
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tianjin University and the Key Laboratory of Optoelectronics Information and Technology (Ministry of Education), Center for Terahertz Waves and College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin, China
2 Oklahoma State University, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Stillwater, Oklahoma, United States
Terahertz science and technology promise many cutting-edge applications. Terahertz surface plasmonic waves that propagate at metal–dielectric interfaces deliver a potentially effective way to realize integrated terahertz devices and systems. Previous concerns regarding terahertz surface plasmonic waves have been based on their highly delocalized feature. However, recent advances in plasmonics indicate that the confinement of terahertz surface plasmonic waves, as well as their propagating behaviors, can be engineered by designing the surface environments, shapes, structures, materials, etc., enabling a unique and fascinating regime of plasmonic waves. Together with the essential spectral property of terahertz radiation, as well as the increasingly developed materials, microfabrication, and time-domain spectroscopy technologies, devices and systems based on terahertz surface plasmonic waves may pave the way toward highly integrated platforms for multifunctional operation, implementation, and processing of terahertz waves in both fundamental science and practical applications. We present a review on terahertz surface plasmonic waves on various types of supports in a sequence of properties, excitation and detection, and applications. The current research trend and outlook of possible research directions for terahertz surface plasmonic waves are also outlined.
plasmonics surface waves terahertz Advanced Photonics
2020, 2(1): 014001
1 上海理工大学 上海市现代光学系统重点实验室, 上海 200093
2 上海理工大学 光电信息与计算机工程学院, 上海 200093
鉴于金属光子晶体结构在滤波、极化、传感、成像等领域的重要作用, 研究了基于三角形晶格的金属光子晶体的超常透射、光子能带和表面波特性。采用三维时域有限差分法对金属光子晶体结构建模, 同时解释超常透射机理;推导和讨论光子能带沿着ΓK和ΓM晶格方向的能带图, 分析不同的表面波特征, 并解释非对称入射下观察到的三角形的两个晶格方向模式分裂效应;建立了描述这种模式分裂效应的精确的表面模式谐振频率公式, 并对金属光子晶体的色散进行了定量分析。研究结果可为太赫兹功能器件的研究提供参考。
时域有限差分 金属光子晶体 光子能带 表面波 角度依赖性 finite difference time domain metallic photonic crystal photonic band surface waves angular dependence
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Terahertz Waves and College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Tianjin University, and the Key Laboratory of Optoelectronics Information and Technology Tianjin, Ministry of Education of China, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Physical Science and Engineering Division, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Thuwal 23955-6900, Saudi Arabia
3 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, Oklahoma 74078, USA
4 e-mail: weili.zhang@okstate.edu
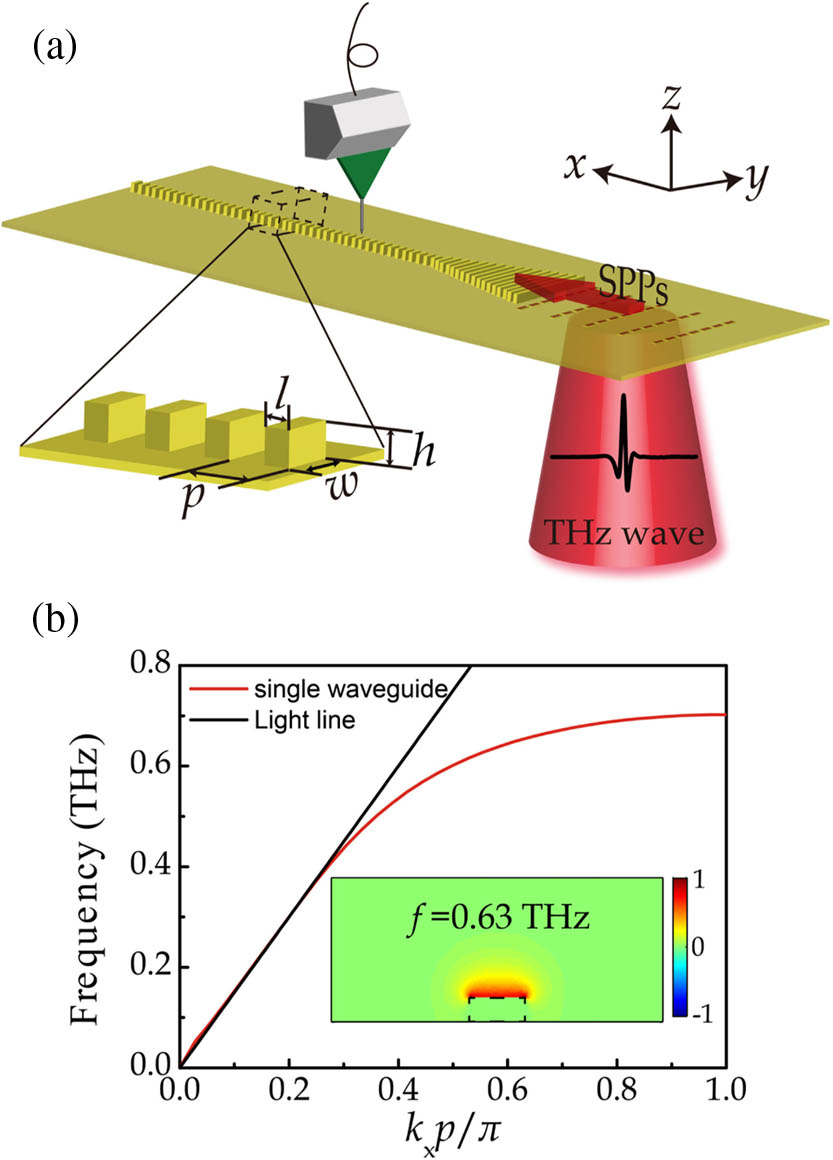
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) with the features of subwavelength confinement and strong enhancements have sparked enormous interest. However, in the terahertz regime, due to the perfect conductivities of most metals, it is hard to realize the strong confinement of SPPs, even though the propagation loss could be sufficiently low. One main approach to circumvent this problem is to exploit spoof SPPs, which are expected to exhibit useful subwavelength confinement and relative low propagation loss at terahertz frequencies. Here we report the design, fabrication, and characterization of terahertz spoof SPP waveguides based on corrugated metal surfaces. The various waveguide components, including a straight waveguide, an S-bend waveguide, a Y-splitter, and a directional coupler, were experimentally demonstrated using scanning near-field terahertz microscopy. The proposed waveguide indeed enables propagation, bending, splitting, and coupling of terahertz SPPs and thus paves a new way for the development of flexible and compact plasmonic circuits operating at terahertz frequencies.
Integrated optics devices Surface waves Far infrared or terahertz Photonics Research
2018, 6(1): 01000018

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
5 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies and School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
Tungsten disulfide (WS2), as a representative layered transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) material, possesses important potential for applications in highly sensitive sensors. Here, a sensitivity-enhanced surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor with a metal film modified by an overlayer of WS2 nanosheets is proposed and demonstrated. The SPR sensitivity is related to the thickness of the WS2 overlayer, which can be tailored by coating a WS2 ethanol suspension with different concentrations or by the number of times of repeated post-coating. Benefitting from its large surface area, high refractive index, and unique optoelectronic properties, the WS2 nanosheet overlayer coated on the gold film significantly improves the sensing sensitivity. The highest sensitivity (up to 2459.3 nm/RIU) in the experiment is achieved by coating the WS2 suspension once. Compared to the case without a WS2 overlayer, this result shows a sensitivity enhancement of 26.6%. The influence of the WS2 nanosheet overlayer on the sensing performance improvement is analyzed and discussed. Moreover, the proposed WS2 SPR sensor has a linear correlation coefficient of 99.76% in refractive index range of 1.333 to 1.360. Besides sensitivity enhancement, the WS2 nanosheet overlayer is able to show additional advantages, such as protection of metal film from oxidation, tunability of the resonance wavelength region, biocompatibility, capability of vapor, and gas sensing.
Plasmonics Surface waves Optical sensing and sensors Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000485
1 北京航空航天大学电子信息工程学院, 北京 100083
2 地球空间信息技术协同创新中心, 湖北 武汉 430079
布洛赫表面波(BSW)技术是一种新型的基于全介质结构的光学传感技术, 具有低光学损耗、大相位跳变以及高设计自由度, 近年来得到了广泛的研究。不同的结构设计和检测方案被提出并得到验证, 相关技术被证明可用于免标记的生物传感检测、气体传感检测、荧光检测等。从BSW技术的基本原理、传感器件、检测系统和方法方面, 介绍了国内外BSW技术的研究进展。
传感器 光学传感 表面波 光子带隙结构 表面等离子体共振
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Département d’Optique P. M. Duffieux, Institut FEMTO-ST, UMR 6174 CNRS, Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté, 15B Avenue des Montboucons, 25030 Besan?on Cedex, France
2 Optics & Photonics Technology Laboratory, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Rue de la Maladière 71b, Neuchatel CH-2000, Switzerland
Strong nonlinear, electro-optical, and thermo-optical properties of lithium niobate (LN) have gained much attention. However, the implementation of LiNbO3 in real devices is not a trivial task due to difficulties in manufacturing and handling thin-film LN. In this study, we investigate an optical device where the Bloch surface wave (BSW) propagates on the thin-film LN to unlock its properties. First, access to the LN film from air (or open space) is important to exploit its properties. Second, for sustaining the BSW, one-dimensional photonic crystal (1DPhC) is necessary to be fabricated under the thin-film LN. We consider two material platforms to realize such a device: bulk LN and commercial thin-film LN. Clear reflectance dips observed in far-field measurements demonstrate the propagation of BSWs on top of the LN surface of the designed 1DPhCs.
(240.0310) Thin films (130.3730) Lithium niobate (160.5298) Photonic crystals (240.6690) Surface waves. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000649

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Optics & Photonics Technology Laboratory (OPT), école Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), rue de la Maladière 71b, CH-2002 Neuchatel, Switzerland
2 Institute of Photonics, University of Eastern Finland, P.O. Box 111, 80101 Joensuu, Finland
We experimentally demonstrate the optical properties of gratings engraved in a single-mode waveguide fabricated on top of a dielectric multilayer platform. The structure can be approached as a reflector for Bloch-surface-wave-based two-dimensional optical systems. The gratings have been fabricated on a thin (~λ/25) titanium dioxide layer with a thickness of a few tens of nanometers deposited on the top of a multilayer platform. The optical properties of the gratings have been characterized in the near field with the aid of multi-heterodyne scanning near-field optical microscopy. We investigate the surface wave’s interference pattern, produced by incident and reflected light in front of the gratings. The presented gratings behave as an efficient Bloch-surface–wave-based reflector at telecommunication wavelength.
(240.0240) Optics at surfaces (240.6690) Surface waves. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000494
1 南昌大学物理系, 江西 南昌 330031
2 南昌大学高等研究院, 江西 南昌 330031
研究了具有周期性孔阵列的金属表面附近的电磁局域态密度(EM-LDOS),详细讨论了孔的填充因子和孔内填充介质对EM-LDOS的影响。相对于金属平板,具有孔阵列的金属表面附近的EM-LDOS的共振峰会发生分裂;随着填充因子的增加,横向表面等离子体激元的共振峰向低频方向移动,而纵向表面等离子体激元的共振峰向高频方向移动。当孔内填充具有更大介电常数的材料时,EM-LDOS谱中分裂的两个峰都会向低频方向移动,但低频峰的移动相对于高频峰的更为显著。
表面光学 表面等离子体激元 局域态密度 有效介质理论 表面波 激光与光电子学进展
2017, 54(7): 072401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
interdisciplinary Photonics Laboratories, School of Chemistry, The University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia
A large dynamic index measurement range (n =1 to n = 1.7) using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) shifts was demonstrated with a ZnSe prism at 632.8 nm, limited by the available high index liquid hosts. In contrast to borosilicate based SPR measurements, where angular limitations restrict solvent use to water and require considerable care dealing with Fresnel reflections, the ZnSe approach allows SPR spectroscopies to be applied to a varied range of solvents. An uncertainty in angular resolution between 1.5° and 6°, depending on the solvent and SPR angle, was estimated. The refractive index change for a given glucose concentration in water was measured to be n = (0.114 ± 0.007) /%[C6H12O6]. Given the transmission properties of ZnSe, the processes can be readily extended into the mid infrared.
Plasmonics surface plasmons surface waves scattering spectroscopy metal optics Photonic Sensors
2015, 5(3): 278–283
利用平面波展开法, 发现双原子正方晶格光子晶体中ΓM方向边界面存在着快慢两类边界模式, 并且通过计算色散关系和电场分布研究了边界参量对这两类边界模式传输特性的影响.依据两种模式的色散关系, 计算了群指数和群速度色散参量, 结果表明边界参量的变化对第一类边界模式传输特性的影响较小, 该模式的平均群指数始终维持在5.0左右; 第二类边界模式与第一类模式明显不同, 边界参量的变化能够有效地影响到这种模式的传输特性, 该模式的最大平均群指数可达178左右.利用时域有限差分法记录了不同时刻电场强度在边界附近的分布及监测点处的电场幅度变化情况, 结果表明, 两类模式都能够被限制在边界附近并向前传播, 时域有限差分法得到的群速度与平面波展开法的结果完全吻合.
纳米光子学 光子器件 时域有限差分法 双原子光子晶体 表面波 光子带隙 慢光 群速度色散 光存储 Nanophotonics Photonic devices Finite difference time domain method Diatomic square lattice Surface waves Optical band gaps Slow light Group velocity dispersion Optical memories





