2016, 4(2) Column
Photonics Research 第4卷 第2期
Bessel–Gauss photon beams with fractional order vortex propagation in weak non-Kolmogorov turbulence Download:1108次
Download:1108次
 Download:1108次
Download:1108次We model the effects of weak fluctuations on the probability densities and normalized powers of vortex models for the Bessel–Gauss photon beam with fractional topological charge in the paraxial non-Kolmogorov turbulence channel. We find that probability density of signal vortex models is a function of deviation from the center of the photon beam, and the farther away from the beam center it is, the smaller the probability density is. For fractional topological charge, the average probability densities of signal/crosstalk vortex modes oscillate along the beam radius except the half-integer order. As the beam waist of the photon source grows, the average probability density of signal and crosstalk vortex modes grow together. Moreover, the peak of the average probability density of crosstalk vortex modes shifts outward from the beam center as the beam waist gets larger. The results also show that the smaller index of non-Kolmogorov turbulence and the smaller generalized refractive-index structure parameter may lead to the higher average probability densities of signal vortex modes and lower average probability densities of crosstalk vortex modes. Lower-coherence radius or beam waist can give rise to less reduction of the normalized powers of the signal vortex modes, which is opposite to the normalized powers of crosstalk vortex modes.Physics (Grant No. 11447174), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51517).
Atmospheric turbulence Atmospheric turbulence Photon statistics Photon statistics Quantum communications Quantum communications Periodic structural defects in Bragg gratings and their application in multiwavelength devices Download:859次
Download:859次
 Download:859次
Download:859次In this paper, we present the finding that periodic structural defects (PSDs) along a Bragg grating can shift the Bragg wavelength. This effect is theoretically analyzed and confirmed by numerical calculation. We find that the Bragg wavelength shift is determined by the defect size and the period of the defects. The Bragg wavelength can be well tuned by properly designing the PSDs, and this may provide an alternative method to fabricate grating-based multiwavelength devices, including optical filter arrays and laser arrays. In regards to wavelength precision, the proposed method has an advantage over the traditional methods, where the Bragg wavelengths are changed directly by changing the grating period. In addition, the proposed method can maintain grating strength when tuning the wavelength since only the period of defects is changed. This will be a benefit for devices such as arrays.(BK20130585, BK20140414), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61435014, 61504170, 61504058), and the National 863 Program (2015AA016902).
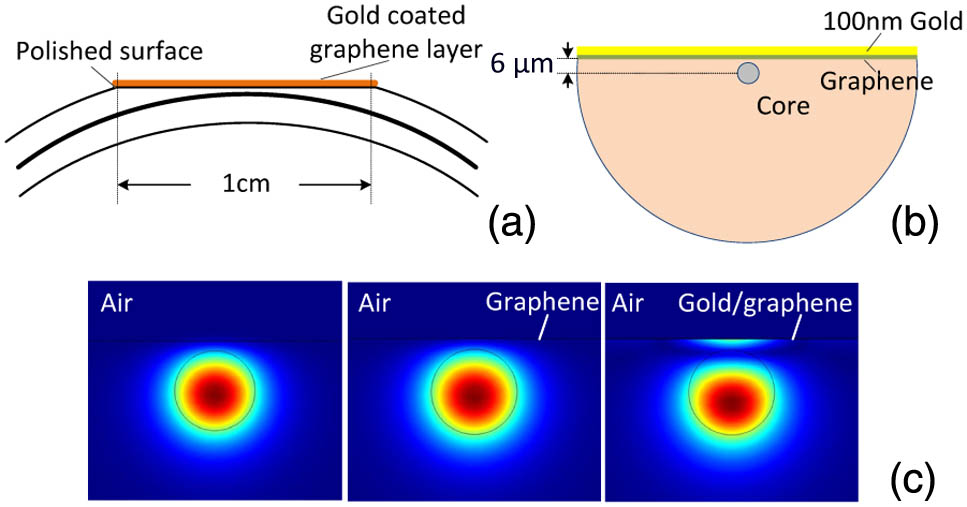
Gratings Gratings Subwavelength structures Subwavelength structures Wavelength filtering devices Wavelength filtering devices Laser arrays Laser arrays By transferring 100 nm gold-coated CVD monolayer graphene onto the well-polished surface of D-shaped fiber, we achieve a graphene in-line polarizer with a high polarization extinction ratio of ~27 dB and low insertion loss of 5 dB at 1550 nm, meanwhile achieving a strong saturable absorption effect of 14%. The manufacture of thisgraphene in-line polarizer also simplifies the graphene transfer process. To explore the potential applications of the new device, we also demonstrate noise-like pulse generation and supercontinuum spectrum generation. By launching the designed graphene device into a fiber ring laser cavity, 51 nm bandwidth noise-like pulse is obtained. Then, launching the high-power noise-like pulse into high nonlinear fiber, a 1000 nm wide supercontinuum spectrum is obtained, which is favorable for sensing and nonlinearities scientific fields.
Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Long-period grating inscription on polymer functionalized optical microfibers and its applications in optical sensing Download:866次
Download:866次
 Download:866次
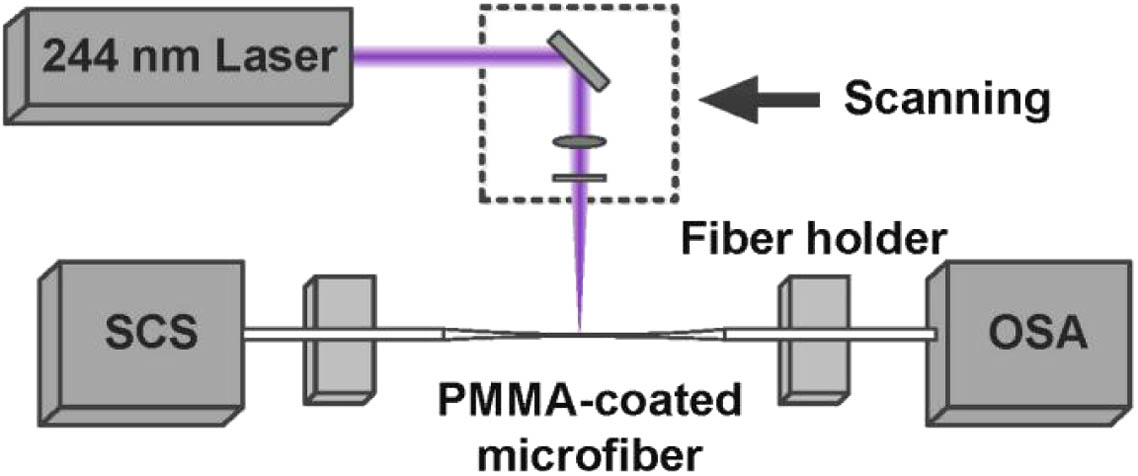
Download:866次We demonstrated long-period grating (LPG) inscription on polymer functionalized optical microfibers and its applications in optical sensing. Optical microfibers were functionalized with ultraviolet-sensitive polymethyl methacrylate jackets and, thus, LPGs could be inscribed on optical microfibers via point-by-point ultraviolet laser exposure. For a 2 mm long microfiber LPG (MLPG) inscribed on optical microfibers with a diameter of 5.4 μm, a resonant dip of 15 dB at 1377 nm was observed. This MLPG showed a high sensitivity of strain and axial force, i.e., ?1.93 pm∕με and ?1.15 pm∕μN, respectively. Although the intrinsic temperature sensitivity of the LPGs is relatively low, i.e., ?12.75 pm∕°C, it can be increased to be ?385.11 pm∕°C by appropriate sealing. Benefiting from the small footprint and high sensitivity, MLPGs could have potential applications in optical sensing of strain, axial force, and temperature.
Fiber optics Fiber optics Fiber optics sensors Fiber optics sensors Polymers Polymers Microstructure fabrication Microstructure fabrication Gratings Gratings In this work, new plain and composite high-energy solitons of the cubic–quintic Swift–Hohenberg equation were numerically found. Starting from a composite pulse found by Soto-Crespo and Akhmediev and changing some parameter values allowed us to find these high energy pulses. We also found the region in the parameter space in which these solutions exist. Some pulse characteristics, namely, temporal and spectral profiles and chirp, are presented. The study of the pulse energy shows its independence of the dispersion parameter but its dependence on the nonlinear gain. An extreme amplitude pulse has also been found.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers In this paper, Er/Yb co-doped fiber amplifiers (EYDFAs) with an Yb-band fiber Bragg grating (FBG) at the pump end to improve the performance of the amplifier is systematically studied. The influence of the reflectivity and center wavelength of the FBG along with the gain-fiber length on the performance of an EYDFA are numericallyanalyzed. The results show that the wavelength of the FBG has critical influence on the efficiency of the EYDFA, whereas the requirement to its reflectivity is relaxed. It is an effective and promising way to improve the efficiency of a high-power pumped EYDFA by introducing a suitable Yb-band FBG at the pump end. Based on the analysis of the underlying principles, suggestions for the practical design and possible further improvement strategies are also proposed.61107035 and 61378043, the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of China under grant 2013YQ03091502, and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) under grant 2014CB340104.
Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Fibers Fibers erbium erbium Lasers Lasers ytterbium ytterbium Fiber Bragg gratings Fiber Bragg gratings We describe and experimentally demonstrate a measuring technique for Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) based integrated photonic biochemical sensors. Our technique is based on the direct measurement of phase changes between the arms of the MZI, achieved by signal modulation on one of the arms of the interferometer together with pseudoheterodyne detection, and it allows us to avoid the use of costly equipment such as tunable light sources or spectrum analyzers. The obtained output signal is intrinsically independent of wavelength, power variations, and global thermal variations, making it extremely robust and adequate for use in real conditions. Using a silicon-on-insulator MZI, we demonstrate the real-time monitoring of refractive index variations and achieve a detection limit of 4.1 × 10?6 refractive index units (RIU).
Sensors Sensors Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Heterodyne Heterodyne Optical pulse repetition rate multiplication based on series-coupled double-ring resonator Download:610次
Download:610次
 Download:610次
Download:610次In this paper, optical pulse repetition rate multiplication based on a series-coupled double-ring resonator is proposed. First, the spectral characteristic of the series-coupled double-ring resonator is simulated and the optimum coupling coefficients to achieve a periodic flat-top passband are obtained. Then, high-quality pulse repetition rate multiplication is realized by periodically filtering out spectral lines of the input pulse train. Different multiplication factors N = 2, 3, 4, 5 can be obtained by adjusting the ring radii. In addition, compared with a single-ring resonator, the multiplied output pulse train by a series-coupled double-ring resonator exhibits much better power uniformity.
Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Coupled resonators Coupled resonators Wavelength filtering devices Wavelength filtering devices Optical forces exerted on a graphene-coated dielectric particle by a focused Gaussian beam Download:958次
Download:958次
 Download:958次
Download:958次In this paper, we derive the analytical expression for the multipole expansion coefficients of scattering and interior fields of a graphene-coated dielectric particle under the illumination of an arbitrary optical beam. By using this arbitrary beam theory, we systematically investigate the optical forces exerted on the graphene-coated particle by a focused Gaussian beam. Via tuning the chemical potential of the graphene, the optical force spectra could be modulated accordingly at resonant excitation. The hybridized whispering gallery mode of the electromagnetic field inside the graphene-coated polystyrene particle is more intensively localized than the pure polystyreneparticle, which leads to a weakened morphology-dependent resonance in the optical forces. These investigations could open new perspectives for dynamic engineering of optical manipulations in optical tweezers applications.61475186, and 11434017).
Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Laser trapping Laser trapping Plasmonics Plasmonics Optical confinement and manipulation Optical confinement and manipulation We propose a depolarizer based on the principle of a collection of half-wave plates with randomly distributed optic axes. The design is demonstrated by means of dynamically photopatterning liquid crystal into randomly aligned homogeneous domains. We characterize the liquid crystal depolarizer for 1550 nm and C-band (1520–1610 nm). A degree of polarization of less than 5% is obtained for any linearly polarized light. This study provides a practical candidate for high-performance depolarizers.of China (NSFC) (Nos. 11304151, 61490714, 61435008 and 61575093).
Liquid-crystal devices Liquid-crystal devices Polarization Polarization Fiber optics Fiber optics infrared infrared Differential absorption lidar (DIAL) is an excellent technology for atmospheric CO2 detection. However, the accuracy and stability of a transmitted on-line wavelength are strictly required in a DIAL system. The fluctuation of a tunable pulsed laser system is relatively more serious than that of other laser sources, and this condition leads to a large measurement error for the lidar signal. These concerns pose a significant challenge in on-line wavelength calibration. This study proposes an alternative method based on wavelet modulus maxima for the accurate on-line wavelength calibration of a pulsed laser. Because of the different propagation characteristics of the wavelet transform modulus maxima between signal and noise, the singularities of a signal can be obtained by detection of the local modulus maxima in the wavelet transform maximum at fine scales. Simulated analysis shows that the method is more accurate than the general method such as quintic polynomial fitting and can steadily maintain high calibration precision at different signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). Last, 16 groups of real experiments were conducted to verify the simulated analysis, which shows that the proposed method is an alternative for accurately calibrating an on-line wavelength. In addition, the proposed method is able to suppress noises in the process of wavelength calibration, which gives it an advantage in accurate on-line wavelength calibration with a low SNR.Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042015kf0015).
Atmospheric optics Atmospheric optics Laser stabilization Laser stabilization DIAL DIAL differential absorption lidar differential absorption lidar We present a novel and simple method to obtain an ultrawide free spectral range (FSR) silicon ring resonator together with a tuning range covering the entire spectrum from 1500 to 1600 nm. A ring resonator with a large FSR together with a high Q factor, high tuning efficiency, and low fabrication cost and complexity is desired formany applications. In this paper, we introduce a novel way to make such a ring resonator, which takes advantage of the well-known resonance-splitting phenomenon. It is a single ring resonator with an FSR of more than 150 nm around 1550 nm and which has an easy thermo-optic tunability that can produce a tuning range around 90 nm or even more. Moreover, the device is simple to implement and can be fabricated in standard complementary metal-oxide semiconductor technology without requiring any kind of complicated processing or extra materials. The potential applications include single mode laser cavities, wavelength division multiplexing filters, (de)multiplexers, optical sensors, and integrated reflectors.
Resonators Resonators Wavelength filtering devices Wavelength filtering devices Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Optical sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Lasers Lasers single-mode single-mode We demonstrate the use of stochastic collocation to assess the performance of photonic devices under the effect of uncertainty. This approach combines high accuracy and efficiency in analyzing device variability with the ease of implementation of sampling-based methods. Its flexibility makes it suitable to be applied to a large range ofphotonic devices. We compare the stochastic collocation method with a Monte Carlo technique on a numerical analysis of the variability in silicon directional couplers.
Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Probability theory Probability theory stochastic processes stochastic processes and statistics and statistics Waveguides Waveguides 公告
动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-25
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 2): 封面|超紧凑片上偏振控制器动态信息 丨 2024-04-11
PR Highlight (Vol. 11, Iss. 12): 亮点 | 十亿像素级、高通量的无透镜偏振编码叠层成像技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 3): 封面 | 基于时空编码神经网络的像差感知超分辨成像动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 1) 光涡旋与手性器件微纳3D打印动态信息 丨 2024-03-14
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 1): 同步双脉冲激光烧蚀中的气泡相互作用效应激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦