短波紫外线的消杀机制与影响因素  下载: 615次
下载: 615次
UVC Sterilization Mechanism and Influencing Factors
中国矿业大学(北京)化学与环境工程学院,北京 100083
图 & 表
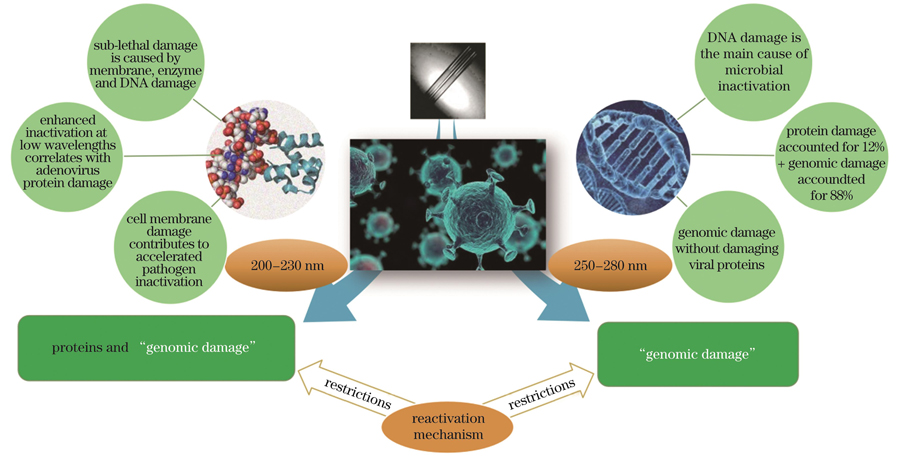
图 1. 短波紫外线的消杀机制
Fig. 1. Elimination mechanism of UVC
下载图片 查看原文
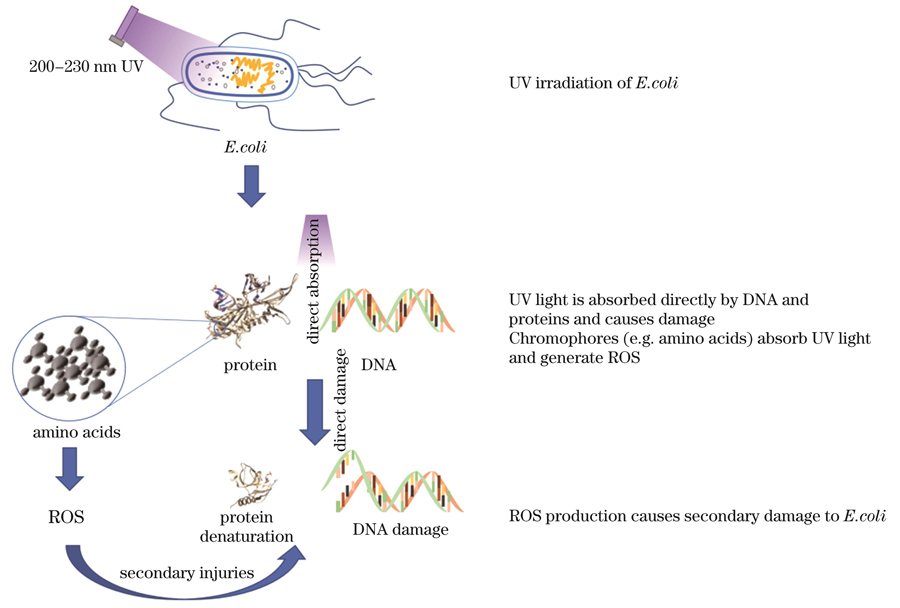
图 2. 200~230 nm紫外线消杀机制
Fig. 2. Killing mechanism of 200–230 nm ultraviolet ray
下载图片 查看原文
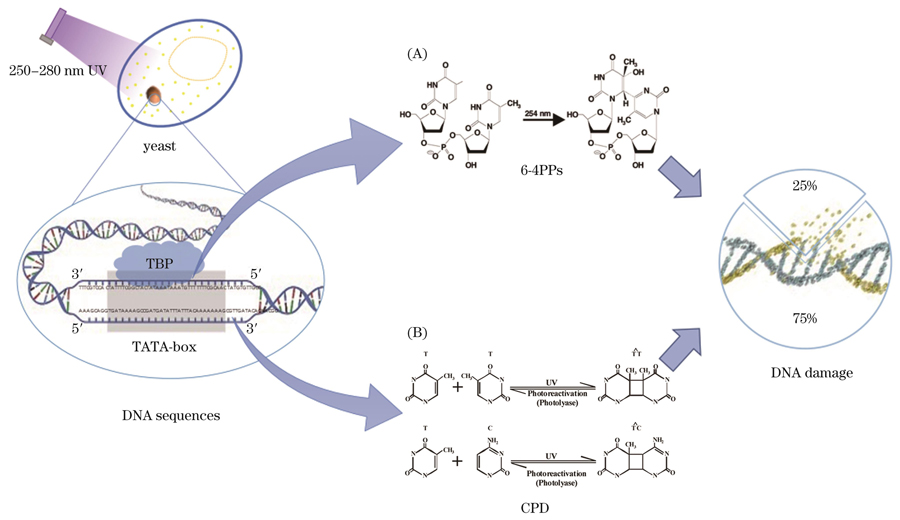
图 3. 250~280 nm紫外线消杀机制图[11]
Fig. 3. Killing mechanism diagram of 250-280 nm ultraviolet rays[11]
下载图片 查看原文
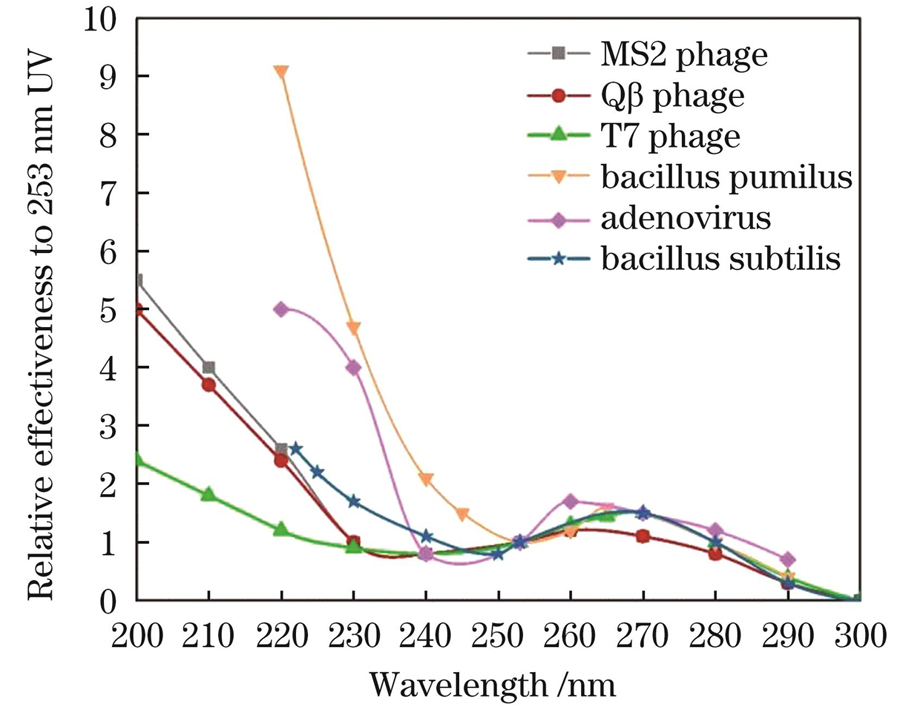
图 4. 不同微生物的杀菌作用光谱
Fig. 4. Bactericidal spectra of different microorganisms
下载图片 查看原文
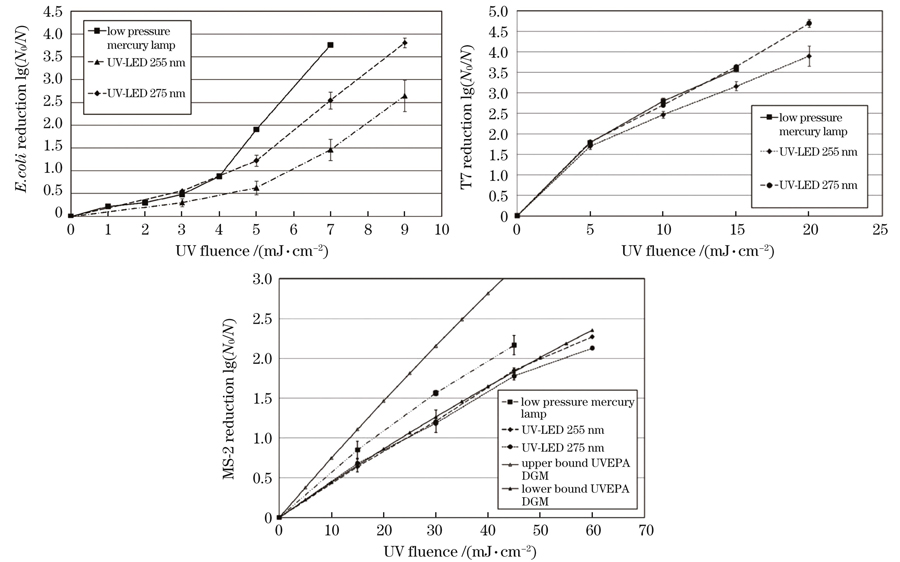
图 5. 紫外线辐照剂量与微生物灭活程度的关系图[41]
Fig. 5. Relationship between UV radiation dose and microbial inactivation degree[41]
下载图片 查看原文
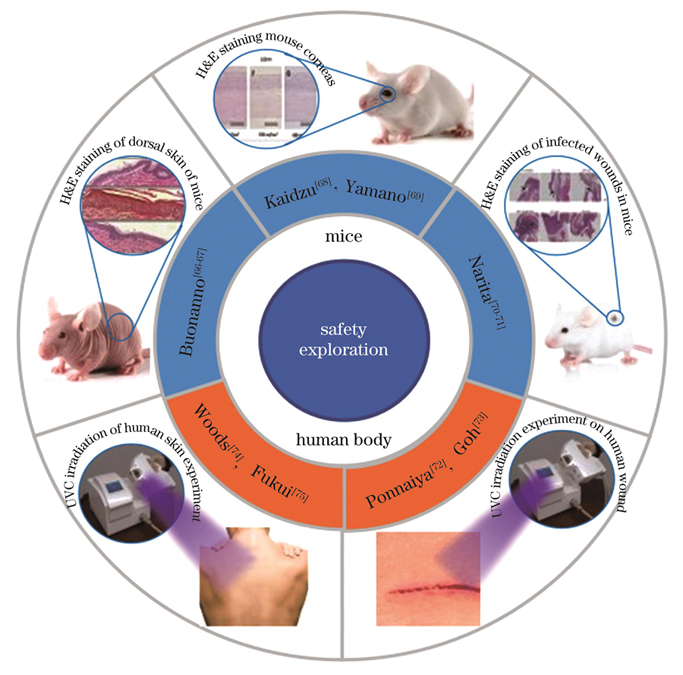
图 6. 短波紫外线消杀安全性
Fig. 6. Sterilization safety of UVC
下载图片 查看原文
表 1紫外线的分类
Table1. Classification of ultraviolet rays
| Classification | Wavelength /nm |
|---|
| Long-wave UV(UVA) | 315-400 | | Medium-wave UV(UVB) | 280-315 | | Short-wave UV(UVC) | 200-280 | | Vacuum UV(VUV) | 100-200 |
|
查看原文
表 2短波紫外线的消杀机制
Table2. Elimination mechanism of UVC
| No. | Research subject | UV wavelength /nm | Elimination mechanism | Reference |
|---|
| 1 | Adenovirus | 210-290 | DNA damage at 240–290 nm is the main cause of microbial inactivation,and the presence of components other than DNA damage below 240 nm leads to microbial inactivation | [13] | | 2 | Bacillus alicyclic acid | 275 | DNA damage is the main cause of microbial inactivation | [28] | | 3 | Foodborne pathogens and yeasts | 266-279 | DNA damage is the main cause of microbial inactivation | [29] | | 4 | MHV-A59 virus | 254 | Protein damage accounts for 12% and genomic damage accounts for 88% | [30] | | 5 | SARS-CoV-2 | 253.7 | Genomic damage without damaging viral proteins | [31] | | 6 | Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria | 222,254 | Sub-lethal damage from 254 nm low pressure mercury(LP Hg)lamp treatment is mainly due to DNA damage,while sub-lethal damage from 222 nm KrCl UV lamp treatment is due to membrane,enzyme,and DNA damage | [6] | | 7 | Salmonella Typhimurium and Lactobacillus monocytogenes | 280,222 | Cell membrane damage contributes to accelerated pathogen inactivation caused by combination therapy | [32] | | 8 | Foodborne pathogens | UVC and HClO | The mechanism of synergistic effects is related to membrane damage and,to a lesser extent,changes in membrane permeability | [33] | | 9 | Foodborne pathogens on the surface of cheese | 222 | The synergistic effect of outer membrane damage and lower photo-reactivation rate may cause an enhanced dissipative effect | [10] | | 10 | Adenovirus | 200-300 | Enhanced inactivation at low wavelengths correlates with adenovirus protein damage at these wavelengths | [16] | | 11 | E. coli O157:H7 | 222,282,and 254 | The higher elimination efficiency of 222 nm than 254 nm and 282 nm UV sources may be due to the damaged cell envelope | [34] |
|
查看原文
表 3短波紫外线在医疗方面上的应用
Table3. Short-wave UV for medical applications
| No. | Medical symptom | Whether it is better than traditional medical? | Illumination time | Whether it it safe? | Ref. |
|---|
| 1 | Herpes pharyngitis in children | Yes | Illumination 8-10 s | Yes | [54] | | 2 | Pediatric herpetic stomatitis | Yes | Once a day,4-6 s each time,for 5 d | Yes | [55] | | 3 | Mouth ulcers after chemotherapy for childhood leukemia | Yes | First irradiation 6 s,1 time per day | Yes | [56] | | 4 | Pediatric pneumonia | Yes | Increases with age,maximum time 5 s, | Yes | [57] | | 5 | Oral mucositis in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients | Yes | 6 s for the first irradiation,1 s for each increment,1 time per day | Yes | [58] | | 6 | Post-burn residual wounds | Yes | Irradiation 20-30 s | Yes | [59] | | 7 | Radioactive oral mucositis | Yes | First treatment 1-10 s,increasing by 1 s day by day | Yes | [60] | | 8 | Acute drug phlebitis | Yes | Irradiation for 10-20 s,1 time per day | Yes | [61] | | 9 | Oral mucositis after chemotherapy for ovarian cancer | Yes | Illumination 5-10 s | | [62] | | 10 | Oral mucositis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation | Yes | The first irradiation is 6 s,and each time increases by 1 s | | [63] | | 11 | Poor incision healing after cesarean section | Yes | Adjustment between 1 and 60 biological doses depending on the actual situation | | [64] | | 12 | Herpes zoster | Yes | Initial dose of 8-10 biological doses,followed by incremental increases of 20%-30% | | [65] |
|
查看原文
竹涛, 付顺江, 谢蔚, 徐欢. 短波紫外线的消杀机制与影响因素[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(9): 0907209. Tao Zhu, Shunjiang Fu, Wei Xie, Huan Xu. UVC Sterilization Mechanism and Influencing Factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(9): 0907209.
 下载: 615次
下载: 615次