光子学报, 2024, 53 (2): 0212002, 网络出版: 2024-03-28
基于温度场与D-Kalman参数估计的光学电压传感温度补偿方法
Temperature Compensation Method for Optical Voltage Sensing Based on Temperature Field and D-Kalman Parameter Estimation
光学电压传感器 温度稳定性 暂态温度场 卡尔曼滤波 中心差分卡尔曼滤波 Optical voltage sensor Temperature stability Transient temperature field Kalman filter Center differential Kalman filter
摘要
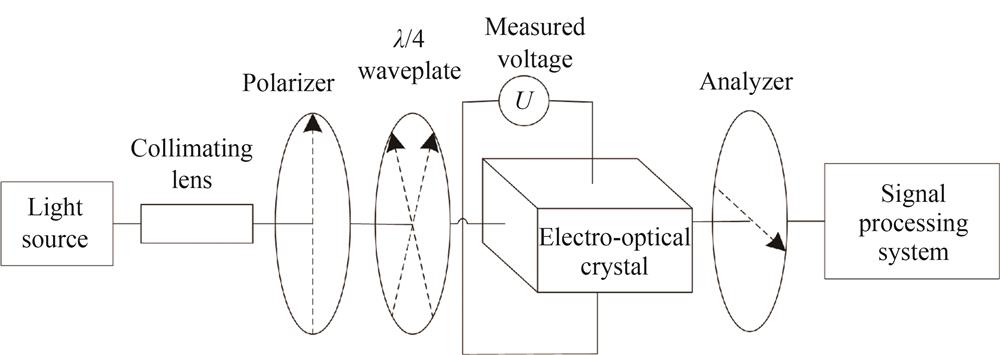
光学电压传感器在温度稳定性方面仍有亟待解决的问题,一是电光晶体在温度变化时存在温度梯度,导致表面温度与光路温度不等;二是晶体物性参数也会受到温度影响。为此提出一种基于温度场与双卡尔曼滤波(Dual Kalman,D-Kalman)参数估计的温度补偿方法。以锗酸铋晶体为研究对象,在对传感器输出信号进行交直流分离的基础上,先利用半解析法建立晶体暂态温度场模型,再分别通过卡尔曼滤波与中心差分卡尔曼滤波实现对晶体内部温度和初始温度下晶体折射率的状态估计,最后将修正参数与传感器输出信号高频分量相结合计算补偿电压。实验结果表明,传感器在外界温度为[20 ℃,40 ℃]以0.5 ℃/min速率不断升高的环境下,暂态温度场解析式的仿真精度在0.02%以内,实验测量精度在0.2%左右,补偿输出电压测量精度优于0.52%。与同平台下反向传播神经网络温度补偿效果以及不同平台下的补偿效果相比,该方法提高了传感器测量精度。
Abstract
Optical voltage sensors based on electro-optical materials have many advantages such as wide measurement band, fast response and small size, which can realize the non-contact measurement of grid voltage, and how to improve the measurement accuracy of optical voltage sensors has become an urgent problem. Temperature stability has become one of the important factors affecting the measurement accuracy of optical voltage sensors. When considering the effect of temperature on the sensing unit electro-optical crystal, two problems are faced: first, there is a temperature gradient in the electro-optical crystal when the temperature changes, resulting in unequal temperature between the crystal surface and the internal optical path; second, the physical parameters of the crystal are also affected by the temperature. Therefore, the bismuth germanate crystal is used as the research object in this paper, and the output response equation of the optical voltage sensor under multi-physics field is analyzed in combination with the previously derived one. In the output response equation, it is concluded that the temperature drift is a low-frequency component and the applied voltage is a high-frequency component, so that the output signal of the sensor is separated from the AC signals and DC signals. However, after adding the temperature variation parameter to the output response equation, the correction result shows that the temperature variation parameter and the refractive index parameter of the crystal affected by temperature also exist in the high-frequency component, so it is necessary to estimate the states of these two parameters. Considering that electro-optical crystals are optical materials, the internal temperature can not be measured directly by destroying the crystal, so it is necessary to establish a relationship between the surface temperature and the internal temperature to calculate the internal temperature indirectly. A semi-analytic method is first used to establish the crystal transient temperature field model, and the direct substitution of the measured surface temperature data to obtain the internal temperature will introduce a large amount of noise error, so the state estimation of the internal temperature of the crystal is realized by Kalman filtering. The refractive index parameters of the crystal queried through the literature are limited by light wavelength or temperature and can not be adapted to the time-varying environment. Therefore, the crystal refractive index at initial temperature is estimated by the central differential Kalman filter combined with the low frequency component of the sensor output signal. Finally, the compensation voltage is calculated by substituting the correction parameters into the high-frequency component of the sensor output signal. In summary, a temperature compensation method based on temperature field and dual Kalman filter parameter estimation is proposed. The experimental results show that the simulation accuracy of the transient temperature field resolution formula is within 0.02% and the experimental measurement accuracy is about 0.2% under the environment where the sensor is exposed to an external temperature of [20 ℃,40 ℃] at a heating rate of 0.5 ℃/min, which verifies the correctness of the transient temperature field model construction. The relative error of the refractive index parameters of the crystal obtained by the central differential Kalman filter is 0.017 6% compared with the calculated results in the literature. The accuracy of the output voltage measurement is better than 0.52% using two correction parameters to compensate. The method improves the sensor measurement accuracy compared with the temperature compensation effect of the Back Propagation Neural Network under the same platform and the temperature compensation effect in the relevant literature.
陈胜硕, 李岩松, 陈东旭, 康世佳, 许智光, 刘君. 基于温度场与D-Kalman参数估计的光学电压传感温度补偿方法[J]. 光子学报, 2024, 53(2): 0212002. Shengshuo CHEN, Yansong LI, Dongxu CHEN, Shijia KANG, Zhiguang XU, Jun LIU. Temperature Compensation Method for Optical Voltage Sensing Based on Temperature Field and D-Kalman Parameter Estimation[J]. ACTA PHOTONICA SINICA, 2024, 53(2): 0212002.