
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
High-precision angle measurement of pulsars is critical for realizing pulsar navigation. Compared to visible light and radio waves, the wavelength of X-rays is incredibly short, which provides the possibility of achieving better spatial resolution. However, due to the lack of applicable X-ray apparatus, extracting the angle information of pulsars through conventional X-ray methods is challenging. Here, we propose an approach of pulsar angle measurement based on spatially modulated X-ray intensity correlation (SMXIC), in which the angle information is obtained by measuring the spatial intensity correlation between two radiation fields. The theoretical model for this method has been established, and a proof-of-concept experiment was carried out. The SMXIC measurement of observing angles has been demonstrated, and the experimental results are consistent with the theoretical values. The potential of this method in future applications is discussed, and theoretically, the angular measurement at the level of micro-arcsecond can be expected. The sphere of pulsar navigation may benefit from our fresh insights.
pulsar measurement X-ray measurement intensity correlation spatial modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Precision Optical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-Structured Materials, Shanghai Frontiers Science Center of Digital Optics, Shanghai Professional Technical Service Platform for Full-Spectrum and High-Performance Optical Thin Film Devices and Applications, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
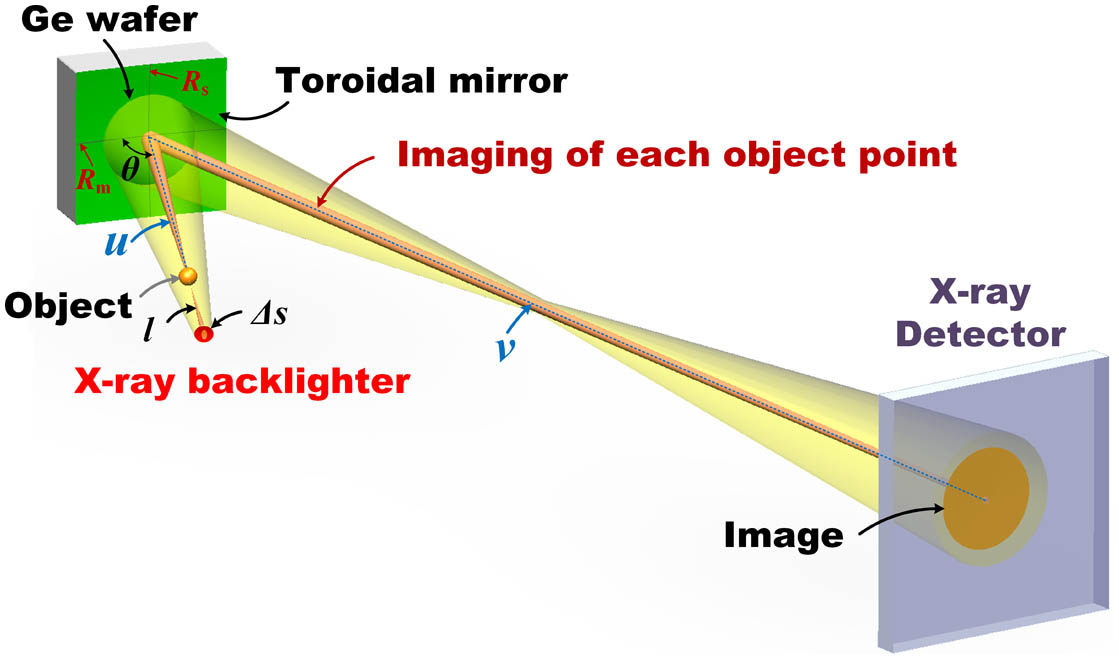
Curved crystal imaging is an important means of plasma diagnosis. Due to the short wavelengths of high-energy X rays and the fixed lattice constant of the spherical crystal, it is difficult to apply the spherical crystal in high-energy X-ray imaging. In this study, we have developed a high-energy, high-resolution X-ray imager based on a toroidal crystal that can effectively correct astigmatism. We prepared a Ge toroidal crystal for backlighting Mo Kα1 characteristic lines ( keV) and verified its high-resolution imaging ability in high-energy X-ray region, achieving a spatial resolution of 5–10 µm in a field of view larger than 1.0 mm.
laser plasma diagnostics toroidal crystal monochromatic X-ray imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 103401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
In this paper, the influence of the delay time between the pre-pulse and the main pulse on the double-pass amplified 46.9 nm laser was studied for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, by using a high-precision polished SiC slice as a rear mirror. The temporal and spatial characteristics of the output laser were measured separately to investigate the effect of the delay time on the laser characteristics. The energy of the double-pass amplified laser was between 510 µJ and 890 µJ. In addition, a theoretical model of double-pass amplification was established to analyze the effect of the delay time on the double-pass amplified 46.9 nm laser.
double-pass amplification delay time 46.9 nm laser capillary discharge Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(5): 053401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-Structured Materials, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Institute of Precision Optical Engineering, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
3 Center for Transformative Science, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
In this paper, a simple theoretical model combining Monte Carlo simulation with the enthalpy method is provided to simulate the damage resistance of B4C/Si-sub mirror under X-ray free-electron laser irradiation. Two different damage mechanisms are found, dependent on the photon energy. The optimum B4C film thickness is determined by studying the dependence of the damage resistance on the film thickness. Based on the optimized film thickness, the damage thresholds are simulated at photon energy of 0.4–25 keV and a grazing incidence angle of 2 mrad. It is recommended that the energy range around the Si K-edge should be avoided for safety reasons.
B4C film XFEL damage mechanism damage threshold enthalpy method Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(2): 023401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Photonics Laboratory, Department of Physics, Dankook University, Cheonan 31116, Republic of Korea
2 Center for Basic Science Research at DKU, Dankook University, Cheonan 31116, Republic of Korea
Non-interferometric X-ray quantitative phase imaging (XQPI), much simpler than the interferometric scheme, has provided high-resolution and reliable phase-contrast images. We report on implementing the volumetric XQPI images using concurrent-bidirectional scanning of the orthogonal plane on the optical axis of the Foucault differential filter; we then extracted data in conjunction with the transport-intensity equation. The volumetric image of the laminate microstructure of the gills of a fish was successfully reconstructed to demonstrate our XQPI method. The method can perform 3D rendering without any rotational motion for laterally extended objects by manipulating incoherent X-rays using the pinhole array.
X-ray imaging phase contrast imaging Foucault differential filter transport-intensity equation Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(1): 013401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
A new type of X-ray fiber dosimeters is proposed that is based on the X-ray response of perovskite-quantum-dots (PQDs) activated silica fiber. Such a fiber sensor is constructed by covering a multimode silica fiber with PQDs embedded glass powders using a transparent high-temperature glue. Under X-ray irradiation, the fiber sensor emits bright green light at 525 nm, which can be readily recorded by a CCD spectrometer. The integrated radioluminescence intensity has an excellent linear response to the X-ray dose. Study is given to the fiber sensor concerning its thermal stability in a temperature range of room temperature up to 300°C, resistance to water erosion, and prolonged X-ray irradiation. The results verify that the proposed fiber sensor has the advantages of good thermal stability, chemical durability, and radiation hardness. The studied X-ray fiber sensor holds promise to be used in a real-time, in-situ, and remote radiation dose monitoring.
perovskite quantum dots glass ceramics X-ray radiation fiber dosimeter Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(6): 063401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility/Zhangjiang Lab, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201204, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
At present, reconstruction of megapixel and high-fidelity images with few measurements is a major challenge for X-ray ghost imaging (XGI). The available strategies require massive measurements and reconstruct low-fidelity images of less than pixels. Inspired by the concept of synthetic aperture radar, synthetic aperture XGI (SAXGI) integrated with compressive sensing is proposed to solve this problem with a binned detector in the object arm. Experimental results demonstrated that SAXGI can accurately reconstruct the pixels image of a binary sample of tangled strands of tungsten fiber from 660 measurements. Accordingly, SAXGI is a promising solution for the practical application of XGI.
X-ray ghost imaging compressive sensing megapixel imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(3): 033401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility/Zhangjiang Lab, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201204, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Carbon fiber (CF)/pyrolytic graphite (PG) composites are promising structural materials for molten salt reactors because of their superior performance. Due to the minor density difference between CF and PG, existing methods are impractical for efficient three-dimensional characterization of CF/PG composites. Therefore, in this study, a method based on in-line phase-contrast X-ray microtomography was developed to solve the aforementioned problem. Experimental results demonstrate that the method is suitable for comprehensive characterization of CF/PG composites. The relationship between the microporous defects and fiber orientations of such composites was also elucidated. The findings can be useful for improving the manufacturing process of CF/PG composites.
X-ray imaging C/C composite 3D characterization Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(7): 073401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology and Systems of the Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China
3 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
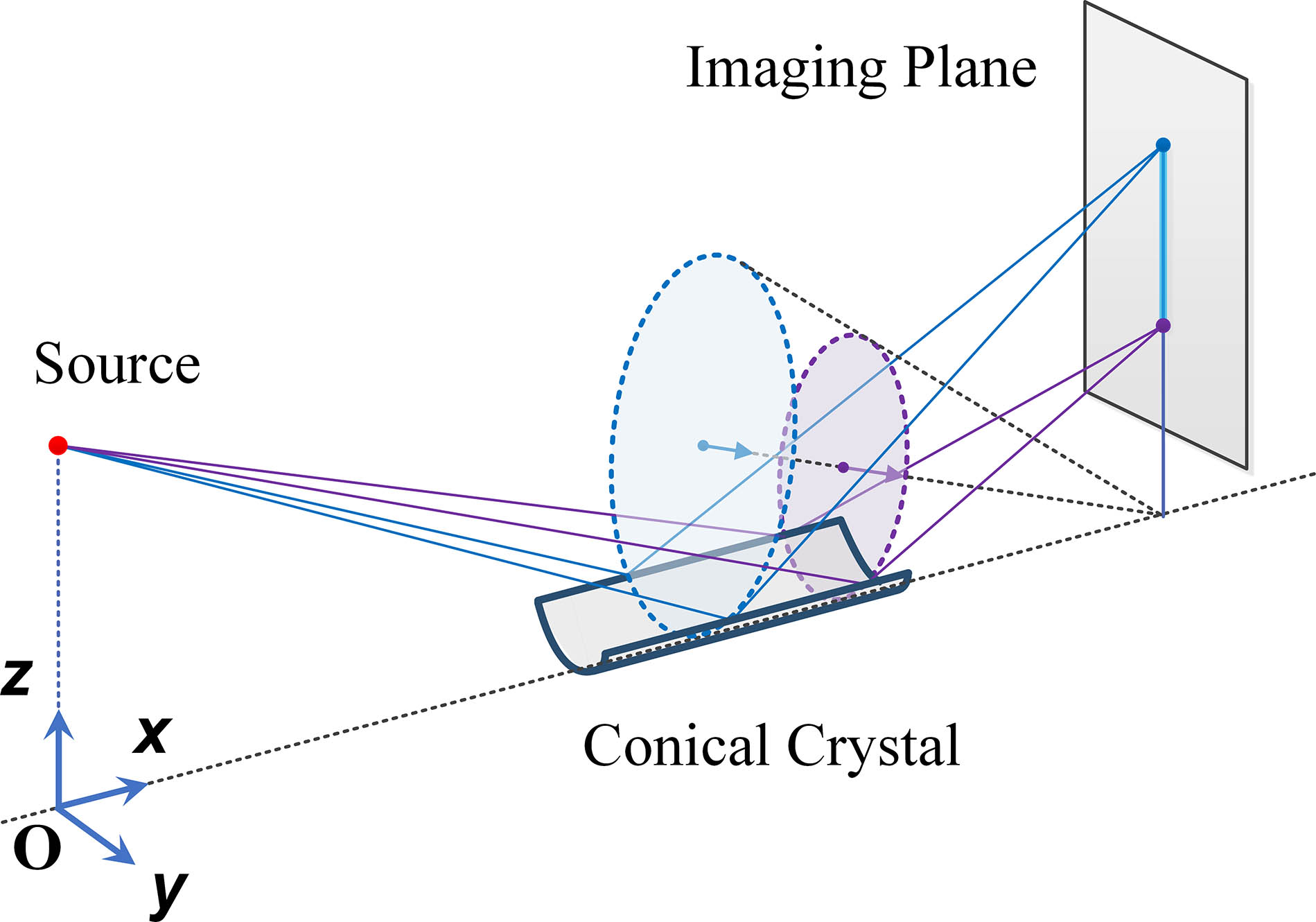
In spectral diagnostic physics experiments of inertial confinement fusion, the spectral signal is weak due to the low diffraction efficiency when using bent crystals. A spectral diagnostic instrument with high efficiency and wide spectral range is urgently needed. A multi-curvature bent crystal with multi-energy focusing ability is proposed based on the traditional conical crystal geometry. It has advantages of wide spectral range, strong focusing ability, and high spectral resolution. It also can eliminate the imaging aberration in principle due to rotational symmetry for the incoming X rays. A spectral diagnostic experiment based on a fabricated multi-curvature α-quartz crystal was accomplished using a titanium X-ray tube of the bent crystal, and the corresponding experimental data using a plane α-quartz crystal was also acquired to demonstrate the strong focusing ability. The result shows that the Kα intensity of the multi-curvature α-quartz crystal is 157 times greater than that of the plane crystal, and the corresponding energy range is about 4.51–5.14 keV. This diagnostic instrument could be combined with a streak camera at a vertical direction so as to intensify the diffracted X-ray signal with a wide spectral range.
inertial confinement fusion X-ray crystal spectrometer multi-curvature bent crystal X-ray diffraction Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(11): 113401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A four-channel multilayer Kirkpatrick-Baez (KB) microscope is developed for the 8-keV X-ray imaging of experiments on laser inertial confinement fusion (ICF). A periodic multilayer that works at 8 keV and with a grazing incidence angle of 1.0o is coated on reflective surfaces to achieve a spatial resolution higher than 5 \mu m and an effective solid angle higher than ~10-7 sr. A precise assembly is realized by a conical reference cone to couple with an X-ray framing camera. This study provides detailed information on an optical and multilayer design, assembly method, and experimental results with a Cu X-ray tube. The instrument provides a high-resolution and high-throughput X-ray image for backlit or self-emission imaging of laser plasma at Cu K\alpha line radiation in Shenguang series laser facilities.
340.7440 X-ray imaging 310.6845 Thin film devices and applications Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(1): 013401





