Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Huawei Technologies Co, Ltd., Bantian Longgang District, Shenzhen 518129, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
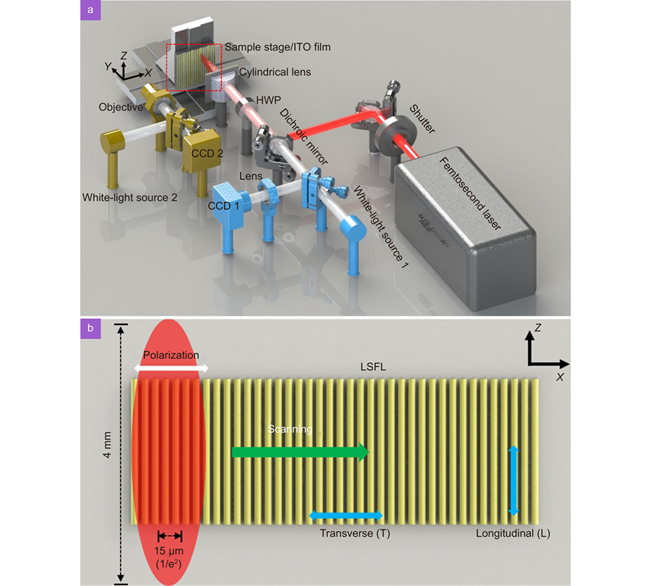
This paper reports the fabrication of regular large-area laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs) in indium tin oxide (ITO) films via femtosecond laser direct writing focused by a cylindrical lens. The regular LIPSSs exhibited good properties as nanowires, with a resistivity almost equal to that of the initial ITO film. By changing the laser fluence, the nanowire resistances could be tuned from 15 to 73 kΩ/mm with a consistency of ±10%. Furthermore, the average transmittance of the ITO films with regular LIPSSs in the range of 1200–2000 nm was improved from 21% to 60%. The regular LIPSS is promising for transparent electrodes of nano-optoelectronic devices—particularly in the near-infrared band.
transparent nanowires periodic surface nanostructures femtosecond laser direct writing ITO film anisotropic electrical conductivity Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(1): 220002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 Beijing Smart-chip Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing 100083, China
3 Zhongguancun Xinhaizeyou Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing 100049, China
4 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The silicon on glasses process is a common preparation method of micro-electro-mechanical system inertial devices, which can realize the processing of thick silicon structures. This paper proposes that indium tin oxides (ITO) film can serve as a deep silicon etching cut-off layer because ITO is less damaged under the attack of fluoride ions. ITO has good electrical conductivity and can absorb fluoride ions for silicon etching and reduce the reflection of fluoride ions, thus reducing the foot effect. The removal and release of ITO use an acidic solution, which does not damage the silicon structure. Therefore, the selection of the sacrificial layer has an excellent effect in maintaining the shape of the MEMS structure. This method is used in the preparation of MEMS accelerometers with a structure thickness of 100 μm and a feature size of 4 μm. The over-etching of the bottom of the silicon structure caused by the foot effect is negligible. The difference between the simulated value and the designed value of the device characteristic frequency is less than 5%. This indicates that ITO is an excellent deep silicon etch stopper material.The silicon on glasses process is a common preparation method of micro-electro-mechanical system inertial devices, which can realize the processing of thick silicon structures. This paper proposes that indium tin oxides (ITO) film can serve as a deep silicon etching cut-off layer because ITO is less damaged under the attack of fluoride ions. ITO has good electrical conductivity and can absorb fluoride ions for silicon etching and reduce the reflection of fluoride ions, thus reducing the foot effect. The removal and release of ITO use an acidic solution, which does not damage the silicon structure. Therefore, the selection of the sacrificial layer has an excellent effect in maintaining the shape of the MEMS structure. This method is used in the preparation of MEMS accelerometers with a structure thickness of 100 μm and a feature size of 4 μm. The over-etching of the bottom of the silicon structure caused by the foot effect is negligible. The difference between the simulated value and the designed value of the device characteristic frequency is less than 5%. This indicates that ITO is an excellent deep silicon etch stopper material.
SOG process DRIE cut-off layer ITO film foot effect Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(4): 044101
南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院, 江苏省能量转换材料与技术重点实验室, 南京 210016
结合反应离子刻蚀法和掩膜法在n型硅片表面制备出圆锥状结构黑硅, 利用湿法氧化法在硅片表面氧化出一层超薄SiOx, 采用磁控溅射法在其表面沉积一层掺锡氧化铟(IndiumTinOxide, ITO)薄膜, 在黑硅衬底上制备出ITO/SiOx/n-Si太阳电池。通过硅片表面纳米结构, 增加光吸收, 进而提高电池转化效率。研究结果表明, 在不同衬底温度下沉积ITO时, 薄膜都呈现出了良好的光学和电学性能.250 ℃时, ITO薄膜性能最优, 在400~1 000 nm波长范围内, 平均透过率达到93.1%, 并展现出优异的电学性能.通过优化H2O2预处理时间, 减小了SiOx层中氧空位缺陷, SIS电池短路电流得到明显提高, 从未处理前的26.84 mA/cm2提升到经H2O2处理15 min后的34.31 mA/cm2.此时, 电池性能最优, 转化效率达到3.61%.
光电材料 太阳能 磁控溅射 SIS太阳电池 黑硅 ITO薄膜 H2O2预处理 光电转化效率 Electro-optical materials Solar energy Magnetron sputtering SIS solar cell Black silicon ITO film H2O2 pretreatment Photoelectric conversion efficiency 光子学报
2017, 46(11): 1116002
1 南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院, 江苏省能量转换材料与技术重点实验室, 南京 210016
2 常州大学 江苏省光伏科学与工程协同创新中心, 江苏 常州 213164
室温下用射频磁控溅射法在玻璃和p型单晶硅衬底上沉积ITO薄膜, 并对其进行不同温度的退火处理。采用XRD衍射仪测试薄膜结晶性, 用紫外-可见分光光度计和霍尔效应测试试样光电性能, 用吉时利2400表测试ITO/p-Si接触的I-V曲线, 用线性传输线模型测试比接触电阻。研究结果表明: 室温下沉积的ITO薄膜与p-Si形成欧姆接触, 但比接触电阻较大。退火处理可以进一步优化接触性能, 200℃退火后试样保持欧姆接触且比接触电阻下降为8.8×10-3Ω·cm2。随着退火温度进一步升高到300℃, 比接触电阻达到最低值2.8×10-3Ω·cm2, 但接触性能变为非线性。
ITO薄膜 欧姆接触 p型单晶硅 退火 ITO film Ohmic contact p-type silicon annealing
1 发光学及应用国家重点实验室 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京100049
对于顶面出光的浅面浮雕VCSEL结构,有源区的电流密度分布的不均性制约着单模稳定性的提高。为此,提出了一种新型结构: 氧化铟锡透明导电薄膜(ITO)浅面浮雕VCSEL。该结构不仅能够增大高阶模式的阈值增益,还能够提高基模的增益,实现基模对高阶模式的稳定抑制。研究了ITO的厚度对阈值增益的影响及ITO对VCSEL有源区电流密度分布的影响。研究结果表明: 在ITO的厚度为半波长的整数倍时, 基模对高阶模式的限制作用最强; ITO通过改善VCSEL有源区的电流密度分布,达到了增大基模的增益和降低高阶模式增益的目的,同时还降低了串联电阻和外电压。
垂直腔面发射半导体激光器 透明导电薄膜 浅面浮雕 单模 VCSEL ITO film surface relief single mode
1 中国科学院国家天文台南京天文光学技术研究所, 江苏 南京 210042
2 中国科学院天文光学技术重点实验室,江苏 南京 210042
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
在极地环境(如南极Dome A)中的光学系统,氧化铟锡(ITO)薄膜加热除霜有突出的优势。简述了ITO 薄膜除霜原理,指出了目前采用的直流电、点状电极的加热设计存在局部过冷、电极过热、整体加热不均的情况,影响成像质量与除霜效果。给出了加热除霜效果的评估指标,提出了多相交流电、线状电极的新设计,并采用“主路径”分析法进行论证。然后以南极巡天望远镜(AST)为背景,对500 mm 口径镜面进行有限元模拟,在等功率条件下,对各加热设计进行评估。使用红外热像仪测量实际镜面:采用新设计后,镜面温度均方差降低了81.65%,峰谷值降低了76.31%。实验结果表明:新设计大幅提高了加热除霜的均匀性和效率,改善了视宁度,有望应用于南极光学望远镜工程中。
薄膜 南极光学望远镜 ITO 薄膜 多相交流电 镜面除霜
将直径为1.5 μm的透明球形微粒(SiO2), 通过自组装的方式在ITO玻璃上形成单层分布, 采用KrF准分子激光(λ=248 nm)进行单脉冲辐照。激光经过单层微粒在ITO薄膜表面得到增强, 在ITO上制备亚微米量级的孔状结构。通过扫描电镜(SEM)和原子力显微镜(AFM)分析评价辐照后样品表面微结构的质量, 用霍尔效应测试仪和分光光度计测试ITO的导电性和透光性。ITO上的亚微米阵列绒面结构使入射光透过率降低, 陷光作用增强。采用适当的激光能量密度(0.27~0.45 J/cm2)可在ITO上制备微孔结构, 同时不影响ITO薄膜本身优良的电学性能。而当能量密度较大时, 激光在与材料作用时产生的应力和热效应会对薄膜整体结构产生破坏, 孔状结构周围出现裂纹, 电阻率升高。
准分子激光 ITO薄膜 微结构 裂纹 excimer laser ITO film microstructure crack
上海大学微电子研究与开发中心, 上海 200072
薄膜式投射电容及玻璃式投射电容是投射电容式触控面板的两种主要技术。当前随着ITO Glass的供不应求,越来越多的厂商投身于ITO Film技术的开发与应用。文章主要介绍了两种投射电容式触控技术的现况、优缺点及未来市场发展趋势。
投射电容式 触控面板 projected capacitive touch panel ITO glass ITO Glass ITO film ITO Film
中国工程物理研究院流体物理研究所,四川 绵阳 621900
液晶光学器件中液晶分子的转动由施加在ITO薄膜电极间的电场来控制,ITO晶体结构中空穴和自由电子与强激光的相互作用,使ITO薄膜电极成为液晶光学器件结构中激光损伤的薄弱环节。为探索ITO薄膜电极的激光损伤机制,使用原子力显微镜(AFM)对厚度约为10nm的ITO薄膜的表面形貌进行了测量。采用多重分形理论,定量分析了薄膜表面粗糙度及微孔洞分布情况,对薄膜在脉冲宽度为10ns,能量分别为50mJ、100mJ、200mJ激光辐照下所获得薄膜的表面粗糙度分布情况进行比较分析,结果显示,随着激光功率的增加,多重分形谱的谱宽�SymbolDA@��SymbolaA@�呈增大趋势,且△f为负值,表明ITO薄膜表面粗糙度增大并形成微孔洞缺陷。
ITO薄膜 纳秒激光 多重分形 ITO film nano-second pulsed laser AFM AFM multi-fractal
1 安徽大学物理与材料科学学院, 安徽 合肥 230029
2 光电信息获取与控制教育部重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230039
3 安徽农业大学理学院, 安徽 合肥 230036
用溅射法在Si片上制备了厚度为140 nm的氧化铟锡(ITO)薄膜。X射线衍射研究表明所制备的薄膜为多晶结构。在1.5~4.5 eV范围内对ITO薄膜进行了椭偏测量。分别用德鲁德洛伦茨谐振子(Drude+Lorenz oscillators)模型、层进模型结合有效介质近似模型对椭偏参量ψ、Δ进行了拟合,得到ITO薄膜的折射指数n的变化范围在1.8~2.6之间,可见光范围内消光系数k接近于零,在350 nm波长附近开始明显变化,且随着波长的减小k迅速增加。计算得到直接和间接光学带隙分别是3.8 eV和4.2 eV。并在1.5~4.5 eV段给出一套较为可靠的、具有实用价值的ITO介电常量和光学常量。
薄膜光学 椭圆偏振术 光学常量测量 椭偏建模及解谱 ITO薄膜





