香港大学物理系新基石科学实验室,香港 999077
耦合等离激元体系在光场调控、光学传感、光学成像及光电器件等领域中有着广泛应用。目前,阻碍耦合等离激元进一步实用化发展的关键问题是金属材料具有较大的损耗。结合数值仿真方法,从理论上研究了耦合等离激元的损耗机理,并进一步分析复频率光源激励对耦合等离激元体系的作用,提出了通过合成复频率波的方法来补偿损耗,从而恢复被削弱的耦合共振信号。所提优化手段具有泛用性高且无需额外成本的优势,研究结果对耦合等离激元体系在各个领域中的研究发展具有借鉴意义,有利于挖掘该体系的潜在应用价值。
物理光学 纳米光学 等离激元 复频率波 光学传感 光学学报
2024, 44(10): 1026019
提出了一种金纳米十字双层等离子体结构阵列(BPNA), 采用有限时域差分法(FDTD), 计算了金纳米十字孔阵列、金纳米十字薄片阵列、二氧化硅阵列对结构透射性能的影响。计算得出的透射光谱中, 三者均对局域表面等离子激元(LSP)产生了影响, 产生的LSP共振峰强度和位置取决于十字孔的宽度、长度以及厚度和十字薄片的宽度、长度以及厚度, 通过增加介质层厚度分析出两个LSP共振峰的产生原因主要取决于十字孔缝产生的LSP或十字薄片产生的LSP, 而替换二氧化硅选用理想介质同样对LSP共振峰产生影响。对等离子体结构进行参数调节可以改变其透射性能, 调节后的半峰宽度(FWHM)高达0.72m, 透射强度高达0.96, 可以用来实现天线的高性能传输, 还获得了较高的灵敏度(FOM)值为17.22m/RIU, 对实现高性能的LSP传感器和光学器件有一定借鉴意义。
双层等离子体结构阵列 局域表面等离子体共振 半峰宽度 灵敏度 bi-layer plasmonic nanostructure array localized surface plasmon full width at half maxima figure of merit 量子光学学报
2023, 29(4): 040801
浙江大学光电科学与工程学院,浙江 杭州 310027
激光耦合隧道结器件是国际前沿研究热点,伴随产生的电磁场局域增强或光整流等效应在等离激元光镊、单分子成像、单光子光源等领域有着重要的应用价值。为了解隧道结中的光电相互作用和特性,首先利用反馈电沉积制备获得了固态隧道结纳米器件,然后测定了激光功率、偏置电压、偏振方向和调制频率与光电流的关系,并结合有限元法和时域有限差分方法进行理论仿真,讨论了器件中光电流的组分及相关效应。结果表明,器件局部热膨胀效应、热伏效应和热载流子效应为光电流产生的主要原因,而光整流效应因受限于激光峰值功率,其结果并不显著。这些发现可为固态隧道结器件中的光学调控以及在纳米尺度上研究激光调制电子隧穿过程提供参考。
光学器件 隧道结纳米器件 光电流 热效应 光整流效应 等离激元效应 中国激光
2023, 50(23): 2313001
郑州航空工业管理学院 材料学院, 河南 郑州 450046
提出一种基于银纳米颗粒等离激元共振和耦合效应的彩色透明显示屏。对银颗粒优化设计,说明在红、绿、蓝三波段能够出现三个散射峰,可用于增强彩色显示性能;接下来,通过溶液热法制备出该屏幕;经投影仪对屏投影测试发现确实具有彩色、高透、高亮和宽视角。另外,研究发现在等离激元共振及耦合作用下,银颗粒在红、绿、蓝三个共振位置均具有偶极子的远场散射形貌,充分解释了显示屏高亮和宽视角的原因。提出的透明显示屏具有透明度和亮度高、观察视角宽、制备工艺简单、成本低等特点,在透明显示领域将有大的应用潜力。
物理光学 表面等离激元 等离激元耦合效应 彩色透明显示 physical optics surface plasmons plasmonic coupling effect full-color transparent display
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Australian National University, Research School of Physics, Nonlinear Physics Center, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia
We review the physics and some applications of photonic structures designed for the realization of strong nonlinear chiroptical response. We pay much attention to the recent strategy of utilizing different types of optical resonances in metallic and dielectric subwavelength structures and metasurfaces, including surface plasmon resonances, Mie resonances, lattice-guided modes, and bound states in the continuum. We summarize earlier results and discuss more recent developments for achieving large circular dichroism combined with the high efficiency of nonlinear harmonic generation.
chirality metaphotonics dielectric metasurfaces plasmonic metasurfaces nonlinear optics bound states in the continuum Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(6): 064001

Jianying Jing 1,2,3Kun Liu 1,2,3,*Junfeng Jiang 1,2,3Tianhua Xu 1,2,3[ ... ]Tiegen Liu 1,2,3
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Precision Instruments and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronics Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
3 Tianjin Optical Fiber Sensing Engineering Center, Institute of Optical Fiber Sensing, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
A dispersion model is developed to provide a generic tool for configuring plasmonic resonance spectral characteristics. The customized design of the resonance curve aiming at specific detection requirements can be achieved. According to the model, a probe-type nano-modified fiber optic configurable plasmonic resonance (NMF-CPR) sensor with tip hot spot enhancement is demonstrated for the measurement of the refractive index in the range of 1.3332–1.3432 corresponding to the low-concentration biomarker solution. The new-type sensing structure avoids excessive broadening and redshift of the resonance dip, which provides more possibilities for the surface modification of other functional nanomaterials. The tip hot spots in nanogaps between the Au layer and Au nanostars (AuNSs), the tip electric field enhancement of AuNSs, and the high carrier mobility of the WSe2 layer synergistically and significantly enhance the sensitivity of the sensor. Experimental results show that the sensitivity and the figure of merit of the tip hot spot enhanced fiber NMF-CPR sensor can achieve up to 2995.70 nm/RIU and 25.04 RIU−1, respectively, which are 1.68 times and 1.29 times higher than those of the conventional fiber plasmonic resonance sensor. The results achieve good agreements with numerical simulations, demonstrate a better level compared to similar reported studies, and verify the correctness of the dispersion model. The detection resolution of the sensor reaches up to 2.00×10−5 RIU, which is obviously higher than that of the conventional side-polished fiber plasmonic resonance sensor. This indicates a high detection accuracy of the sensor. The dense Au layer effectively prevents the intermediate nanomaterials from shedding and chemical degradation, which enables the sensor with high stability. Furthermore, the terminal reflective sensing structure can be used as a practical probe and can allow a more convenient operation.
fiber photonics sensor customized plasmonic resonance curve nano-modified fiber core tip hot spot effect high sensitivity and stability Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(6): 220072
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Superlattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
4 Joint Laboratory of Advanced Semiconductor, Nanjing Guoke Semiconductor CO., Ltd, Nanjing 210000, China
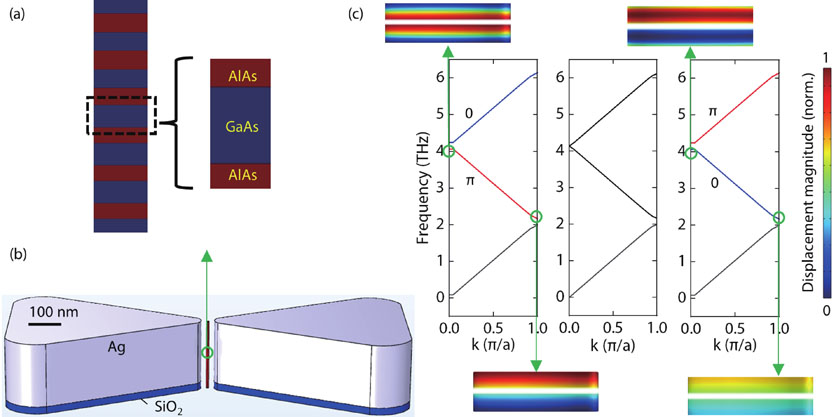
Interaction between photons and phonons in cavity optomechanical systems provides a new toolbox for quantum information technologies. A GaAs/AlAs pillar multi-optical mode microcavity optomechanical structure can obtain phonons with ultra-high frequency (~THz). However, the optical field cannot be effectively restricted when the diameter of the GaAs/AlAs pillar microcavity decreases below the diffraction limit of light. Here, we design a system that combines Ag nanocavity with GaAs/AlAs phononic superlattices, where phonons with the frequency of 4.2 THz can be confined in a pillar with ~4 nm diameter. The Qc/V reaches 0.22 nm?3, which is ~80 times that of the photonic crystal (PhC) nanobeam and ~100 times that of the hybrid point-defect PhC bowtie plasmonic nanocavity, where Qc is optical quality factor and V is mode volume. The optomechanical single-photon coupling strength can reach 12 MHz, which is an order of magnitude larger than that of the PhC nanobeam. In addition, the mechanical zero-point fluctuation amplitude is 85 fm and the efficient mass is 0.27 zg, which is much smaller than the PhC nanobeam. The phononic superlattice-Ag nanocavity optomechanical devices hold great potential for applications in the field of integrated quantum optomechanics, quantum information, and terahertz-light transducer.
Optomechanics phononic crystal Ag plasmonic nanocavity confinement coupling Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(8): 082901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 School of Integrated Circuits, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
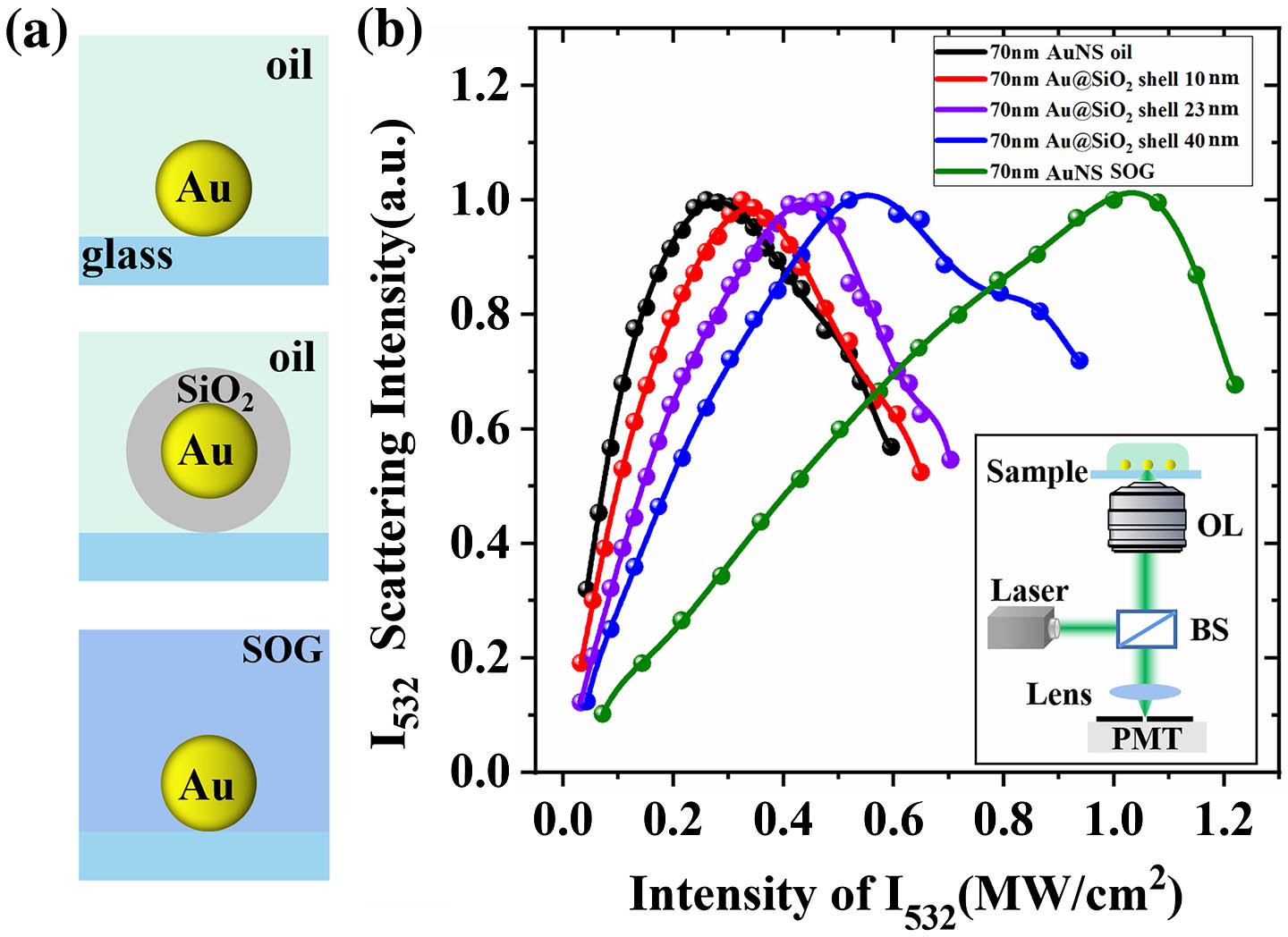
In this Letter, we report on the investigations of nonlinear scattering of plasmonic nanoparticles by manipulating ambient environments. We create different local thermal hosts for gold nanospheres that are immersed in oil, encapsulated in silica glass and also coated with silica shells. In terms of regulable effective thermal conductivity, silica coatings are found to contribute significantly to scattering saturation. Benefitting from the enhanced thermal stability and the reduced plasmonic coupling provided by the shell-isolated nanoparticles, we achieve super-resolution imaging with a feature size of 52 nm (), and we can readily resolve pairs of nanoparticles with a gap-to-gap distance of 5 nm.
noble metal nanoparticles plasmonic scattering effective thermal conductivity super-resolution Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 103601
1 中北大学 仪器科学与动态测试教育部重点实验室, 山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学 软件学院, 山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学 信息与通信工程学院, 山西 太原 030051
4 岭南师范学院 物理科学与技术学院, 广东 湛江 524048
为了研究超表面结构的耦合及折射率传感特性,设计了一种由两种长度不同的纳米棒组成的二聚体结构,并研究该结构的透射光谱,共振峰处的电场和电荷分布以及结构参数对透射光谱的影响。本文采用有限元法对光学性能进行仿真分析,采用准静态逼近模型解释了平行双纳米棒结构的耦合机理。在共振波长上模拟电场分布,分析电子振动模式,在透射光谱中出现了不对称线型的双Fano共振。结果表明,双Fano共振是由纳米棒和衬底之间的耦合作用产生的,可以通过结构参数和周围介质的折射率来调控,且基于Fano共振的折射率灵敏度最大可达1.137 μm/RIU。这些研究结果为设计等离激元传感器提供了理论依据。
等离激元超表面 Au纳米棒 双Fano共振 折射率传感器 plasmonic metasurfaces Au nanorods double Fano resonance refractive index sensor 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Terahertz Waves and College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin University and the Key Laboratory of Optoelectronics Information and Technology (Ministry of Education), Tianjin 300072, China
2 Guangxi Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing, School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China
3 School of Electronic and Computer Engineering, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK 74078, USA
Plasmonic vortices confining orbital angular momentums to surface have aroused wide research interest in the last decade. Recent advances of near-field microscopes have enabled the study on the spatiotemporal dynamics of plasmonic vortices, providing a better understanding of optical orbital angular momentums in the evanescent wave regime. However, these works only focused on the objective characterization of plasmonic vortex and have not achieved subjectively tailoring of its spatiotemporal dynamics for specific applications. Herein, it is demonstrated that the plasmonic vortices with the same topological charge can be endowed with distinct spatiotemporal dynamics by simply changing the coupler design. Based on a near-field scanning terahertz microscopy, the surface plasmon fields are directly obtained with ultrahigh spatiotemporal resolution, experimentally exhibiting the generation and evolution divergences during the whole lifetime of plasmonic vortices. The proposed strategy is straightforward and universal, which can be readily applied into visible or infrared frequencies, facilitating the development of plasmonic vortex related researches and applications.
plasmonic vortex surface plasmon spatiotemporal dynamics optical orbital angular momentum Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(4): 220133





