西安工业大学光电工程学院,陕西 西安 710021
为了降低高精密使用场合下多层介质高反射薄膜的表面散射,首先从多层介质薄膜双向反射分布函数(BRDF)出发,理论分析了双向反射分布函数与薄膜界面电场强度的关系。在入射光为正入射且中心波长632.8 nm处的反射率大于99%的要求下,采用SiO2、Ta2O5两种材料设计了膜系G/(HL)8/A和膜系G/(HL)8H/A,并分析了两种膜系界面的电场强度分布。然后以膜系G/(HL)8H/A界面的电场分布为基础对场强进一步优化,得到了膜系G/(HL)60.4L1.6H1.5L0.5H/A。理论计算了正入射条件下三种膜系的双向反射分布函数,发现当散射角为-45°~45°时,膜系G/(HL)6H0.4L1.6H1.5L0.5H/A表面的BRDF小于膜系G/(HL)8/A和膜系G/(HL)8H/A。同时计算了三种膜系表面的总散射损耗(S),与膜系G/(HL)8/A和膜系G/(HL)8H/A相比,优化膜系G/(HL)6H0.4L1.6H1.5L0.5H/A的S降低了91.44%、37.98%。实验验证了利用膜层界面电场强度调控薄膜表面散射的有效性。
薄膜 多层设计 光散射 双向反射分布函数 总散射损耗

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Professional Basic Department, Changzhou Vocational Institute of Mechatronic Technology, Changzhou 213164, China
2 Joint International Research Laboratory of Information Display and Visualization, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
3 Public Resource Trading Center, Municipal Administrative Services Management Bureau, Lianyungang 222006, China
The effects of the diameter of SiO2 nanopillars, the diameter of Ag nanospheres, the arrays’ period, and the medium environment on the plasmonic lattice resonance (PLR) formed by Ag nanospheres on SiO2 nanopillar arrays are systematically investigated. Larger diameters of SiO2 nanopillars with other parameters kept constant will widen the PLR peak, redshift the PLR wavelength, and weaken the PLR intensity. Larger diameters of Ag nanospheres with other parameters kept constant will widen the PLR peak, redshift the PLR wavelength, and strengthen the PLR intensity. Larger array periods or larger refractive index of medium environment corresponds to larger PLR wavelengths.
plasmonics diffraction theory resonance multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(3): 033601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of High-Power Semiconductor Laser, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
The effect of thermal annealing on the optical properties, microstructure, and laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of HfO2/Ta2O5/SiO2 HR films has been investigated. The transmission spectra shift to a short wavelength and the X-ray diffraction peaks of monoclinic structure HfO2 are enhanced after thermal annealing. The calculated results of the m( 111) diffraction peak show that the HfO2 grain size is increased, which is conducive to increasing the thermal conductivity. Thermal annealing also reduces the laser absorption of high-reflection films. The improvement of thermal conductivity and the decrease of laser absorption both contribute to the improvement of LIDT. The experimental results show that the highest LIDT of 22.4 J/cm2 is obtained at 300°C annealing temperature. With the further increase of annealing temperature, the damage changes from thermal stress damage to thermal explosion damage, resulting in the decrease of LIDT.
310.1620 Interference coatings 310.4165 Multilayer design 310.4925 Other properties (stress, chemical,etc.) Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 113101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
A λ/4–λ/4 broadband antireflective (AR) coating is developed with a sol-gel dip-coating method. By adding SAR-5 organosilicon resin into a base-catalyzed silica sol top layer and treating at 300°C, a broadband AR coating used for blast shields with a high average transmission of 99.34% (450–950 nm) and good hydrophobicity (with a water-contact angle of 119°) was obtained. After being subjected to rubbing 50 times and being maintained at a relative humidity of around 95% for 50 days, the average transmission of the coating decreased by 0.29% and 0.04%, respectively. This indicates that the organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) broadband AR coating has good abrasion resistance and humidity stability.
310.1210 Antireflection coatings 160.6060 Solgel 310.4165 Multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(3): 033101
1 长春理工大学 理学院,吉林 长春 130022
2 中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 光学系统先进制造技术重点实验室,吉林 长春 130033
3 中国科学技术大学 国家同步辐射实验室,安徽 合肥 230029
极紫外(EUV)宽带多层膜的光谱性能对膜厚控制精度要求较高,仅由时间控制膜厚的镀膜系统难以满足其精度控制要求。本文提出了基于进化算法的宽带EUV多层膜离散化膜系设计方法,与传统膜系设计相比,离散化膜系所制备多层膜具有更为优良的EUV反射光谱性能。为验证离散化膜系设计在宽带EUV多层膜研制中的优越性,采用磁控溅射方法对具有离散化膜系的宽带多层膜反射镜进行了制备和测试。测试结果表明: 研制的宽角度多层膜反射镜可实现入射角带宽为0°~17°,高于41%的反射率; 研制的堆栈宽角度多层膜反射镜可实现入射角带宽为0°~18.5°,高于35%的反射率; 研制的宽光谱多层膜反射镜可实现波长带宽为12.9~14.9 nm,高于21%的反射率。
多层膜设计 极紫外 离散化设计 宽带多层膜 multilayer design extreme ultraviolet discrete design broadband multilayer 光学 精密工程
2018, 26(10): 2395
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Physics Department, State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (MOE), Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures (Nanjing), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
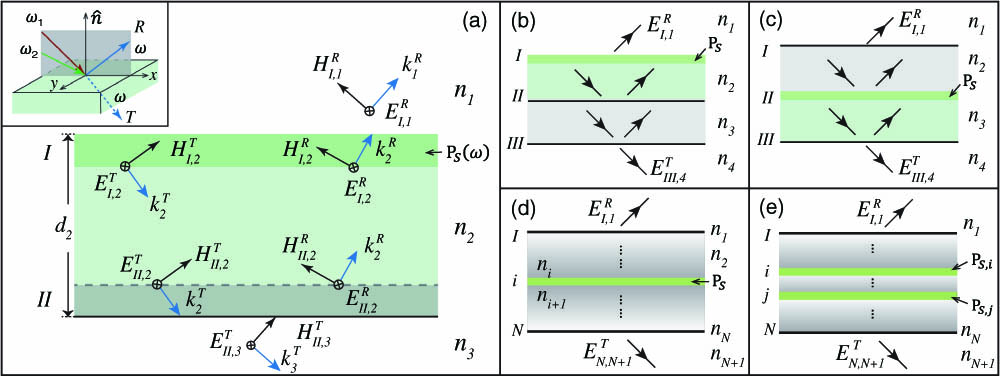
In optical studies on layered structures, quantitative analysis of radiating interfaces is often challenging due to multiple interferences. We present here a general and analytical method for computing the radiation from two-dimensional polarization sheets in multilayer structures of arbitrary compositions. It is based on the standard characteristic matrix formalism of thin films, and incorporates boundary conditions of interfacial polarization sheets. We use the method to evaluate the second harmonic generation from a nonlinear thin film, and the sum-frequency generation from a water/oxide interface, showing that the signal of interest can be strongly enhanced with optimal structural parameters.
190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 260.3160 Interference 310.4165 Multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 081901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-Structured Materials MOE, Institute of Precision Optical Engineering, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Institute of Nuclear Physics and Chemistry CAEP, Mianyang 621900, China
The Pd/B4C multilayer is a promising candidate for high reflectance mirrors operating in the 8–12 nm extreme ultraviolet wavelength region. To extend the working bandwidth beyond the L-edge of silcon, we theoretically design broadband Pd/B4C multilayers. We discuss the influence of the desired reflectance of the plateau, number of bilayers, and the real structural parameters, including the interface widths, layer density, and thickness deviation, on the reflectivity profile. Assuming the interface width to be 0.6 nm, we design aperiodic multilayers for broad wavebands of 9.0–10.0, 8.5–10.5, and 8.0–11.0 nm, with average reflectivities of 3.1%, 5.0%, and 9.5%, respectively.
310.4165 Multilayer design 230.4170 Multilayers 340.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) 350.1270 Astronomy and astrophysics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 073101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 3, 117576, Singapore
2 The Blackett Laboratory, Physics Department, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK
3 State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
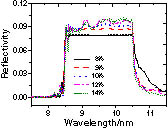
A tunable plasmonic perfect absorber with a tuning range of ~650 nm is realized by introducing a 20 nm thick phase-change material Ge2Sb2Te5 layer into the metal–dielectric–metal configuration. The absorption at the plasmonic resonance is kept above 0.96 across the whole tuning range. In this work we study this extraordinary optical response numerically and reveal the geometric conditions which support this phenomenon. This work shows a promising route to achieve tunable plasmonic devices for multi-band optical modulation, communication, and thermal imaging.
Spectral properties Plasmonics Subwavelength structures, nanostructures Multilayer design Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000054
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200083, China
2 School of Physical Science and Technology, Shanghai Tech University, Shanghai 200031, China
In our investigation, lead germanium telluride, which is a pseudo-binary alloy of IV-VI narrow-gap semiconductor compounds of PbTe and GeTe, can be used in the fabrication of mid-wavelength infrared narrow bandpass filters as a high-index coating material, due to its high refractive index, lower absorption, and tunability of fundamental absorption edges. It is demonstrated that a half-width of 160 nm and a better rejection ratio can be obtained for a simple 8-layer double cavity filter with a central wavelength at 4 μm, compared with a half-width of 390 nm for those conveniently fabricated using Ge as high-index material.
310.1620 Interference coatings 310.3840 Materials and process characterization 310.6188 Spectral properties 310.4165 Multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 123101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Engineering Research Center of Optical Instruments and Systems, Ministry of Education and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Systems, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
In this Letter, we propose a method of fabricating linear variable filters by ion beam etching with masking mechanisms. A triangle-shaped mask is designed and set between the ion source and sample. During the ion etching, the sample is moved back and forth repeatedly with a constant velocity for the purpose of obtaining the linearly varied thickness of the cavity. Combined with ion beam assistant thermal oxidative electron beam evaporation deposition technology, we finish the fabrication of linear variable filters, whose filtering range is from 500 to 580 nm. The measured results indicate that the transmittance and bandwidth at the peak wavelength are around 40% and 3 nm.
230.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 220.4610 Optical fabrication 310.4165 Multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 122301





