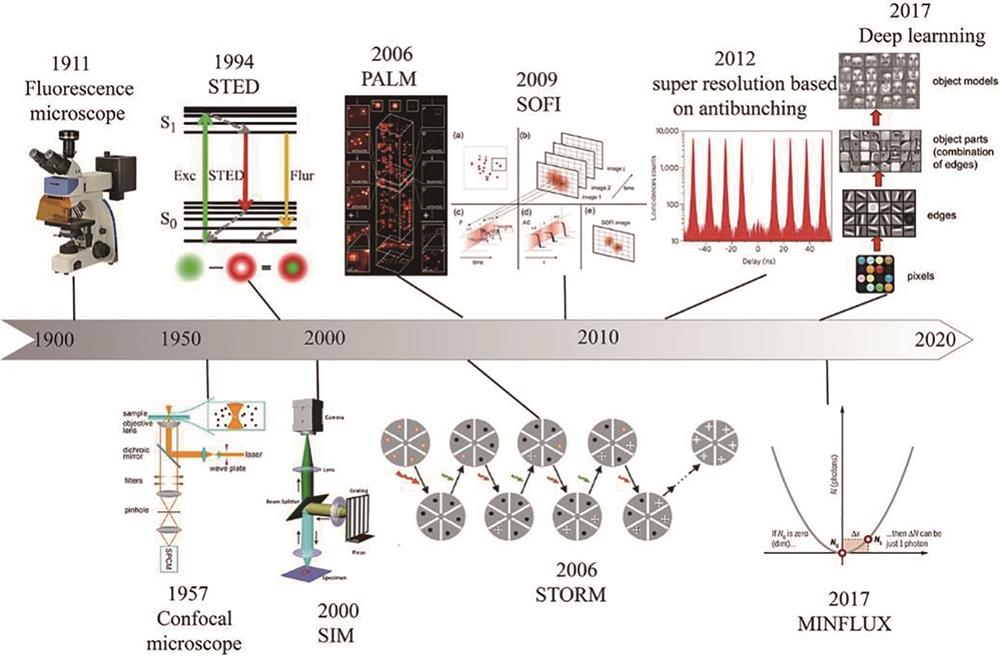
超分辨荧光显微成像的若干研究进展  下载: 650次特邀综述
下载: 650次特邀综述
卫奥尼, 秦成兵, 董帅, 孟新钦, 宋蕴睿, 李向东, 梁喜龙, 张国峰, 陈瑞云, 胡建勇, 杨志春, 霍建忠, 肖连团, 贾锁堂. 超分辨荧光显微成像的若干研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(11): 1106012.
Aoni Wei, Chengbing Qin, Shuai Dong, Xinqin Meng, Yunrui Song, Xiangdong Li, Xilong Liang, Guofeng Zhang, Ruiyun Chen, Jianyong Hu, Zhichun Yang, Jianzhong Huo, Liantuan Xiao, Suotang Jia. Research Progress of Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(11): 1106012.
[1] Lim C S, Kim E S, Kim J Y, et al. Measurement of the nucleus area and nucleus/cytoplasm and mitochondria/nucleus ratios in human colon tissues by dual-colour two-photon microscopy imaging[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-11.
[2] Kampmann M, Atkinson C E, Mattheyses A L, et al. Mapping the orientation of nuclear pore proteins in living cells with polarized fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2011, 18(6): 643-649.
[3] Okabe K, Inada N, Gota C, et al. Intracellular temperature mapping with a fluorescent polymeric thermometer and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3(1): 1-9.
[4] Summers P A, Lewis B W, Gonzalez-Garcia J, et al. Visualising G-quadruplex DNA dynamics in live cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1-11.
[5] Schermelleh L, Ferrand A, Huser T, et al. Super-resolution microscopy demystified[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2019, 21(1): 72-84.
[6] Abbe E. Beiträge zur theorie des mikroskops und der mikroskopischen wahrnehmung[J]. Archiv Für Mikroskopische Anatomie, 1873, 9(1): 413-418.
[7] Moerner W E, Kador L. Optical detection and spectroscopy of single molecules in a solid[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1989, 62(21): 2535-2538.
[8] Dickson R M, Cubitt A B, Tsien R Y, et al. On/off blinking and switching behaviour of single molecules of green fluorescent protein[J]. Nature, 1997, 388(6640): 355-358.
[9] Betzig E, Patterson G H, Sougrat R, et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5793): 1642-1645.
[10] Rust M J, Bates M, Zhuang X W. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM)[J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3(10): 793-796.
[11] Hell S W, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 1994, 19(11): 780-782.
[12] Gustafsson M G. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2000, 198(2): 82-87.
[13] Sigal Y M, Zhou R B, Zhuang X W. Visualizing and discovering cellular structures with super-resolution microscopy[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405): 880-887.
[14] Qiao C, Chen X Y, Zhang S W, et al. 3D structured illumination microscopy via channel attention generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2021, 27(4): 6801711.
[15] Vicidomini G, Bianchini P, Diaspro A. STED super-resolved microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(3): 173-182.
[16] Balzarotti F, Eilers Y, Gwosch K C, et al. Nanometer resolution imaging and tracking of fluorescent molecules with minimal photon fluxes[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6325): 606-612.
[17] Xiao J, Ha T. Flipping nanoscopy on its head[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6325): 582-584.
[18] Eilers Y, Ta H S, Gwosch K C, et al. MINFLUX monitors rapid molecular jumps with superior spatiotemporal resolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(24): 6117-6122.
[19] Gwosch K C, Pape J K, Balzarotti F, et al. MINFLUX nanoscopy delivers 3D multicolor nanometer resolution in cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(2): 217-224.
[20] Pape J K, Stephan T, Balzarotti F, et al. Multicolor 3D MINFLUX nanoscopy of mitochondrial MICOS proteins[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(34): 20607-20614.
[21] Masullo L A, Steiner F, Zähringer J, et al. Pulsed interleaved MINFLUX[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(1): 840-846.
[22] Schmidt R, Weihs T, Wurm C A, et al. MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1478.
[23] Masullo L A, Szalai A M, Lopez L F, et al. An alternative to MINFLUX that enables nanometer resolution in a confocal microscope[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2022, 11(1): 1-9.
[24] Masullo L A, Stefani F D. Multiphoton single-molecule localization by sequential excitation with light minima[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2022, 11(1): 1-4.
[25] Zhao K, Xu X Z, Ren W, et al. Two-photon MINFLUX with doubled localization precision[J]. eLight, 2022, 2(1): 1-10.
[26] Müller C B, Enderlein J. Image scanning microscopy[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(19): 198101.
[28] Cnossen J, Hinsdale T, Thorsen R Ø, et al. Localization microscopy at doubled precision with patterned illumination[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(1): 59-63.
[29] Weber M, Leutenegger M, Stoldt S, et al. MINSTED fluorescence localization and nanoscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(5): 361-366.
[30] Schnitzbauer J, Strauss M T, Schlichthaerle T, et al. Super-resolution microscopy with DNA-PAINT[J]. Nature Protocols, 2017, 12(6): 1198-1228.
[31] Ostersehlt L M, Jans D C, Wittek A, et al. DNA-PAINT MINFLUX nanoscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(9): 1072-1075.
[32] Dertinger T, Colyer R, Iyer G, et al. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(52): 22287-22292.
[33] Dertinger T, Colyer R, Vogel R, et al. Achieving increased resolution and more pixels with superresolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI)[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(18): 18875-18885.
[34] Geissbuehler S, Dellagiacoma C, Lasser T. Comparison between sofi and storm[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2011, 2(3): 408-420.
[35] Michalet X, Pinaud F F, Bentolila L A, et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5709): 538-544.
[36] Murray C B, Kagan C R, Bawendi M G. Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse nanocrystals and close-packed nanocrystal assemblies[J]. Annual Review of Materials Science, 2000, 30(1): 545-610.
[37] Zeng Z P, Chen X Z, Wang H N, et al. Fast super-resolution imaging with ultra-high labeling density achieved by joint tagging super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-7.
[38] Grußmayer K S, Geissbuehler S, Descloux A, et al. Spectral cross-cumulants for multicolor super-resolved SOFI imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-8.
[39] Uno S N, Kamiya M, Yoshihara T, et al. A spontaneously blinking fluorophore based on intramolecular spirocyclization for live-cell super-resolution imaging[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6(8): 681-689.
[40] Grußmayer K, Lukes T, Lasser T, et al. Self-blinking dyes unlock high-order and multiplane super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(7): 9156-9165.
[41] Dedecker P, Mo G C H, Dertinger T, et al. Widely accessible method for superresolution fluorescence imaging of living systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(27): 10909-10914.
[42] Glogger M, Spahn C, Enderlein J, et al. Multi-color, bleaching-resistant super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging with oligonucleotide-based exchangeable fluorophores[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2021, 60(12): 6310-6313.
[43] Kim M, Park C, Rodriguez C, et al. Superresolution imaging with optical fluctuation using speckle patterns illumination[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-10.
[44] Yi X Y, Son S, Ando R, et al. Moments reconstruction and local dynamic range compression of high order superresolution optical fluctuation imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2019, 10(5): 2430-2445.
[45] Geissbuehler S, Bocchio N L, Dellagiacoma C, et al. Mapping molecular statistics with balanced super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (bSOFI)[J]. Optical Nanoscopy, 2012, 1(1): 1-7.
[46] Dedecker P, Duwé S, Neely R K, et al. Localizer: fast, accurate, open-source, and modular software package for superresolution microscopy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2012, 17(12): 126008.
[47] Moeyaert B, Vandenberg W, Dedecker P. SOFIevaluator: a strategy for the quantitative quality assessment of SOFI data[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(2): 636-648.
[48] Girsault A, Lukes T, Sharipov A, et al. SOFI simulation tool: a software package for simulating and testing super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0161602.
[49] Geissbuehler S, Sharipov A, Godinat A, et al. Live-cell multiplane three-dimensional super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 1-7.
[51] Sroda A, Makowski A, Tenne R, et al. SOFISM: super-resolution optical fluctuation image scanning microscopy[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(10): 1308-1316.
[52] Aßmann M. Quantum-optically enhanced STORM (QUEST) for multi-emitter localization[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-12.
[53] Mo G C H, Ross B, Hertel F, et al. Genetically encoded biosensors for visualizing live-cell biochemical activity at super-resolution[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(4): 427-434.
[54] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L. Quantum-enhanced measurements: beating the standard quantum limit[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5700): 1330-1336.
[55] Brida G, Genovese M, Ruo Berchera I. Experimental realization of sub-shot-noise quantum imaging[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(4): 227-230.
[56] Tsang M. Quantum imaging beyond the diffraction limit by optical centroid measurements[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(25): 253601.
[57] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L, et al. Sub-Rayleigh-diffraction-bound quantum imaging[J]. Physical Review A, 2009, 79(1): 013827.
[58] D’Angelo M, Chekhova M V, Shih Y. Two-photon diffraction and quantum lithography[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 87(1): 013602.
[59] Walls D F, Zoller P. Reduced quantum fluctuations in resonance fluorescence[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1981, 47(10): 709-711.
[60] Mandel L. Sub-Poissonian photon statistics in resonance fluorescence[J]. Optics Letters, 1979, 4(7): 205-207.
[61] Senellart P, Solomon G, White A. High-performance semiconductor quantum-dot single-photon sources[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(11): 1026-1039.
[62] Kimble H J, Dagenais M, Mandel L. Photon antibunching in resonance fluorescence[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1977, 39(11): 691-695.
[63] Schwartz O, Oron D. Improved resolution in fluorescence microscopy using quantum correlations[J]. Physical Review A, 2012, 85(3): 033812.
[64] Schwartz O, Levitt J M, Tenne R, et al. Superresolution microscopy with quantum emitters[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(12): 5832-5836.
[65] Cui J M, Sun F W, Chen X D, et al. Quantum statistical imaging of particles without restriction of the diffraction limit[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(15): 153901.
[66] Monticone D G, Katamadze K, Traina P, et al. Beating the Abbe diffraction limit in confocal microscopy via nonclassical photon statistics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(14): 143602.
[67] Israel Y, Tenne R, Oron D, et al. Quantum correlation enhanced super-resolution localization microscopy enabled by a fibre bundle camera[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14786.
[68] Classen A, von Zanthier J, Scully M O, et al. Superresolution via structured illumination quantum correlation microscopy[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(6): 580-587.
[69] Tenne R, Rossman U, Rephael B, et al. Super-resolution enhancement by quantum image scanning microscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2019, 13(2): 116-122.
[70] Li W W, Wang Z Y. Breaking the diffraction limit using fluorescence quantum coherence[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(8): 12684-12694.
[71] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444.
[72] Alom M Z, Taha T M, Yakopcic C, et al. A state-of-the-art survey on deep learning theory and architectures[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(3): 292.
[73] Fukushima K. Neocognitron: a hierarchical neural network capable of visual pattern recognition[J]. Neural Networks, 1988, 1(2): 119-130.
[74] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144.
[75] Cheng J R, Yang Y, Tang X Y, et al. Generative adversarial networks: a literature review[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2020, 14(12): 4625-4647.
[76] RonnebergerO, FischerP, BroxT. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]∥Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W M, et al. Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention-MICCAI 2015. Lecture notes in computer science. Cham: Springer, 2015, 9351: 234-241.
[77] Rivenson Y, Göröcs Z, Günaydin H, et al. Deep learning microscopy[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(11): 1437-1443.
[78] Wang H D, Rivenson Y, Jin Y Y, et al. Deep learning enables cross-modality super-resolution in fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(1): 103-110.
[79] Zhang H, Fang C Y, Xie X L, et al. High-throughput, high-resolution deep learning microscopy based on registration-free generative adversarial network[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2019, 10(3): 1044-1063.
[80] Li X Y, Zhang G X, Qiao H, et al. Unsupervised content-preserving transformation for optical microscopy[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2021, 10(1): 1-11.
[81] Jin L H, Liu B, Zhao F Q, et al. Deep learning enables structured illumination microscopy with low light levels and enhanced speed[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-7.
[82] Qiao C, Li D, Guo Y T, et al. Evaluation and development of deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(2): 194-202.
[84] Zhang Q N, Chen J W, Li J S, et al. Deep learning-based single-shot structured illumination microscopy[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 155: 107066.
[85] Ouyang W, Aristov A, Lelek M, et al. Deep learning massively accelerates super-resolution localization microscopy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(5): 460-468.
[86] Gaire S K, Zhang Y, Li H Y, et al. Accelerating multicolor spectroscopic single-molecule localization microscopy using deep learning[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(5): 2705-2721.
[87] Speiser A, Müller L R, Hoess P, et al. Deep learning enables fast and dense single-molecule localization with high accuracy[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(9): 1082-1090.
[88] Nehme E, Weiss L E, Michaeli T, et al. Deep-STORM: super-resolution single-molecule microscopy by deep learning[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(4): 458-464.
[89] Fang L J, Monroe F, Novak S W, et al. Deep learning-based point-scanning super-resolution imaging[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(4): 406-416.
卫奥尼, 秦成兵, 董帅, 孟新钦, 宋蕴睿, 李向东, 梁喜龙, 张国峰, 陈瑞云, 胡建勇, 杨志春, 霍建忠, 肖连团, 贾锁堂. 超分辨荧光显微成像的若干研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(11): 1106012. Aoni Wei, Chengbing Qin, Shuai Dong, Xinqin Meng, Yunrui Song, Xiangdong Li, Xilong Liang, Guofeng Zhang, Ruiyun Chen, Jianyong Hu, Zhichun Yang, Jianzhong Huo, Liantuan Xiao, Suotang Jia. Research Progress of Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(11): 1106012.