1 武汉长盈通光电技术有限公司, 湖北 武汉 430205
2 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院, 北京 100044
光纤作为光信息和光能量的传输元器件已成为基础建设不可或缺的组成部分。针对功能光纤进行概括性介绍。着重介绍了微结构光纤的导光机理以及制备方案。微结构光纤由于其实现了灵活的预制棒制备方式、空芯传输以及理论上的超低衰耗,广泛地应用于光电传感和激光器应用。未来光纤发展的趋势将是光、电功能集成于一根光纤中,详细介绍了纳米机械光纤的制备和潜在应用,为全光器件和光集成技术发展提供重要的研究方向。
光纤光学 光纤设计与制造 微结构光纤 光子晶体光纤 光微机电器件 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170615
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-Fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, College of Science, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 Photonics Research Center, School of Electric Engineering and Automation, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
In-fiber integrated optics is an attempt to use silica fiber as a substrate, integrating various optical paths or optical components into a single fiber, to build a functional optical device or component, and to realize a micro optical system, achieving various functions. In-fiber integrated optics is expected to be a new branch of photonics integration. This integration technique enables convenient light beams control and manipulation inside in one fiber. It also provides a research platform with micro and nano scale for interaction between light wave and microfluidic materials. In this review, we briefly summarize the main ideas and key technologies of the in-fiber integrated optics by series integration examples.
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.4005 Microstructured fibers 130.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(11): 110601
天津理工大学计算机科学与工程学院, 天津 300380
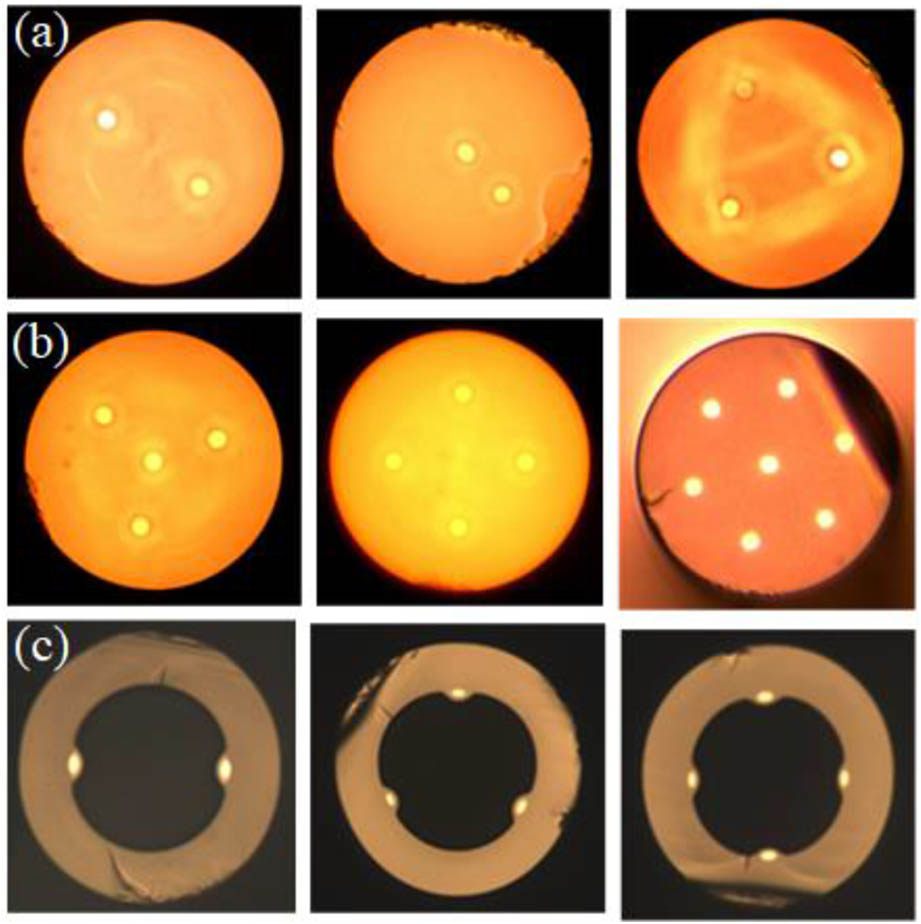
设计了一种可支持22个轨道角动量(OAM)模式传输的新型微结构光纤,该光纤具有低平坦色散、低损耗等优点,光纤中可支持的各个矢量模式之间有效折射率差值均大于10
-4,对应的22个OAM模式都能够在纤芯中稳定传输。在1500~1600 nm波段范围内,通过优化包层最内圈两层空气孔的物理参数,该光纤中可支持传输的模式色散均能控制在0~50 ps·(nm·km)
-1范围内,HE71和EH51模式的色散变化值低于12.8 ps·(nm·km)
-1,其余模式的色散变化范围低于5 ps·(nm·km)
-1。在1550 nm波段处,该光纤所支持的所有模式损耗均低于1.35×10
-9 dB/m。
光纤光学 微结构光纤 轨道角动量

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Light-Matter Interactions Unit, Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University, Onna, Okinawa 904-0495, Japan
Tapered fibers with diameters ranging from 1 to 4 μm are widely used to excite the whispering-gallery (WG) modes of microcavities. Typically, the transmission spectrum of a WG cavity coupled to a waveguide around a resonance assumes a Lorentzian dip morphology due to resonant absorption of the light within the cavity. In this paper, we demonstrate that the transmission spectra of a WG cavity coupled with an ultrathin fiber (500–700 nm) may exhibit both Lorentzian dips and peaks, depending on the gap between the fiber and the microcavity. By considering the large scattering loss of off-resonant light from the fiber within the coupling region, this phenomenon can be attributed to partially resonant light bypassing the lossy scattering region via WG modes, allowing it to be coupled both to and from the cavity, then manifesting as Lorentzian peaks within the transmission spectra. This implies the system could be implemented within a bandpass filter framework.
Resonators Micro-optical devices Microstructured fibers Photonics Research
2017, 5(4): 04000362

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P.O. Box 603, Beijing 100190, China
2 School of Physics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
We theoretically design and experimentally realize a broadband ultrasmall microcavity for sensing a varying number of microparticles whose diameter is 2 μm in a freely suspended microfiber. The performance of the microcavity is predicted by the theory of one-dimensional photonic crystals and verified by the numerical simulation of finite-difference time domain and the experimental characterization of reflection and transmission spectra. A penetrating length into the reflectors as small as about four periods is demonstrated in the numerical simulation, giving rise to an ultrasmall effective mode volume that can increase the sensitivity and spatial resolution of sensing. Moreover, a reflection band as large as 150 nm from the reflectors of the microcavity has been realized in silica optical microfiber in the experiment, which highly expands the wavelength range of sensing. Our proposed microcavity integrated into a freely suspended optical fiber offers a convenient and stable method for long-distance sensing of microparticles without the need for complicated coupling systems and is free from the influence of substrates.
Fiber optics sensors Microstructured fibers Nanostructure fabrication Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000143

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, Staudtstr. 2, D-91058 Erlangen, Germany
Understanding bend loss in single-ring hollow-core photonic crystal fibers (PCFs) is becoming of increasing importance as the fibers enter practical applications. While purely numerical approaches are useful, there is a need for a simpler analytical formalism that provides physical insight and can be directly used in the design of PCFs with low bend loss. We show theoretically and experimentally that a wavelength-dependent critical bend radius exists below which the bend loss reaches a maximum, and that this can be calculated from the structural parameters of a fiber using a simple analytical formula. This allows straightforward design of single-ring PCFs that are bend-insensitive for specified ranges of bend radius and wavelength. It also can be used to derive an expression for the bend radius that yields optimal higher-order mode suppression for a given fiber structure.
Fiber design and fabrication Fiber optics Microstructured fibers Photonic crystal fibers Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000088
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physical Sciences, National Institute of Science Education and Research, HBNI Bhubaneswar, Jatni 752050, India
We propose a broadband fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) based on a near-zero ultra-flat dispersion profile with a single zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) by using a selective liquid infiltration technique. The amplifier gain and bandwidth is investigated for a variety of fiber lengths, pump power, and operating wavelengths. It is observed that sufficient peak gains and broader bandwidths can be achieved with a small negative anomalous dispersion (β2≤0) and a positive value of the 4th-order dispersion parameter (+ β4) around the pump. We can optimize an FOPA with a bandwidth of more than 220 nm around the communications wavelength.
060.4005 Microstructured fibers 060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers 190.4970 Parametric oscillators and amplifiers Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(7): 070606
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 e-mail: cliao@szu.edu.cn
3 School of Information Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
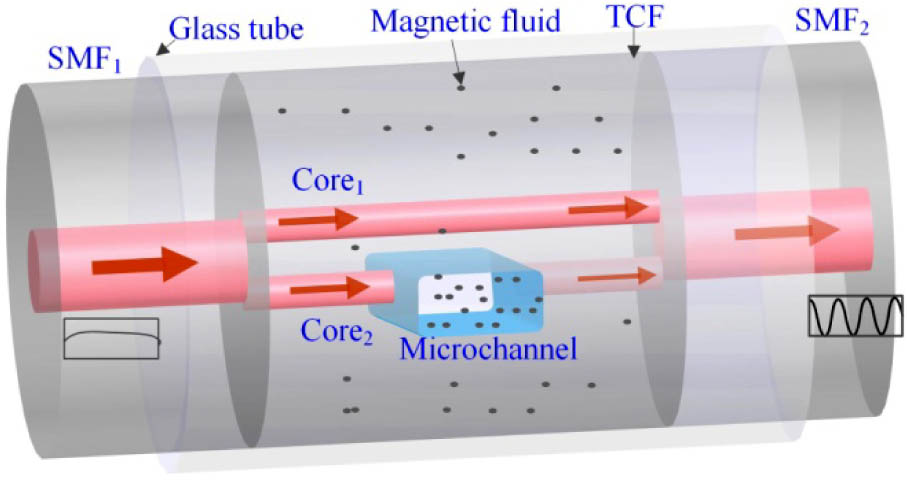
An ultrasensitive magnetic field sensor based on a compact in-fiber Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) created in twin-core fiber (TCF) is proposed, and its performance is experimentally demonstrated. A section of TCF was spliced between two sections of standard single-mode fibers, and then a microchannel was drilled throughone core of the TCF by means of femtosecond laser micromachining. The TCF with one microchannel was then immersed in a water-based Fe3O4 magnetic fluid (MF), forming a direct component of the light propagation path, and then sealed in a capillary tube, achieving a magnetic sensing element, which merges the advantages of an MZI with an MF. Experiments were conducted to investigate the magnetic response of the proposed sensor. The developed magnetic field sensor exhibits a linear response within a measurement range from 5 to 9.5 mT and an ultrahigh sensitivity of 20.8 nm/mT, which, to our best knowledge, is 2 orders of magnitude greater than other previously reported magnetic sensors. The proposed sensor is expected to offer significant potential for detecting weak magnetic fields.
Interference Interference Microstructured fibers Microstructured fibers Fiber optics sensors Fiber optics sensors Photonics Research
2016, 4(5): 05000197
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology,Changsha, Hunan 410073, China
Core mode cutoff is a useful concept not only for a tapered single-core fiber (SCF) but also for a tapered multicore fiber (MCF) to realize cladding mode transmission. In this paper, cut-off conditions of either core mode for tapered SCFs or supermodes for MCFs are theoretically investigated. Rigorous analytical formulas are derived for the modes of SCF by a three-layer waveguide model, and an approximation formula of the cut-off condition is given for the LP01 mode. The supermodes of MCFs are analyzed by the coupling mode theory, and the cut-off condition is calculated by a numerical method. Simulation results show that the in-phase supermode of MCFs has a similar cut-off condition with that of SCF. Based on this property, a convenient approximate formula is given to estimate the cut-off condition of the in-phase supermode for tapered MCFs.
Fiber optics Fiber optics Fiber optics and optical communications Fiber optics and optical communications Microstructured fibers Microstructured fibers Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000224
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We measure the transmission characteristics of hollow-core photonic crystal fiber (HC-PCF) gas cells with ferrule- and fusion-spliced configurations, and near- and far-field images of the HC-PCF are observed. Results show that the center of mass (COM) of the far-field image varies with the laser frequency and temperature, and the moving COM relates to the oscillatory transmission. Using a model of the spatial interference, we first demonstrate that mainly the modes with asymmetric phase distributions affect the COM position. The frequency stabilization performances of the lasers are compared. The fusion-spliced gas cell shows better performance than the ferrule-spliced one.
060.2270 Fiber characterization 060.4005 Microstructured fibers 140.3425 Laser stabilization 350.6090 Space optics Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(8): 080602





