2020, 18(1) Column
Atomic and Molecular Optics Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Holography Image Processing and Machine Vision Optical Sensing, Measurements, and Metrology Lasers and Laser Optics Biomedical Optics Nonlinear Optics Optics in Computing and Optical Data Storage Optical Design and Fabrication Optoelectronics Thin Films and Optics At Surfaces Nanophotonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第18卷 第1期
Coulomb potential may induce a significant angular offset to the two-dimensional photoelectron momentum distributions for atoms subject to strong elliptically polarized laser fields. In the attoclock experiment, this offset usually cannot be easily disentangled from the contribution of tunneling delay and poses a main obstacle to the precise measurement of tunneling delay. Based on semiclassical calculations, here, we propose a method to extract the equivalent temporal offset induced solely by Coulomb potential (TOCP) in an attoclock experiment. Our calculations indicate that, at constant laser intensity, the TOCP shows distinctive wavelength dependence laws for different model atoms, and the ratio of the target atom’s TOCP to that of H becomes insensitive to wavelength and linearly proportional to (2Ip) 3/2, where Ip is the ionization potential of the target atom. This wavelength and Ip dependence of TOCP can be further applied to extract the Coulomb potential influence. Our work paves the way for an accurate measurement of the tunneling delay in the tunneling ionization of atoms subject to intense elliptically polarized laser fields.
tunneling delay Coulomb potential influence attoclock Polarization in D-shaped fiber modulated by magneto-optical dichroism of magnetic fluid Download:847次
Download:847次
 Download:847次
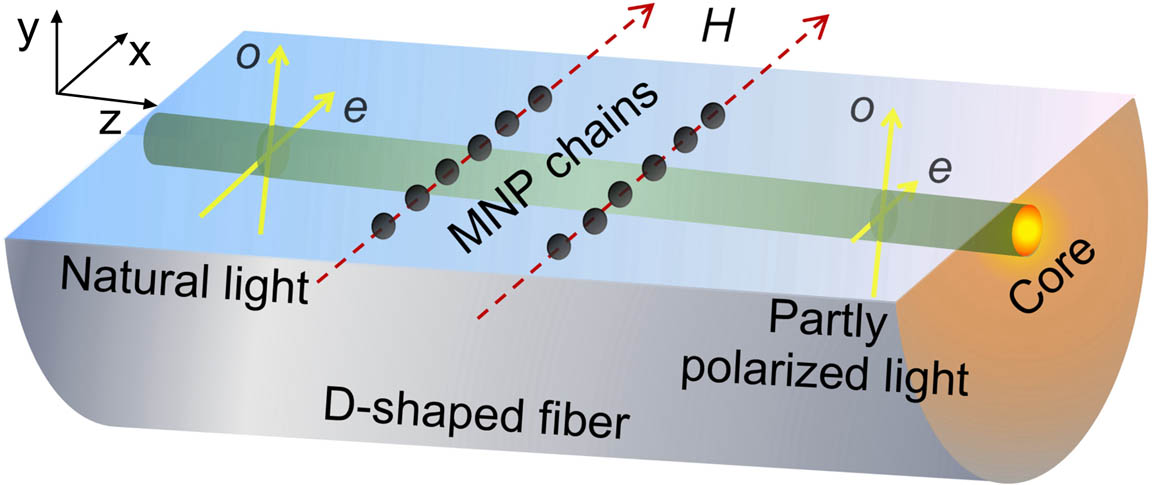
Download:847次The polarization of a D-shaped fiber is modulated after immersing it in magnetic fluid (MF) and applying a magnetic field. Theoretical analysis predicts that magneto-optical dichroism of MF plays a key role in light polarization modulation. During light polarization modulation, the evanescent wave polarized parallel to the magnetic field has greater loss than its orthogonal component. Light polarization of a D-shaped fiber with a wide polished surface can be modulated easily. High concentration MF and a large magnetic field all have great ability to modulate light polarization.
fiber optics components polarization-selective devices magneto-optic systems magneto-optical materials Brillouin gain spectra (BGS) in an As2Se3 photonic crystal fiber (PCF) are investigated numerically. The profiles of the BGS are simulated by calculating the characteristics of different-order optical and acoustic waves in the PCFs with different core diameters. For the small-core PCF, there are two peaks in BGS, but there is only one peak for the large-core PCF. We also reveal that in the small-core PCF, the difference of Brillouin frequency shift between the LP01 and LP11 modes is obvious, while it is not obvious in the large-core PCF. The Brillouin threshold increases with the core diameter increasing.
stimulated Brillouin scattering optical mode acoustic mode chalcogenide fiber photonic crystal fiber We demonstrate real-time three-dimensional (3D) color video using a color electroholographic system with a cluster of multiple-graphics processing units (multi-GPU) and three spatial light modulators (SLMs) corresponding respectively to red, green, and blue (RGB)-colored reconstructing lights. The multi-GPU cluster has a computer-generated hologram (CGH) display node containing a GPU, for displaying calculated CGHs on SLMs, and four CGH calculation nodes using 12 GPUs. The GPUs in the CGH calculation node generate CGHs corresponding to RGB reconstructing lights in a 3D color video using pipeline processing. Real-time color electroholography was realized for a 3D color object comprising approximately 21,000 points per color.
color electroholography real-time electroholography multiple-graphics processing unit cluster graphics processing unit An effective interference suppression algorithm for visible light communication system based on DBSCAN Download:879次
Download:879次
 Download:879次
Download:879次In order to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and mitigate the damage of noise to the communication quality, an effective interference suppression algorithm, which is based on the improved density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise algorithms, is proposed for visible light communication systems using the complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor image sensor as the receiver. Experimental results show that the algorithm can learn the region where the payload data is located, filter out the noise data, and greatly decrease the interference. The effect of the algorithm is also studied through bit error ratio performance.
visible light communication optical data processing digital image processing Blind identification of occurrence of multi-modality in laser-feedback-based self-mixing sensor Download:637次
Download:637次
 Download:637次
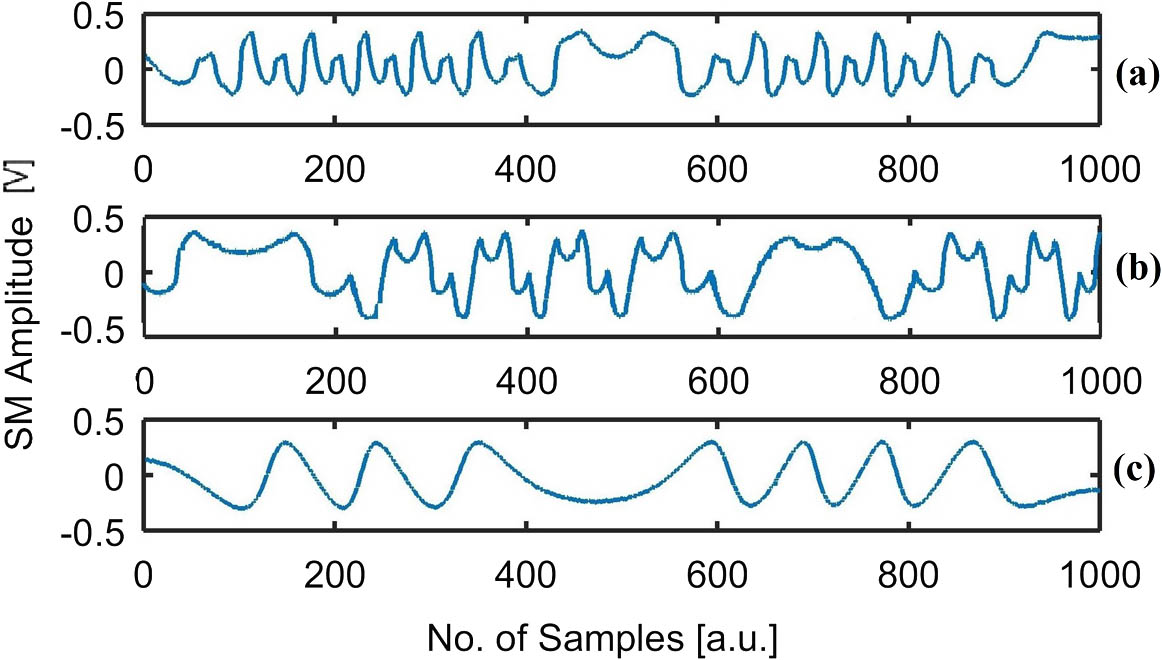
Download:637次Self-mixing interferometry (SMI) is an attractive sensing scheme that typically relies on mono-modal operation of an employed laser diode. However, change in laser modality can occur due to change in operating conditions. So, detection of occurrence of multi-modality in SMI signals is necessary to avoid erroneous metric measurements. Typically, processing of multi-modal SMI signals is a difficult task due to the diverse and complex nature of such signals. However, the proposed techniques can significantly ease this task by identifying the modal state of SMI signals with 100% success rate so that interferometric fringes can be correctly interpreted for metric sensing applications.
self-mixing interferometry laser diode multi-modality optical feedback High sensitivity conductivity-temperature-depth sensing based on an optical microfiber coupler combined fiber loop Download:783次
Download:783次
 Download:783次
Download:783次In order to meet the practical needs of all-fiber conductivity-temperature-depth sensors with high sensitivity, compact structure, and easy packaging, this Letter uses a microfiber coupler combined with fiber loop (MCFL) reflective photonic device to conduct salinity, temperature, and deep sensing experiments. These MCFLs’ dynamic range and resolution of salinity, temperature, and depth can meet the requirements of actual marine environment monitoring. This structure opens up a new design idea for the practical research of microfiber coupler-based marine environmental parameter sensors.
microfiber coupler fiber loop salinity temperature and depth sensing cross sensitivity conductivity-temperature-depth measurement system Three-level all-fiber laser at 915 nm based on polarization-maintaining Nd3+-doped silica fiber Download:846次
Download:846次
 Download:846次
Download:846次Nd3+-doped fiber lasers at around 900 nm based on the 4F3/2 → 4I9/2 transition have obtained much research attention since they can be used as the laser sources for generating pure blue fiber lasers through the frequency doubling. Here, an all-fiber laser at 915 nm was realized by polarization-maintaining Nd3+-doped silica fiber. A net gain per unit length of up to 1.0 dB/cm at 915 nm was obtained from a 4.5 cm fiber, which to our best knowledge is the highest gain coefficient reported in this kind of silica fiber. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency varies with the active fiber length and the reflectivity of the output fiber Bragg grating (FBG), presenting an optimal value of 5.3% at 5.1 cm fiber length and 70% reflectivity of the low reflection FBG. Additionally, the linear distributed Bragg reflector short cavity was constructed to explore its potential in realizing single-frequency 915 nm fiber laser. The measurement result of longitudinal-mode properties shows it is still multi-longitudinal mode laser operation with 40 mm laser cavity. These results indicate that the Nd3+-doped silica fiber could be used to realize all-fiber laser at 915 nm, which presents potential to be the seed source of high-power fiber laser.
fiber laser laser materials neodymium In this Letter, a dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystal (DDCLC)-filled hollow glass microsphere is demonstrated to be a resonator with good temperature response. A diglycerol layer is used to wrap the DDCLCs microdroplet to keep it steady and control its orientation. The whispering gallery mode (WGM) lasing and photonic band gap (PBG) lasing caused by two different mechanisms were obtained under the pump of a pulsed laser, and the temperature response of these two kinds of lasing was studied. For the liquid crystal and chiral material used in this Letter, both the WGM lasing and the PBG lasing have a blue shift in wavelength with increasing temperature.
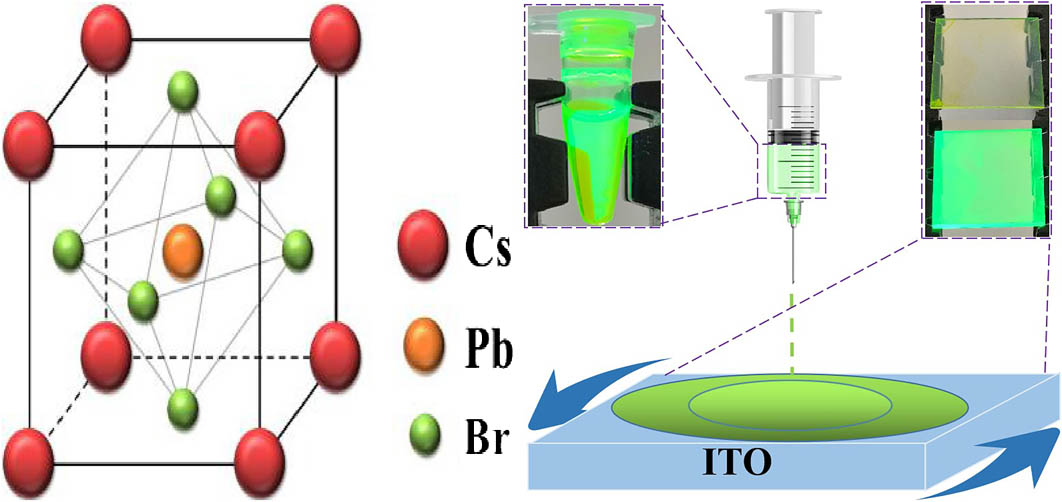
cholesteric liquid crystal microdroplet lasing emission whispering gallery mode Aiming at the application requirements of information optics, this Letter proposed a perovskite quantum dot random lasing pumping method suitable for high-speed modulation. At the same time, the luminescence characteristics of perovskite quantum dot films under electron beam pumping conditions are analyzed, and the random lasing mechanism of electron beam pumping CsPbBr3 quantum dot films is revealed. Finally, it is confirmed that perovskite quantum dots are easy to realize random lasing under electron beam pumping conditions.
perovskite quantum dots electron beam random laser Real-time phase measurement and correction of dynamic multimode beam using a single spatial light modulator Download:652次
Download:652次
 Download:652次
Download:652次In this Letter, a novel system for adaptively correcting the phase of a dynamic multimode beam is proposed. While using merely one spatial light modulator, the phase measurement of the first-order diffraction pattern and the correction of the zeroth diffraction order are simultaneously realized. The real-time experimental result is obtained at a control rate of 10 Hz. The power-in-the-bucket value is improved from 38.5% to 61.8%, even with fundamental mode content that is consistently below 30%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first implementation of real-time adaptive correction of the entire multimode beam.
fiber laser mode decomposition adaptive optics phase correction Watt-level Pr3+:YLF deep red laser pumped by a fiber-coupled blue LD module or a single-emitter blue LD Download:932次
Download:932次
 Download:932次
Download:932次A power-scaled laser operation of Pr:YLiF4 (YLF) crystal at 720.9 nm pumped by a 443.6 nm laser diode (LD) module was demonstrated. The 20 W module was used to pump the Pr:YLF crystal, and a maximum output power of 3.03 W with slope efficiency of 30.04% was obtained. In addition, a 5 W blue LD was also used to pump the Pr:YLF laser, and a maximum output power of 0.72 W was obtained at room temperature. The output power was limited by the wavelength mismatch between the single-emitter LD and the absorption peak of the crystal.
rare earth and transition metal solid-state lasers visible lasers diode-pumped lasers Tikhonov-regularization-based projecting sparsity pursuit method for fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction Download:908次
Download:908次
 Download:908次
Download:908次For fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT), image quality could be improved by incorporating a sparsity constraint. The L1 norm regularization method has been proven better than the L2 norm, like Tikhonov regularization. However, the Tikhonov method was found capable of achieving a similar quality at a high iteration cost by adopting a zeroing strategy. By studying the reason, a Tikhonov-regularization-based projecting sparsity pursuit method was proposed that reduces the iterations significantly and achieves good image quality. It was proved in phantom experiments through time-domain FMT that the method could obtain higher accuracy and less oversparsity and is more applicable for heterogeneous-target reconstruction, compared with several regularization methods implemented in this Letter.
fluorescence molecular tomography sparsity pursuit Tikhonov regularization good image quality high efficiency The dipole resonances of gold nanocages were investigated theoretically using finite difference time domain method. The results show that field enhancement is obtained at the walls of the gold nanocages. It is believed that the effect can cause a strong optical nonlinear property. To test the hypothesis, nonlinear absorption was investigated using a broadband 5 ns Z scan. It was found that at low intensities the sample shows saturable absorption (SA), while at higher intensities a switch from SA to reverse SA occurs. Moreover, the nonlinear absorption of the sample is sensitively wavelength-dependent, and, in the resonant region, saturation intensity is the largest.
saturable absorption reverse saturable absorption gold nanocages FDTD Z-scan Bi2S3-xSex/poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) nanocomposite films were prepared using microwave assisted synthesis with different compositions of x. Crystal structure, surface morphology, and optical properties were investigated to characterize the prepared nanocomposite films. The crystallinity and optical band gap of the prepared Bi2S3-xSex/PMMA were affected by x. The prepared samples showed a blue shift in the absorption edge. The laser power dependent nonlinear refraction and absorption of Bi2S3-xSex/PMMA nanocomposite films were investigated by using the Z-scan technique. The optical nonlinearity of the nanocomposite films exhibited switchover from negative nonlinear refraction to positive nonlinear refraction to negative nonlinear refraction effects, and from saturable absorption to reverse saturable absorption to saturable absorption with an increase and decrease in the composition. An interesting all-optical figure of merit was reported to assess the nanocomposite films for a practical device. It was calculated that the device all-figures of merit were based on the nonlinear response, which is important for the all-optical switching device. The results demonstrate that the optimized all-optical figures of merit can be achieved by adjusting the composition and input laser power, which can be used for the design of different all-photonic devices, and the results of nonlinear switching behavior can open new possibilities for using the nanocomposite films in laser Q-switching and mode-locking.
bismuth chalcogenides Bi2S3-xSex/PMMA nanocomposite Z-scan technique nonlinear absorption and refraction all-optical figures of merit In this Letter, a new approach of optical tape for high capacity multilayer data storage is proposed. We show that a length of 5 cm and width of 2 cm of soft and transparent optical tape can be used for two-photon three-dimensional bit data storage. We successfully demonstrate writing and reading of six layers of data storage with a transverse bit separation of 2 μm and an axial separation of 2.5 μm in a tetraphenylethylene-doped photobleaching polymer. The fluorescence intensity is insensitive to the storage depth of the photopolymer matrix. Thus, the optical tape that we put forward in the experiment can help people realize true large data storage in the future, like magnetic tape. This method significantly paves a novel way for solving big data storage problems.
optical tape polymer curing multilayer recording big data storage In this Letter, we fabricate integrated metasurface of encoded dynamic phases and experimentally generate nonconventional Kagome-type lattices of no-second-order phase vortices. The thin metasurface acts analogous to an integration of three conventional optical elements, i.e., six pinholes located at the vertices of two concentric regular triangles of size ratio 1:2, six transparent discs of different thicknesses to introduce a total phase shift difference of
Kagome lattice metasurface phase modulation We have designed and fabricated zero-bias operational two-element symmetric-connected photodetector arrays (SC-PDAs). The designed SC-PDAs have higher saturation currents, larger RF power, and better frequency responses than the single photodetector (PD) under zero bias. The bias-free SC-PDA with 15 μm diameter of each PD demonstrated a 3 dB bandwidth of 19.4 GHz at 0.5 mA. The RF saturation photocurrent and maximum RF output power of the SC-PDA with 40 μm, 50 μm, and 60 μm diameters under zero bias are over 9.31 mA and ?5.86 dBm at 3 GHz, 14.52 mA and 1.17 dBm at 1 GHz, and 13.72 mA and ?1.76 dBm at 1 GHz, respectively.
photodetectors photodiode array microwave photonics We investigate a channel-interleaved photonic analog-to-digital conversion (PADC) system’s ability to work stably over a long duration with an optimal driving voltage. The influence of optimum bias point drift of a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM)-based photonic switch on this system was analyzed theoretically and experimentally. The feasibility of extracting feedback signals from the PADC system was derived. A high-stability channel-interleaved PADC was constructed by extracting a feedback signal from a parallel demultiplexing module to control the MZM-based photonic switch’s driving voltage. Consequently, the amplitude mismatch between the channels was limited to within 0.3 dB over 12 hours of operation.
photonic analog-to-digital converter Mach–Zehnder modulator stability optimization In this study, we propose an effective method for the fabrication of annulus micro-/nanostructures by a femtosecond laser doughnut beam. Compared with the traditional Bessel annulus beam shaping system, this method greatly compresses the light propagation path. It is theoretically and experimentally demonstrated that the obtained axial section of the peak envelope in the processing area is two waists of the isosceles triangle. By moving the relative position of the sample, annulus microstructures with different diameters on copper sheet could be fabricated. In addition, laser induced periodic surface structures with controllable direction are fabricated by this optical system.
femtosecond laser pulse shaping doughnut beam laser induced periodic surface structures A reconfigurable terahertz polarization converter based on metal–graphene hybrid metasurface Download:984次
Download:984次
 Download:984次
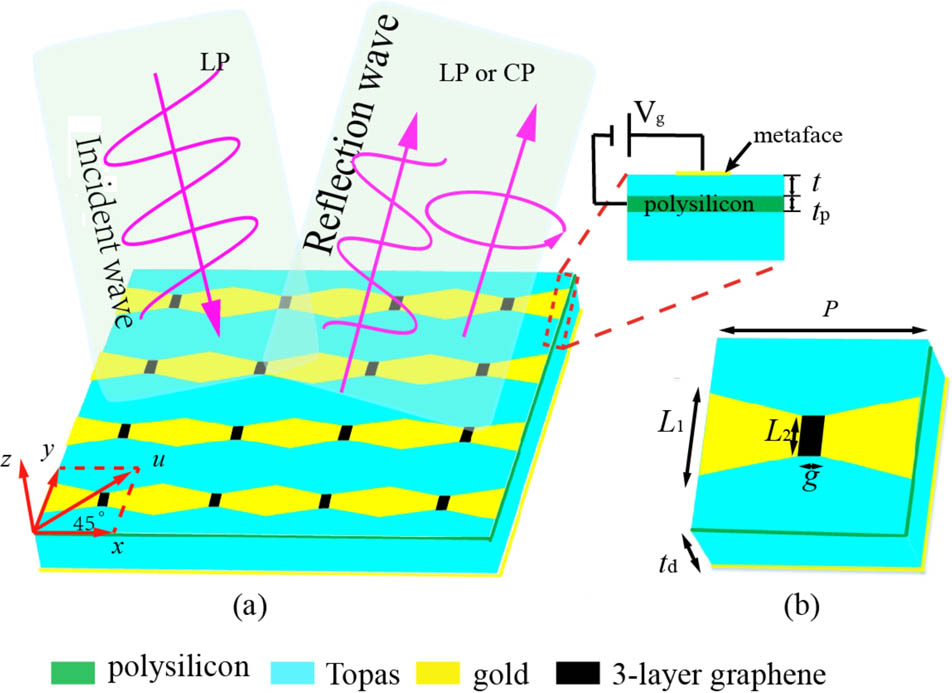
Download:984次A metal–graphene hybrid metasurface polarization converter is designed in this Letter. The unit cell of the hybrid metasurface is composed of a butterfly-shaped structure whose branches are connected by multi-layer graphene sheets. The proposed device can be reconfigured from linear-to-circular polarization to cross-polarization by changing the Fermi energy of graphene. The simulation results show that for three-layer graphene, the device acts as a linear-to-circular polarization converter when EF = 0 eV and switches to a cross-polarization converter when EF = 0.5 eV. Compared with single-layer graphene, the device with three-layer graphene can maintain the cross-polarization conversion performance under low Fermi energy. Furthermore, two equivalent circuits in the x and y directions are developed to understand the working mechanism of the device.
graphene metasurface polarization converter THz A controllable coupling structure for silicon microring resonators based on adiabatic elimination Download:1007次
Download:1007次
 Download:1007次
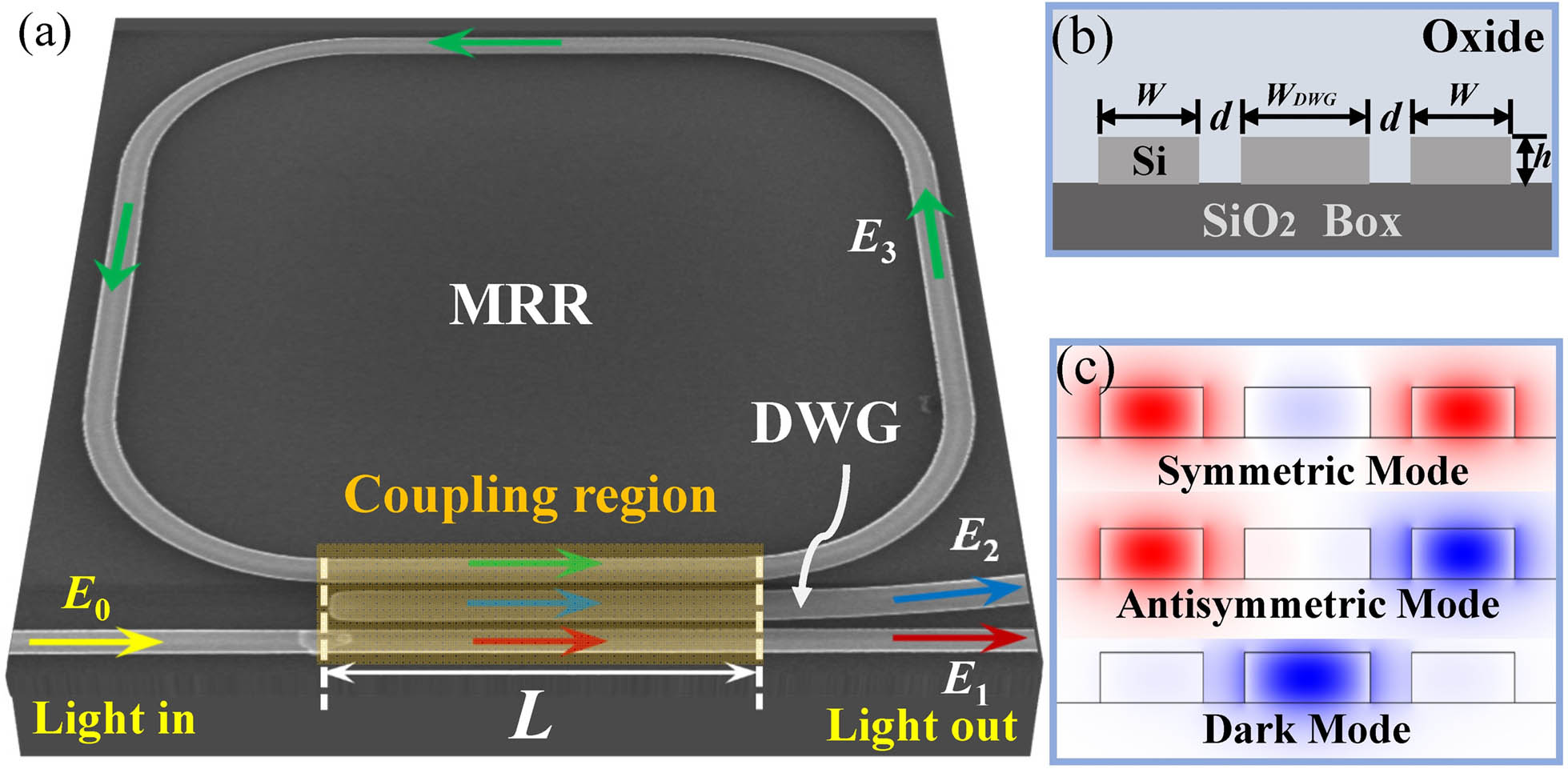
Download:1007次Optical microring resonators are extensively employed in a wide range of physical studies and applications due to the resonance enhancement property. Incorporating coupling control of a microring resonator is necessary in many scenarios, but modifications are essentially added to the resonator and impair the capability of optical enhancement. Here, we propose a flexible coupling structure based on adiabatic elimination that allows low-loss active coupling control without any modifications to the resonators. The self-coupling coefficient can be monotonically or non-monotonically controllable by the proposed coupler, potentially at a high speed. The characteristic of the coupler when implemented in silicon microring resonators is investigated in detail using substantiated analytical theory and experiments. This work provides a general method in coupling control while ensuring the resonance enhancement property, making active coupling control in a resonator-waveguide system feasible.
silicon photonics adiabatic elimination resonance system 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦