Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Beijing Institute for Advanced Study, National University of Defense Technology, Beijing 100020, China
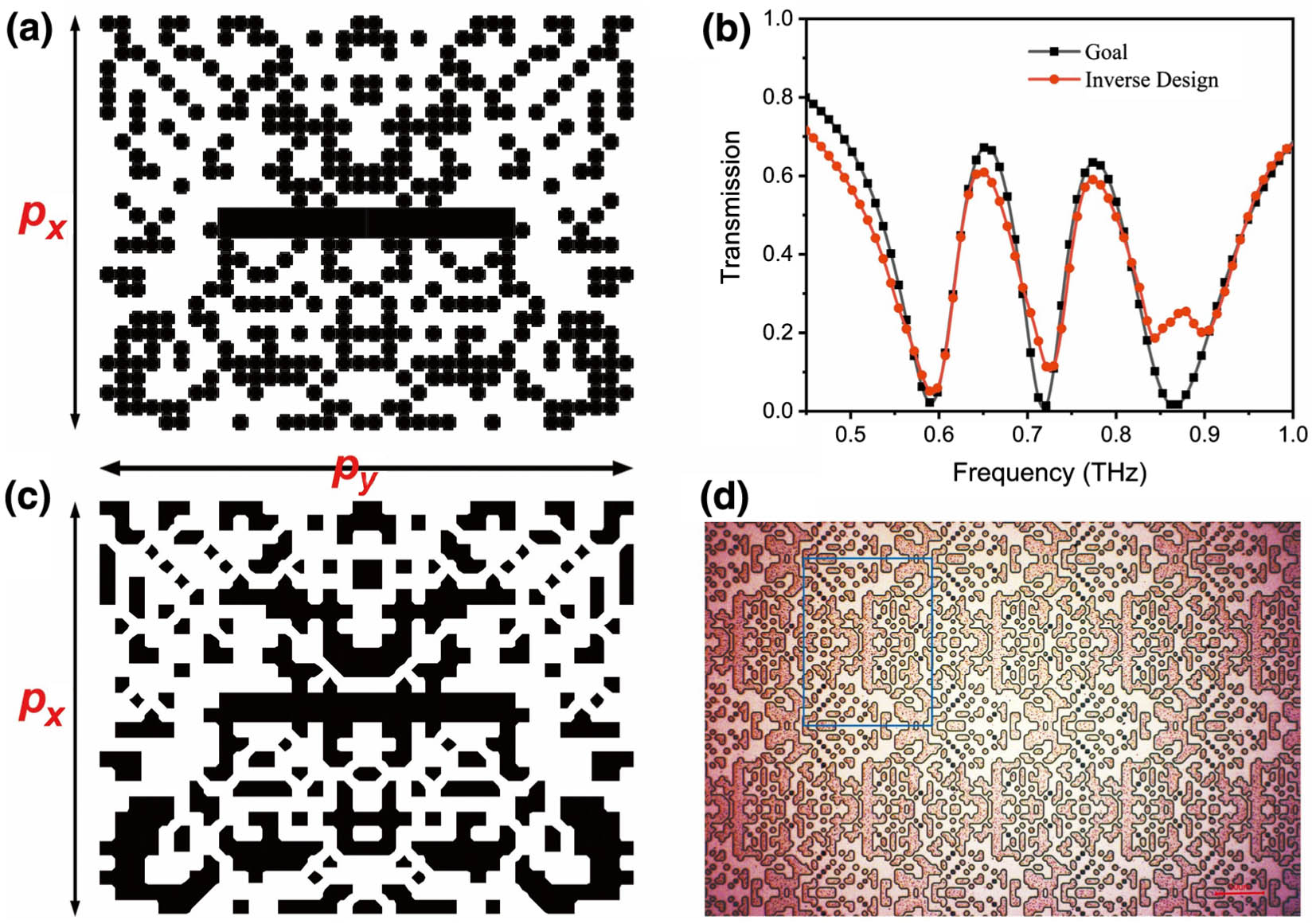
Terahertz metasurfaces have great applications for efficient terahertz modulation, but there are still problems in designing terahertz metadevices in terms of complexity and inefficiency. Herein, we demonstrate an inversely-designed terahertz metasurface with double electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like windows by incorporating a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. We prepared and tested the metadevices, and the experimental terahertz signals are close to the designed results. By hybridizing amorphous germanium film with the inversely-designed metasurface, two EIT-like windows, including transmission and slow-light effect, exhibit ultrafast modulation behavior in 25 ps excited by a femtosecond laser. The modulation depths of transmission in two transparency windows are 74% and 65%, respectively. The numerical simulations also illustrate the ultrafast dynamic process and modulation mechanism, which match well with the experiment results. Our work thus offers opportunities for designing other objective functions of the terahertz metadevice.
terahertz metasurfaces inverse design double electromagnetically induced transparency Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(11): 113701
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(1): 011010
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Pulsed Power Laser Technology, Hefei 230037, China
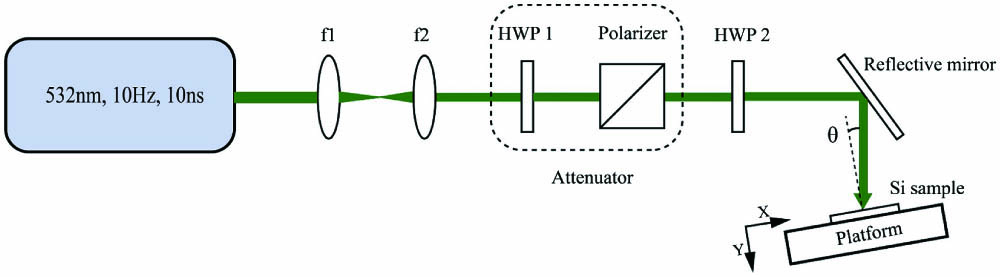
In this paper, an effective method is proposed to generate specific periodical surface structures. A 532 nm linearly polarized laser is used to irradiate the silicon with pulse duration of 10 ns and repetition frequency of 10 Hz. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs) are observed when the fluence is and the number of pulses is 1000. The threshold of fluence for generating LIPSS gradually increases with the decrease of the number of pulses. In addition, the laser incident angle has a notable effect on the period of LIPSS, which varies from 430 nm to 1578 nm, as the incident angle ranges from 10° to 60° correspondingly. Besides, the reflectivity is reduced significantly on silicon with LIPSS.
laser-induced periodic surface structure nanostructures fluence number of pulses incident angle Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(1): 013802
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Interdisciplinary Center of Quantum Information, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4 National Institute of Defense Technology Innovation, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100010, China
Broadband transient reflectivity traces were measured for Bi2Se3 thin films with various substrates via a 400 nm pump–white-light-probe setup. We have verified the existence of a second Dirac surface state in Bi2Se3 and qualitatively located it by properly analyzing the traces acquired at different probe wavelengths. Referring to the band structure of Bi2Se3, the relaxation mechanisms for photo-excited electrons with different energies are also revealed and studied. Our results show a second rise of the transient reflection signal at the time scale of several picoseconds. The types of substrate can also significantly affect the dynamics of the rising signal. This phenomenon is attributed to the effect of lattice heating and coherent phonon processes. The mechanism study in this work will benefit the fabrication of high-performance photonic devices based on topological insulators.
160.4236 Nanomaterials 300.6500 Spectroscopy, time-resolved Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020005
国防科学技术大学 光电科学与工程学院, 长沙 410073
通过实验研究了由四透镜组成的中红外透射光学成像系统的鬼像在像平面上的分布规律。研究表明, 随着光源入射角度的变化, 像平面上透射光聚焦点与鬼像中心的位置相对视场中心发生偏移, 且在相同条件下, 鬼像中心的偏移量与透射光聚焦点的偏移量并不相同。根据该成像规律, 针对鬼像中心的偏移量比透射光聚焦点的偏移量大的透射光学系统, 提出一种抑制鬼像的有效方法, 即通过调整造成鬼像的核心透镜的角度, 使鬼像位移出视场, 并利用软件仿真验证该方法的正确性, 为以后复杂光学系统的鬼像规避设计提供有益的参考。
鬼像 中红外光学系统 鬼像抑制 软件仿真 光学系统设计 ghost image mid-infrared optical system suppression of ghost software simulation design of optical system
1 国防科学技术大学 光电科学与工程学院, 长沙 410073
2 光电信息控制和安全技术重点实验室, 河北 三河 065201
用1064nm皮秒脉冲激光辐照PV型线阵HgCdTe探测器,随着激光能量的增大,探测单元出现了不同程度的损伤,发现了致损单元的反常响应现象,致损单元响区蓝移,对波长为1064nm的光响应灵敏度明显增强。结果表明:受损单元p型碲镉汞层出现汞析出现象后,受损光敏元碲镉汞材料组分和载流子浓度发生变化,pn结耗尽层宽度的变化导致pn结等效电阻变化,这是导致芯片损伤单元出现反常响应的主要因素。研究发现受损光敏元随着碲镉汞材料组分增大,碲镉汞材料能带禁带宽度增大,使探测器响区出现蓝移现象,这是损伤单元对波长为1064nm激光响应更加灵敏的主要原因。
HgCdTe线阵探测器 激光 反常响应 耗尽层电阻 响区蓝移 禁带宽度 HgCdTe linear array detector laser abnormal response depletion layer resistance response range blue shift band gap width
1 国防科学技术大学 光电科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科学技术大学 高性能计算国家重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410073
采用1064 nm纳秒脉冲激光辐照单晶Si、单结GaAs太阳能电池, 针对不同强度激光辐照太阳能电池的损伤特性进行了实验研究, 得出激光光斑聚焦在电池栅线上时, 电池更易损伤, 单晶Si电池的栅线打断之后仍能很好工作, 单结GaAs电池却完全失效, 这是由于高掺杂的基底锗熔融凝固连接栅线, 导通电池正负极.实验结果还表明, 激光辐照在电池表面时, 对单晶Si电池基本没有影响, 而GaAs电池输出性能也没有很大幅度的下降.理论分析了纳秒激光对电池的损伤主要是热、力效应共同作用的结果.热效应使材料熔化、气化, 力效应主要沿着激光传输的方向, 垂直于材料表面.常温下Si材料对1 064 nm有较强的本征吸收, GaAs电池的GaAs层透过1 064 nm, Ge基底本征吸收1 064 nm, Ge材料的熔点低于Si材料且其禁带宽度更窄, 故其初始损伤阈值略低.通过SEM扫描电镜、激光拉曼材料分析及X射线光电子能谱仪等分析手段对实验结果进行了验证.
太阳能电池 激光损伤 单晶Si 单结GaAs 扫描电镜 X射线光电子能谱仪 solar cells laser-induced damage monocrystalline silicon single junction GaAs COMSOL COMSOL SEM XPS
国防科学技术大学光电科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
在红外成像系统中,串扰会降低图像的清晰度,影响焦平面阵列的分辨率性能和成像质量,因此对串扰的测试及产生机理等研究至关重要。对比了串扰效应的3 种测试原理和测试方法,从光学串扰和电学串扰两个方面揭示了串扰效应的产生机理,综述了两种串扰类型的解决方案,并对未来红外成像器件的发展趋势进行展望,以期为改进相关器件的技术、结构和制造工艺提供有益的借鉴。
成像系统 红外 串扰 光学串扰 电学串扰 激光与光电子学进展
2015, 52(10): 100004
国防科学技术大学 光电科学与工程学院, 长沙 410073
针对前照式有源型可见光互补金属氧化物半导体(CMOS)器件,开展了1080 nm连续激光与1064 nm单脉冲ns激光损伤效应的对比研究,观察到了CMOS出现点损伤、半边黑线损伤与十字交叉黑线损伤三个典型的硬损伤阶段,并分析了损伤机理。在连续激光辐照下,损伤效应主要是热效应的影响。当辐照时间小于稳态时间时,辐照时间越长,损伤阈值越低,当辐照时间大于稳态时间时,损伤阈值趋于稳定值。对损伤后的CMOS器件的微观结构进行了显微观察,结合CMOS电路结构深入分析了各种典型实验现象的损伤机理,半边黑线损伤与十字交叉黑线损伤主要是不同层金属线路熔断导致信号断路。在单脉冲ns激光作用下, CMOS像元表面的硬损伤主要是激光加热作用和等离子体冲击波作用引起的。
前照式互补金属氧化物半导体 单脉冲 热效应 辐照时间 稳态时间 front illuminated complementary metal oxide semico single pulse laser thermal effect duration time thermal balance time 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(9): 091007
国防科学技术大学光电科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
针对532 nm纳秒单脉冲激光辐照单晶硅、砷化镓(GaAs)太阳能电池的损伤效应,结合电池的结构和等效电路,分析了纳秒单脉冲激光对两种太阳能电池的损伤机理。结果表明,激光辐照区域的太阳能电池组成成份改变,PN结内部缺陷增多,载流子复合几率增大,导致太阳能电池输出性能下降,单晶硅材料的电池输出性能下降并不明显,而GaAs材料的电池由于砷等元素的升华,镓等金属元素的熔融再凝固过程,形成一个连接电池正负极的导电通路,导致GaAs电池不能正常工作。
太阳能电池 脉冲激光 损伤 单晶硅 砷化镓 光学学报
2014, 34(s1): s116005





