Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
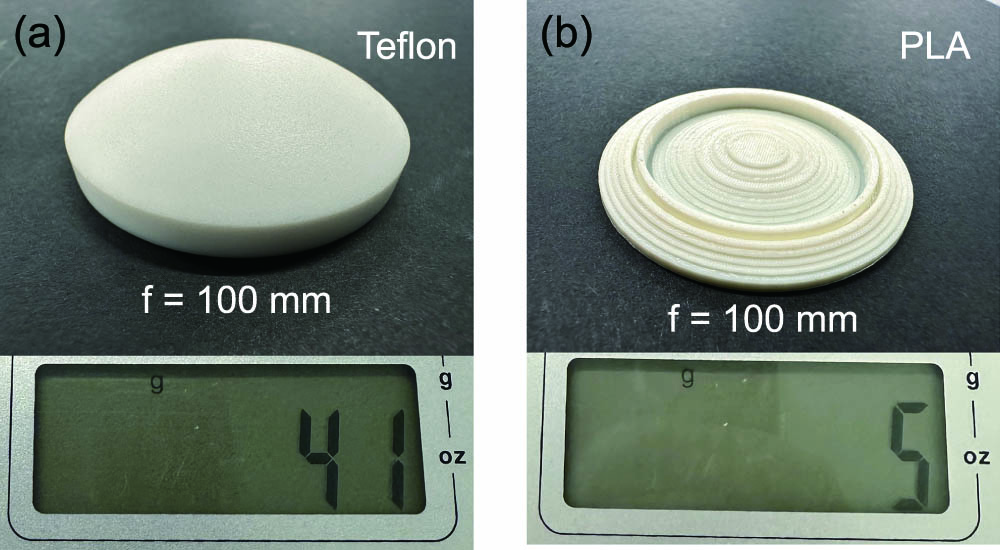
Terahertz (THz) lenses have numerous applications in imaging and communication systems. Currently, the common THz lenses are still based on the traditional design of a circular convex lens. In this work, we present a method for the design of a 3D-printed multilevel THz lens, taking advantage of the benefits offered by 3D printing technology, including compact size, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness. The approach utilizes an inverse design methodology, employing optimization methods to promise accurate performance. To reduce simulation time, we employ the finite-difference time-domain method in cylindrical coordinates for near-field computation and couple it with the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory to address far-field calculations. This technology holds great potential for various applications in the field of THz imaging, sensing, and communications, offering a novel approach to the design and development of functional devices operating in the THz frequency range.
THz lens 3D printing achromatic lens THz communication Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Sun Yat-sen University, School of Microelectronics Science and Technology, Zhuhai, China
2 Sun Yat-sen University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing Chips and Systems, Zhuhai, China
On-chip focusing of plasmons in graded-index lenses is important for imaging, lithography, signal processing, and optical interconnects at the deep subwavelength nanoscale. However, owing to the inherent strong wavelength dispersion of plasmonic materials, the on-chip focusing of plasmons suffers from severe chromatic aberrations. With the well-established planar dielectric grating, a graded-index waveguide array lens (GIWAL) is proposed to support the excitation and propagation of acoustic graphene plasmon polaritons (AGPPs) and to achieve the achromatic on-chip focusing of the AGPPs with a focus as small as about 2% of the operating wavelength in the frequency band from 10 to 20 THz, benefiting from the wavelength-independent index profile of the GIWAL. An analytical theory is provided to understand the on-chip focusing of the AGPPs and other beam evolution behaviors, such as self-focusing, self-collimation, and pendulum effects of Gaussian beams as well as spatial inversions of digital optical signals. Furthermore, the possibility of the GIWAL to invert spatially broadband digital optical signals is demonstrated, indicating the potential value of the GIWAL in broadband digital communication and signal processing.
achromatic lens self-focusing lens graded-index lens waveguide array broadband focusing graphene plasmon Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056003
1 江苏大学物理与电子工程学院, 江苏 镇江 212013
2 江苏大学京江学院, 江苏 镇江 212013
3 江苏大学机械工程学院, 江苏 镇江 212013
超构透镜作为一种灵活调控空间光场相位、振幅及偏振的有效选择,在超分显微成像中受到了广泛的关注。为了提高多波长显微成像的分辨率,解决传统光学系统结构厚重、设计复杂等问题,基于相位补偿理论,运用传输相位法以及粒子群优化算法,设计了一种基于二氧化钛纳米单元柱的反射式消色差超构透镜,在500~550nm之间实现了恒定聚焦,且该透镜具有偏振不敏感的特性。与数值孔径相同但有色散的超构透镜的对比结果有效证实了该超构透镜的消色差功能。所设计的透镜可应用于多波长显微成像系统中并提高成像的分辨率。此外,该消色差透镜在数码相机和光学仪器等领域中也有较好的应用价值。
光学设计 光学材料 超构透镜 消色差透镜 免偏振敏感 多波长 显微成像
1 湖北工业大学 机械工程学院, 武汉 430068
2 湖北省纤维检验局, 武汉 430060
依据标量衍射理论,在分析消除轴向及倍率色差条件的基础上, 利用纯相位液晶空间光调制器的可编程控制特性, 将红、绿、蓝三种色光调制的菲涅耳透镜与闪耀光栅镶嵌在一起, 通过随机等概率的复用方法, 在液晶空间光调制器上编程, 实现了具有共同焦距的三色光复用透镜, 消除了轴向色差.同时, 通过对红、绿、蓝三色光调制的菲涅耳透镜孔径的约束, 实现了三色光在焦平面处相同的聚焦光斑半径大小和强度, 消除了倍率色差.实验结果表明, 通过该方法, 复用透镜的轴向色差以及倍率色差都得到了有效矫正,在三色光入射下其艾里斑半径为67 pixel, 与具有相同焦距和分辨率的单色透镜产生的艾里斑半径65 pixel接近.
消色差透镜 空间光调制器 随机等概率 多波长复用 孔径约束 Achromatic lens Spatial light modulator Random equal probability Multi-wavelength multiplexing Aperture constraints
1 浙江工业大学理学院, 浙江 杭州 310023
2 浙江工业大学计算机学院, 浙江 杭州 310023
为实现基于Placido盘的角膜地形图仪中图像的有效采集, 根据人眼角膜的特点以及所选用的CCD面阵参数, 设计了一套对称式消色差物镜及准直照明透镜系统。利用初级像差理论及PW法计算成像镜头的初始结构, 根据近轴光线追迹公式计算准直照明透镜参数, 利用Zemax光学软件进行系统优化。成像镜头结构由2组4片镜片组成, 有效焦距为20 mm, 后工作距离为19.2 mm, 相对孔径为1/3, 全视场角为8°, 光学总长控制在20 mm以内。在镜头分辨率66 lp·mm-1处, 所有视场的调制传递函数值均大于0.3, 全视场畸变量小于0.5%。该系统具有整体结构简单、紧凑、易加工、成本低、成像质量好等特点, 其性能很好地满足了整机的要求。
光学设计 对称式消色差物镜 像差理论 角膜地形图仪 光学学报
2016, 36(12): 1222001
1 中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院 研究生院,北京 100039
3 吉林大学 电子科学与工程学院,吉林 长春 130012
设计并研制了一套可在视频监控和红光指示下实施半导体激光鼓膜造孔术的光学系统。首先,利用光束整形和波长合束技术将半导体激光单管出射的650 nm激光和半导体激光列阵出射的810 nm激光耦合到芯径为200 μm,数值孔径为0.22的光纤中; 然后,利用消色差透镜准直光纤出射的双波长激光,再利用另一个消色差透镜将光束聚焦到耳鼓膜上,该聚焦镜可通过机械部件沿光轴方向移动,从而调节鼓膜上光斑的大小; 成像部分则直接使用商用视频耳镜; 热反射镜用于使激光和成像光同轴。手术时,根据显示器上的红色指示光斑确定造孔位置。测量结果显示:该系统出光孔处的激光功率在0~13.3 W间连续可调,造孔直径在1~3 mm内连续可调。使用本系统可缩短手术时间,减少并发症; 儿童患者手术时无需全身麻醉。另外,该系统还具有整机体积小、重量轻、电光转换效率高等优点。
光纤耦合半导体激光器 激光鼓膜造孔术 红光指示 热反射镜 消色差透镜 fiber coupled diode laser diode laser myringotomy red laser pilot hot mirror achromatic lens





