2018, 16(1) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第1期
Manipulation of the overall polarization orientation in the focal volume of high numerical objectives Download:1006次
Download:1006次
 Download:1006次
Download:1006次We propose an approach for tuning the three-dimensional polarization of a focusing subwavelength spot by a high numerical aperture objective. The incident beams are composed of a radially polarized beam, an azimuthally polarized beam, and a linearly polarized beam with three different weighting factors, respectively. A specially designed adjustable amplitude angular selector is also inserted at the back aperture of the objective for tuning the polarization azimuthally. It is shown that any desired overall polarization orientation can be obtained. We calculated the overall polarization orientation in the focal volume. It is found that the polar angle of the overall polarization orientation can be arbitrarily tuned by the combination of a radially polarized beam and a linearly polarized beam with different weighting factors, and the azimuthal angle can be tuned by rotating the orientation of the linearly polarized beam azimuthally.
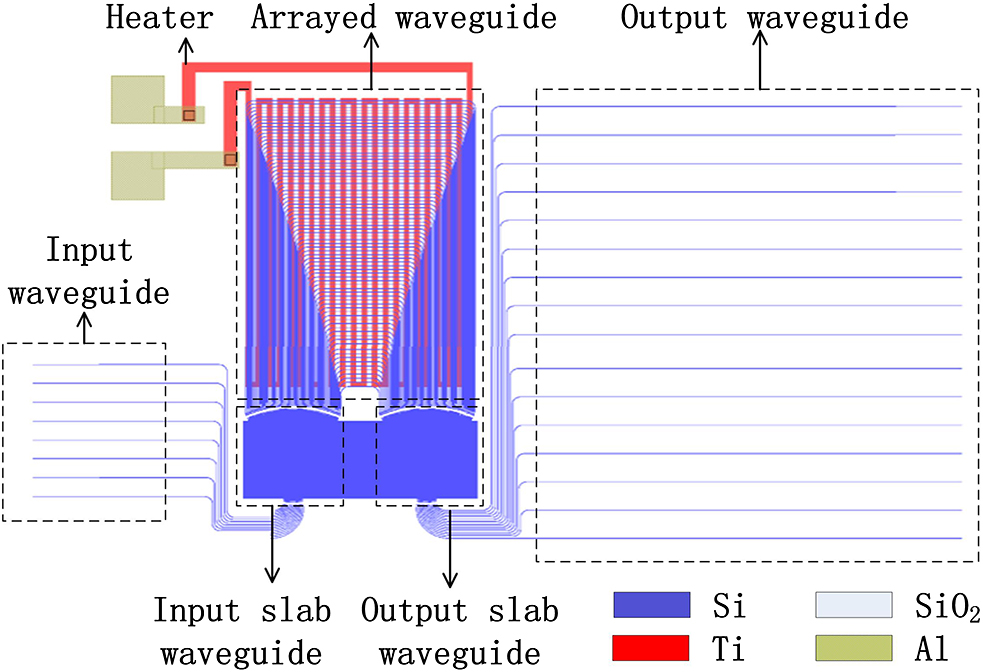
050.1940 Diffraction 130.5440 Polarization-selective devices In this Letter, a 16 channel 200 GHz wavelength tunable arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) is designed and fabricated based on the silicon on insulator platform. Considering that the performance of the AWG, such as central wavelength and crosstalk, is sensitive to the dimension variation of waveguides, the error analysis of the AWG with width fluctuations is worked out using the transfer function method. A heater is designed to realize the wavelength tunability of the AWG based on the thermo-optic effect of silicon. The measured results show that the insertion loss of the AWG is about 6 dB, and the crosstalk is 7.5 dB. The wavelength tunability of 1.1 nm is achieved at 276 mW power consumption, and more wavelength shifts will gain at larger power consumption.
060.1810 Buffers, couplers, routers,switches, and multiplexers 060.4230 Multiplexing 230.7390 Waveguides, planar Generation of cylindrical vector beams in a mode-locked fiber laser using a mode-selective coupler Download:1124次
Download:1124次
 Download:1124次
Download:1124次We experimentally obtain cylindrical vector beams (CVBs) in a passively mode-locked fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation. A mode-selective coupler composed of both a single-mode fiber (SMF) and a two-mode fiber (TMF) is incorporated into the cavity to act as a mode converter from LP01 mode to LP11 mode with broad spectral bandwidth. CVBs in different mode-locked states including single-pulse, multi-pulse, and bound pulse are obtained, for the first time to our best knowledge. The ultrafast CVBs with different operation states have potential applications in many fields such as laser beam machining, nanoparticle manipulation, and so on.
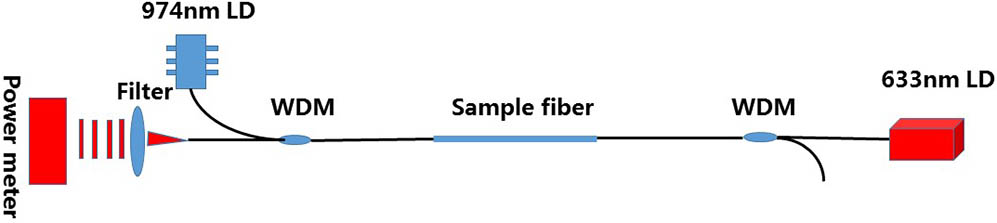
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3300 Laser beam shaping Induced loss at 633 nm is tested in Yb 3 + / Al 3 + Yb 3 + / Al 3 +
060.2270 Fiber characterization 060.2290 Fiber materials 060.2300 Fiber measurements Polarization-maintained coupled optoelectronic oscillator incorporating an unpumped erbium-doped fiber Download:805次
Download:805次
 Download:805次
Download:805次A polarization-maintained coupled optoelectronic oscillator (COEO) with its performance significantly improved by a short-length unpumped erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is reported and experimentally investigated. A 10 GHz optical pulse train with a supermode suppression ratio of 61.8 dB and a 10 GHz radio frequency signal with a sidemode suppression ratio of 94 dB and a phase noise of 121.9 dBc / Hz
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing Robust fiber-based frequency synchronization system immune to strong temperature fluctuation Download:729次
Download:729次
 Download:729次
Download:729次In order to make the fiber-based frequency synchronization system suitable for the use of large-scale scientific and engineering projects in which the ambient temperature of the fiber links change dramatically, we design a non-harmonic frequency dissemination system immune to strong temperature fluctuation. After the lab tests, in which the ambient temperature of the fiber fluctuates 40°C/day and 20°C/h, respectively, the relative frequency stabilities of this system reaches 4.0 × 10 14 / s 3.0 × 10 16 / 10 4 s
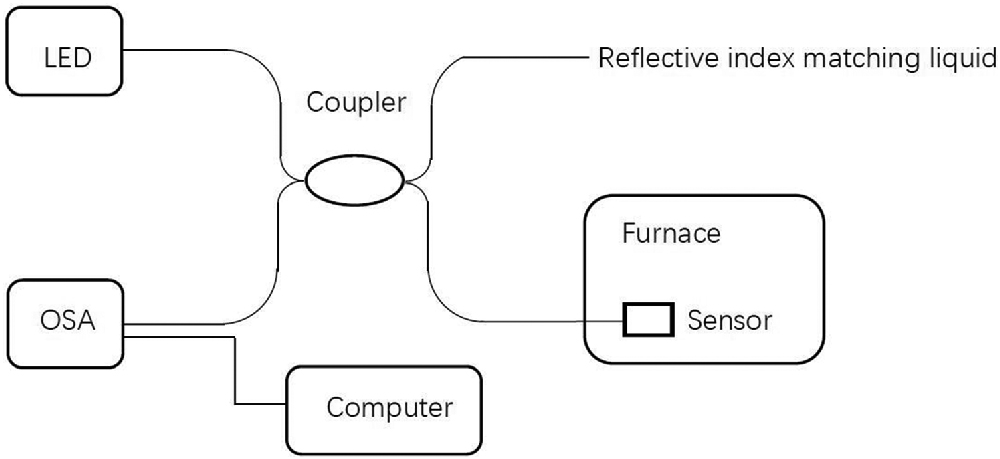
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications We propose a cavity length demodulation method that combines virtual reference interferometry (VRI) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) algorithm for fiber-optic Fabry–Perot (F-P) sensors. In contrast to the conventional demodulating method that uses fast Fourier transform (FFT) for cavity length estimation, our method employs the VRI technique to obtain a raw cavity length, which is further refined by the MMSE algorithm. As an experimental demonstration, a fiber-optic F-P sensor based on a sapphire wafer is fabricated for temperature sensing. The VRI-MMSE method is employed to interrogate cavity lengths of the sensor under different temperatures ranging from 28°C to 1000°C. It eliminates the “mode jumping” problem in the FFT-MMSE method and obtains a precision of 4.8 nm, corresponding to a temperature resolution of 2.0°C over a range of 1000°C. The experimental results reveal that the proposed method provides a promising, high precision alternative for demodulating fiber-optic F-P sensors.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2300 Fiber measurements In order to improve the precision of the laser–radio-frequency (RF) synchronization system from sub-picosecond to femtosecond (fs), a synchronization system between a picosecond laser and a 1.3 GHz RF generator has been developed based on a fiber-loop optical-microwave phase detector (FLOM-PD). Synchronization with fs-level (3.8 fs) rms jitter, integrated from 10 Hz to 1 MHz, is achieved for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, in this kind of configuration. This system will be used for the superconducting RF accelerator at Peking University.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers 350.4010 Microwaves Suppression of backscattering induced noise by the sideband locking technique in a resonant fiber optic gyroscope Download:788次
Download:788次
 Download:788次
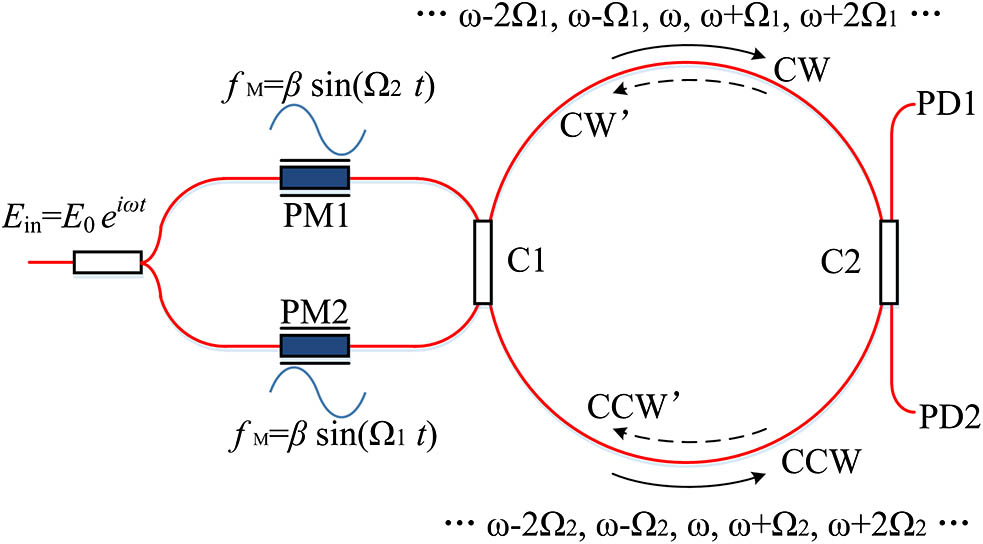
Download:788次Polarization fluctuation induced noise and backscattering-induced noise are the dominant noises in resonant fiber optic gyroscopes. This Letter proposes a new method to suppress the carrier and backscattering induced noise by the sideband locking technique. Besides choosing an optimized modulation depth and different clockwise and counterclockwise modulation frequencies, the sideband is locked to the cavity resonance. With the proper modulation frequency, the carrier frequency component locates at a position far away from the resonant frequency, and then it is suppressed by the cavity itself, which can be taken as a bandpass filter. The amplitude of the carrier frequency can be suppressed by 20–25 dB additionally by the cavity and the total intensity suppression ratio can reach 115.74 dB. The backscattering induced noise can be eliminated for the adoption of different frequencies. The method can realize a stable and high suppression ratio without high requirements for parameter accuracy or device performance.
060.2800 Gyroscopes 010.1350 Backscattering 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 120.4640 Optical instruments Passively Q-switched S-band thulium fluoride fiberlaser with multi-walled carbon nanotube Download:697次
Download:697次
 Download:697次
Download:697次A stable, passively Q-switched thulium fluoride fiber laser (TFFL) using a multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)-based saturable absorber (SA) for operation in the S-band region is proposed and demonstrated. The proposed TFFL has a central lasing wavelength of 1486.4 nm and an input power range of 87.1–126.6 mW. The output pulses have a repetition rate and pulse width range of 30.1–40.0 kHz and 9.0–3.2 μs, respectively, with a maximum pulse energy of 28.9 nJ. This is the first time, to the author’s knowledge, of the successful demonstration of a passively Q-switched S-band TFFL using an MWCNT-based SA.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.2430 Fibers, single-mode 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Coupling length variation and multi-wavelength demultiplexing in photonic crystal waveguides Download:824次
Download:824次
 Download:824次
Download:824次In this Letter, the effects of material/structure parameters of photonic crystal (PhC) parallel waveguides on the coupling length are investigated. The results show that, increasing the effective relative permittivity of the PhC leads to a downward shift of the photonic bandgap and a variation of the coupling length. A compact PhC 1.31/1.55 μm wavelength division multiplexer (WDM)/demultiplexer with simple structure is proposed, where the output power ratios are more than 24 dB. This WDM can multiplex/demultiplex other light waves efficiently.
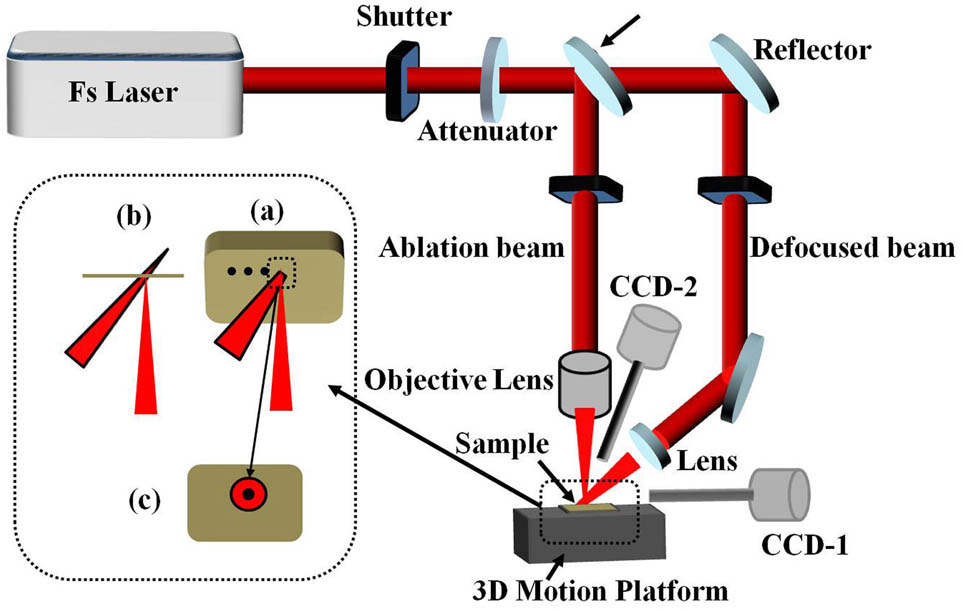
130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 060.4510 Optical communications 060.4230 Multiplexing Ablation enhancement by defocused irradiation assisted femtosecond laser fabrication of stainless alloy Download:910次
Download:910次
 Download:910次
Download:910次We evaluate the effects of the holes geometry drilled by a femtosecond laser on a stainless alloy with various defocused irradiation time, which ranges from 0 min to 1 h. The laser ablation efficiency is increased by a factor of 3 when the irradiation time is elevated from 0 to 30 min. Also, the morphology of the hole is observed by a scanning electron microscope, where the result indicates that the defocused irradiation time has a significant influence on the morphology changes. The reason for such changes is discussed based on the pretreatment effect and the confined plasma plume. As an application example, the microchannel is fabricated by a femtosecond laser combined with the defocused irradiation to demonstrate the advantage of the proposed method in fabricating functional structures.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics In this Letter, the loss and gain characteristics of an unconventional In x Ga 1 x As / Ga As In x Ga 1 x As
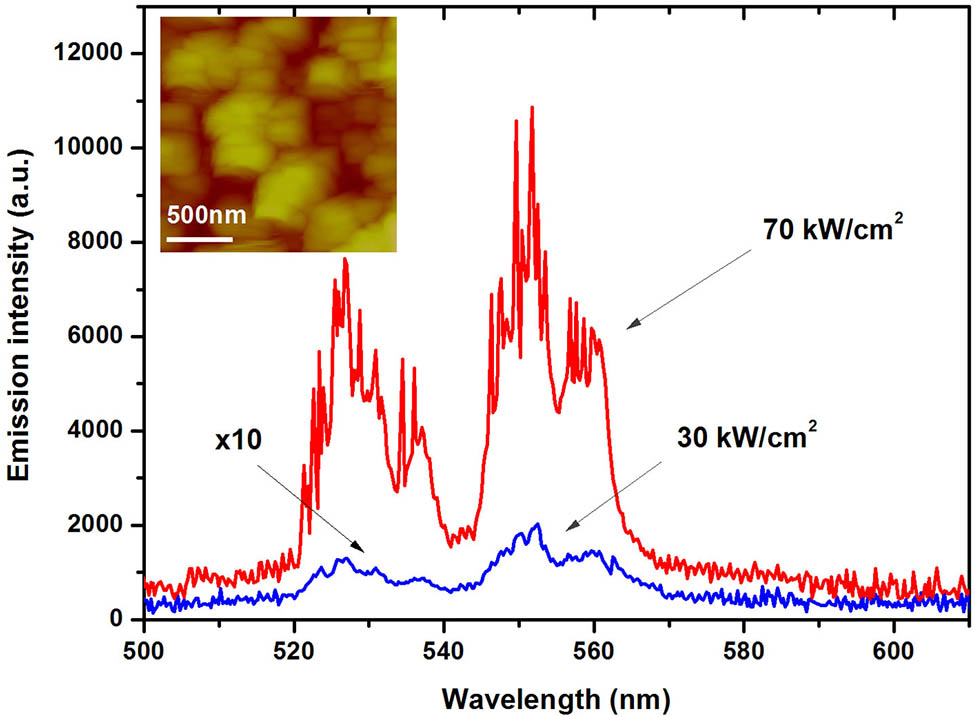
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers A solid-state green-light-emitting upconversion coherent random laser was realized by pumping macroporous erbium-doped lithium niobate with a 980 nm laser. The lasing threshold was determined to be about 40 kW / cm 2
140.7300 Visible lasers 290.4210 Multiple scattering 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials The stress damage process of a single crystal silicon wafer under millisecond laser irradiation is studied by experiments and numerical simulations. The formation process of low-quality surface is monitored in real-time. Stress damage can be observed both in laser-on and -off periods. Plastic deformation is responsible for the first stress damage in the laser-on period. The second stress damage in the laser-off period is a combination of plastic deformation and fracture, where the fundamental cause lies in the residual molten silicon in the ablation hole.
140.3330 Laser damage 140.3390 Laser materials processing We report experimental realization of Raman spectra enhancement of copper phthalocyanine, using an on-chip metallic planar waveguide of the sub-millimeter scale. The oscillating ultrahigh order modes excited by the direct coupling method yield high optical intensity at resonance, which is different from the conventional strategy to create localized “hot spots.” The observed excitation efficiency of the Raman signal is significantly enhanced, owing to the high Q factor of the resonant cavity. Furthermore, effective modulation of the Raman intensity is available by adjusting the polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) thickness in the guiding layer, i.e., by tuning the light–matter interaction length. A large modulation depth is verified through the fact that 10 times variation in the enhancement factor is observed in the experiment as the PMMA thickness varies from 7 to 23 μm.
230.7370 Waveguides 310.2785 Guided wave applications An optomechanical cavity embedded with a V-type three-level atom is exploited to control single-photon transport in a one-dimensional waveguide. The effects of the atom–cavity detuning, the optomechanical effect, the coupling strengths between the cavity and the atom or the waveguide, and the atomic dissipation on the single-photon transport properties are analyzed systematically. Interestingly, the single-photon transmission spectra show multiple double electromagnetically induced transparency. Moreover, the double electromagnetically induced transparency can be switched to a single one by tuning the atom–cavity detuning.
270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.5580 Quantum electrodynamics 020.5580 Quantum electrodynamics Using a measurement system based on fluorescence induced by variable pulse light, photosynthesis parameters of chlorella pyrenoidosa are obtained, employing single-turnover and multiple-turnover protocols under dark-adapted and light-adapted conditions. Under the light-adapted condition, σ P S I I ′ F v ′ / F m ( ST ) ′ F v ′ / F m ( MT ) ′ F m ( MT ) F m ( MT ) ′ F v / F m ( MT ) F v ′ / F m ( MT ) ′ F m ( ST ) 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology
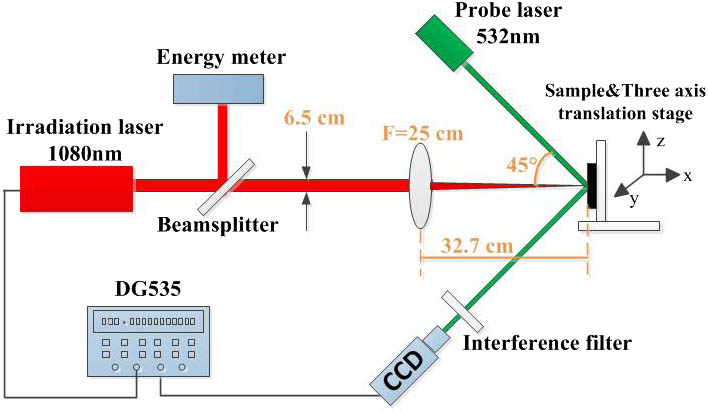
The femtosecond laser pulses reflected from the self-induced plasma mirror (PM) surface are characterized. More than two orders of magnitude improvement on intensity contrast both in nanosecond and picosecond temporal scales are measured. The far-field distribution, i.e., focusability, is measured to degrade in comparison with that without using a PM. Experiments on proton accelerations are performed to test the effect of the balance between degraded focusability and increased reflectivity. Our results show that PM is an effective and robust device to improve laser contrast for applications.
320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Fusion of the low-light-level visible and infrared images for night-vision context enhancement Download:1055次
Download:1055次
 Download:1055次
Download:1055次For better night-vision applications using the low-light-level visible and infrared imaging, a fusion framework for night-vision context enhancement (FNCE) method is proposed. An adaptive brightness stretching method is first proposed for enhancing the visible image. Then, a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with edge-preserving filtering is proposed to decompose the source images. Finally, the fused result is obtained via a combination of the decomposed images in three different rules. Experimental results demonstrate that the FNCE method has better performance on the details (edges), the contrast, the sharpness, and the human visual perception. Therefore, better results for the night-vision context enhancement can be achieved.
350.2660 Fusion 040.3780 Low light level 100.2980 Image enhancement 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦