging mode deep learning 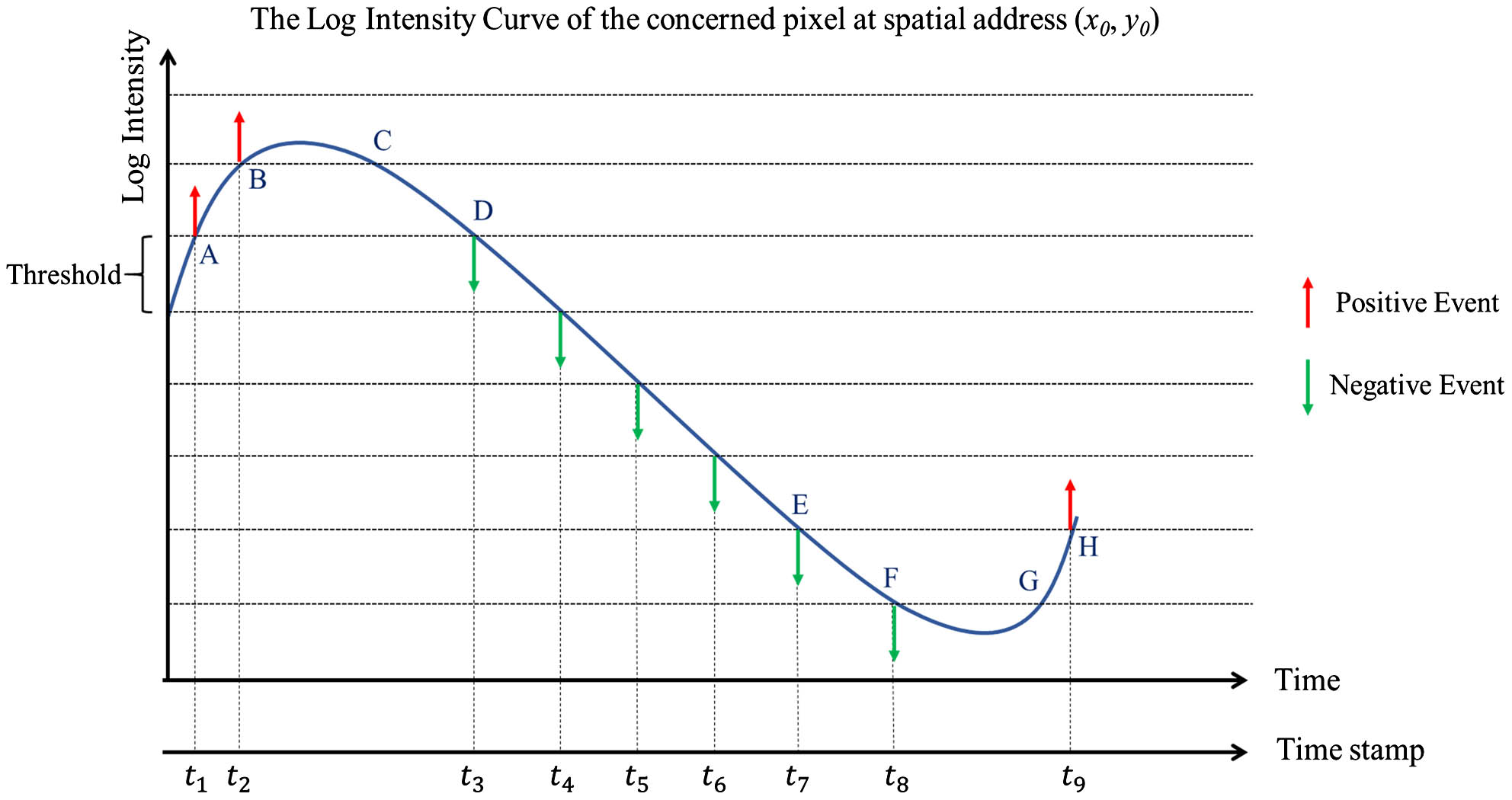
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic Imaging Technology and System of Ministry of Education of China, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology (BNRist), Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging is an emerging technique for detecting objects behind obstacles or around corners. Recent studies on passive NLOS mainly focus on steady-state measurement and reconstruction methods, which show limitations in recognition of moving targets. To the best of our knowledge, we propose a novel event-based passive NLOS imaging method. We acquire asynchronous event-based data of the diffusion spot on the relay surface, which contains detailed dynamic information of the NLOS target, and efficiently ease the degradation caused by target movement. In addition, we demonstrate the event-based cues based on the derivation of an event-NLOS forward model. Furthermore, we propose the first event-based NLOS imaging data set, EM-NLOS, and the movement feature is extracted by time-surface representation. We compare the reconstructions through event-based data with frame-based data. The event-based method performs well on peak signal-to-noise ratio and learned perceptual image patch similarity, which is 20% and 10% better than the frame-based method.
non-line-of-sight imaging event camera event-based representation Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(6): 061103
中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院,浙江 杭州 310018
非视域成像可对视域外场景进行重建成像。与传统成像不同,其将隐藏场景返回的间接信号导入重建算法实现目标场景重建,在**、生物医学、自动驾驶、航空航天及灾后搜救等领域具有重要的应用价值。总结近年来国内外对非视域成像技术的研究进展,依次介绍3种非视域成像模式,包括基于飞行时间的非视域成像、基于相干信息的非视域成像(含基于散斑图案和空间相干两种方法)、基于强度信息的非视域成像。基于相干信息和强度信息成像模式的硬件参数、重建算法、重建时间和图像分辨率等的特点和存在的局限性,分析并讨论非视域成像的发展趋势。
非视域成像 飞行时间 相干成像 强度成像 散射成像 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(14): 1400001
1 伊犁师范大学网络安全与信息技术学院,新疆 伊宁 835000
2 南京大学电子科学与工程学院,江苏 南京 210046
非视域成像技术采用非传统光学技术,利用间接成像的方法对无法直接观测的隐藏物体进行探测。针对目前试验系统复杂且需要场景扫描,导致数据采集过程复杂且需要大量时间的问题,提出基于阵列式APD的透射式非视域成像试验设置,试验设置操作简单且不需要场景扫描,实现快速数据采集。针对非视域成像技术一般只能获取不完全(缺失)角度的数据,使用反投影算法不能得到理想的重建结果的问题,提出利用联合代数迭代(SART)重建算法对非视域成像物体进行三维重建。试验结果表明:SART算法能够在部分角度数据下,更好地去除反投影算法中的伪影和噪点;在最初的第2和第3次迭代后,通过计算,其峰值信噪比PSNR值提高了1.392 8、2.466 3,其结构相似度SSIM值提高了0.119 8、0.231 2,表明该方法能有效提高非视域物体的图像重建精度。
非视域成像 联合代数迭代重建算法 缺失数据 三维图像重建 non-line-of-sight imaging simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique re missing data 3D image reconstruction
1 伊犁师范大学网络安全与信息技术学院, 新疆 伊宁 835000
2 南京大学电子科学与工程学院, 江苏 南京 210046
非视域成像技术是一种新型光学成像技术, 主要是对拐角处的隐藏物体进行成像。针对目前成像设备复杂和需要场景扫描, 导致数据采集速度慢的问题, 提出采用纳秒激光和APD阵列探测器的透射式成像试验装置, 可以实现快速数据采集, 不需要进行场景扫描, 相比之前的系统大大缩短了数据采集时间。针对仅能在稀疏角度或有限角度下采集数据而导致图像重建结果差的问题, 提出使用最大似然期望最大化(maximize likelihood estimate maximization, MLEM)迭代算法进行隐藏物体三维图像重建。试验结果表明, MLEM迭代算法能够较好地重建隐藏物体的形状, 并有效抑制传统的反投影算法带来的伪影。对比反投影算法, 隐藏物体在深度位置150 cm处, 3次迭代(第3、6和10次)结果图的结构相似度(SSIM)值分别提高了0.232 1、0.387 8和0.438 9; 在深度位置190 cm处, 3次迭代(第3、6和10次)结果图的SSIM值分别提高了0.314 6、0.401 3和0.431 3。这表明MLEM算法对重建图像质量有较大提升。
非视域成像 APD阵列 稀疏角度 最大似然期望最大化算法 图像重建 non-line-of-sight imaging APD array spare angles maximize likelihood estimate maximization image reconstruction
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
针对非相干光照明下的非视域成像问题,提出一种基于深度学习的解决方法。结合计算机视觉领域中经典的语义分割及残差模型,构造一种URNet网络结构,并改进了经典瓶颈层结构。实验结果表明,改进的网络可以恢复更多的图像细节,并具有一定泛化性,相比于基于非相干光照明的散斑自相关成像技术,该网络恢复性能有较大提升。
成像系统 非视域成像 深度学习 语义分割 残差模型
海军工程大学 兵器工程系, 湖北 武汉430033
介绍了采用距离选通技术进行非视域成像探测的原理, 基于窄脉冲激光器和选通型成像器件搭建了非视域主动成像实验系统。以玻璃作为中介反射面, 以黑白条纹靶板作为目标, 对目标和周围环境处于不同光照情形时, 系统的非视域成像效果进行测试。结果表明, 基于距离选通的非视域成像技术是一种能够在不同光照条件下实现对视觉盲区进行有效观察的成像技术。
距离选通 非视域成像 背景光 range-gated imaging non-line-of-sight imaging background illumination





