Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Research Center for Intelligent Sensing, Zhejiang Lab, Hangzhou 311100, China
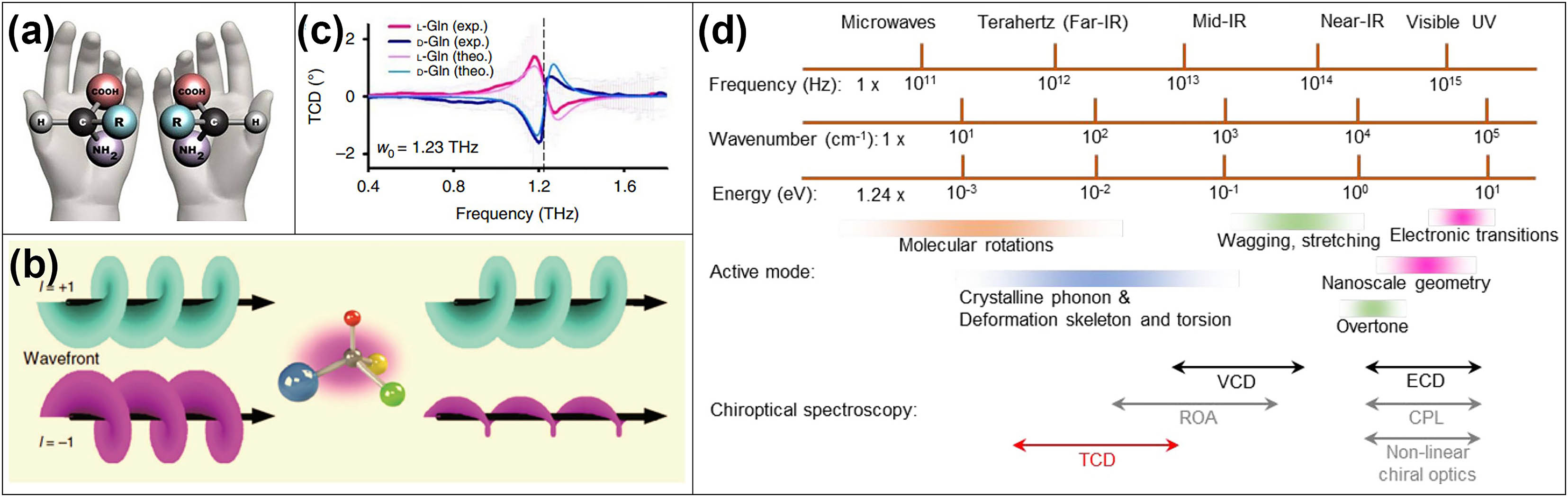
Specific and highly-sensitive biochemical detection technology is particularly important in global epidemics and has critical applications in life science, medical diagnosis, and pharmaceutics. As a newly developed technology, the THz metamaterial-based sensing method is a promising technique for extremely sensitive biomolecular detection. However, due to the significant resonant peaks generated by THz metamaterials, the characteristic absorption peaks of the analyte are usually masked, making it difficult to distinguish enantiomers and specifically identify target biomolecules. Recently, new ways to overcome this limitation have become possible thanks to the emergence of chiral metasurfaces and the polarization sensing method. Additionally, functionalized metasurfaces modified by antibodies or other nanomaterials are also expected to achieve specific sensing with high sensitivity. In this review, we summarize the main advances in THz metamaterials-based sensing from a historical perspective as well as application in chiral recognition and specific detection. Specifically, we introduce the basic theory and key technology of THz polarization spectrum and chiral sensing for biochemical detection, and immune sensing based on biomolecular interaction is also discussed. We mainly focus on chiral recognition and specific sensing using THz metasurface sensors to cover the most recent advances in the topic, which is expected to break through the limitations of traditional THz absorption spectroscopy and chiral spectroscopy in the visible-infrared band and develop into an irreplaceable method for the characterization of biochemical substances.
THz metamaterials polarization sensing technology specific sensing enhancement THz chiral spectrum biochemical substances detection Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 21(11): 110003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Nanophotonics Research Centre, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics & State Key Laboratory of Radio Frequency Heterogeneous Integration, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
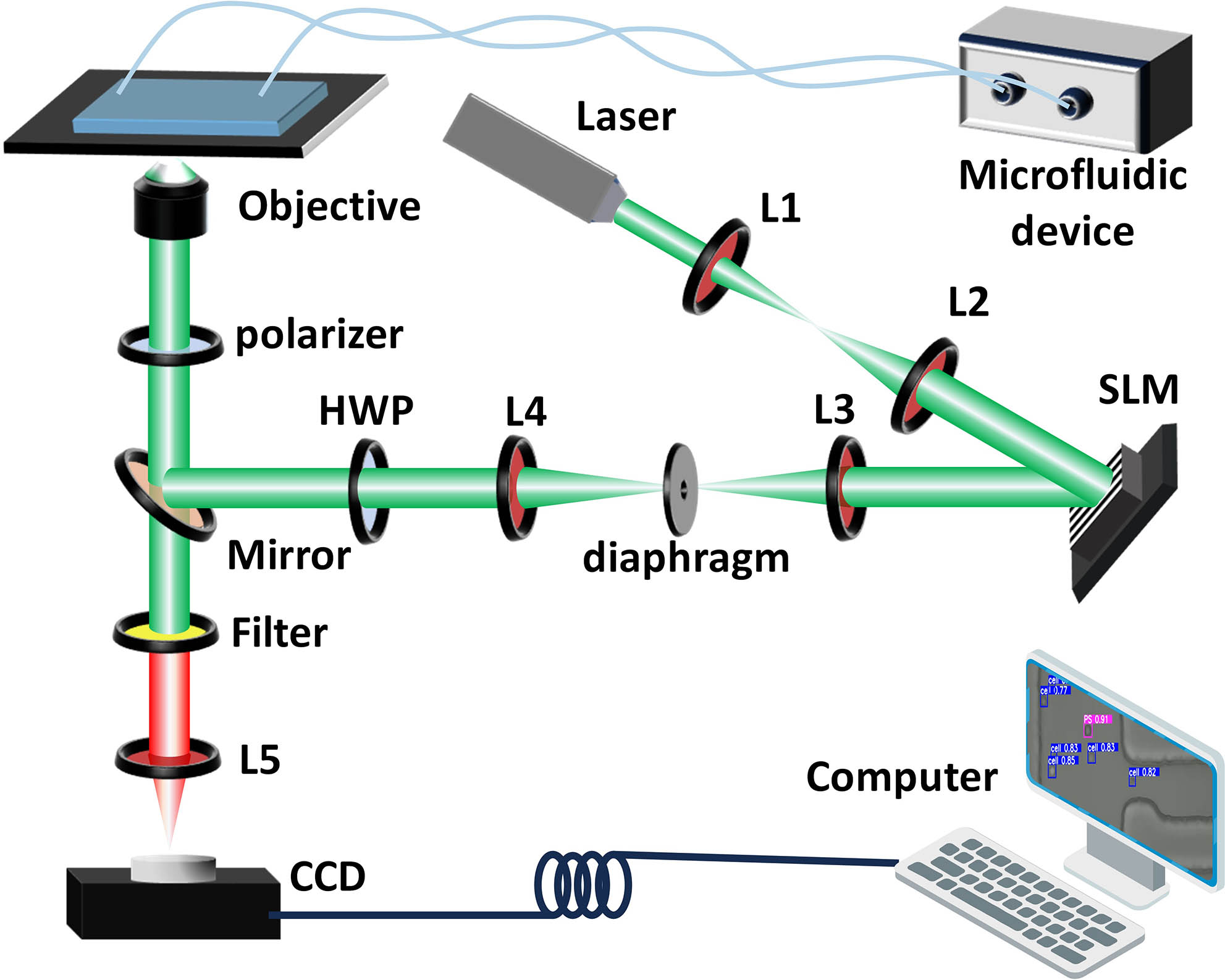
Cell identification and sorting have been hot topics recently. However, most conventional approaches can only predict the category of a single target, and lack the ability to perform multitarget tasks to provide coordinate information of the targets. This limits the development of high-throughput cell screening technologies. Fortunately, artificial intelligence (AI) systems based on deep-learning algorithms provide the possibility to extract hidden features of cells from original image information. Here, we demonstrate an AI-assisted multitarget processing system for cell identification and sorting. With this system, each target cell can be swiftly and accurately identified in a mixture by extracting cell morphological features, whereafter accurate cell sorting is achieved through noninvasive manipulation by optical tweezers. The AI-assisted model shows promise in guiding the precise manipulation and intelligent detection of high-flux cells, thereby realizing semi-automatic cell research.
AI algorithm cell identification and sorting optical tweezers microfluidic chip Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110009
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre for Micro Nano Systems, School of Information Science and Technology (SIST), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Zhangjiang Laboratory, Shanghai 201210, China
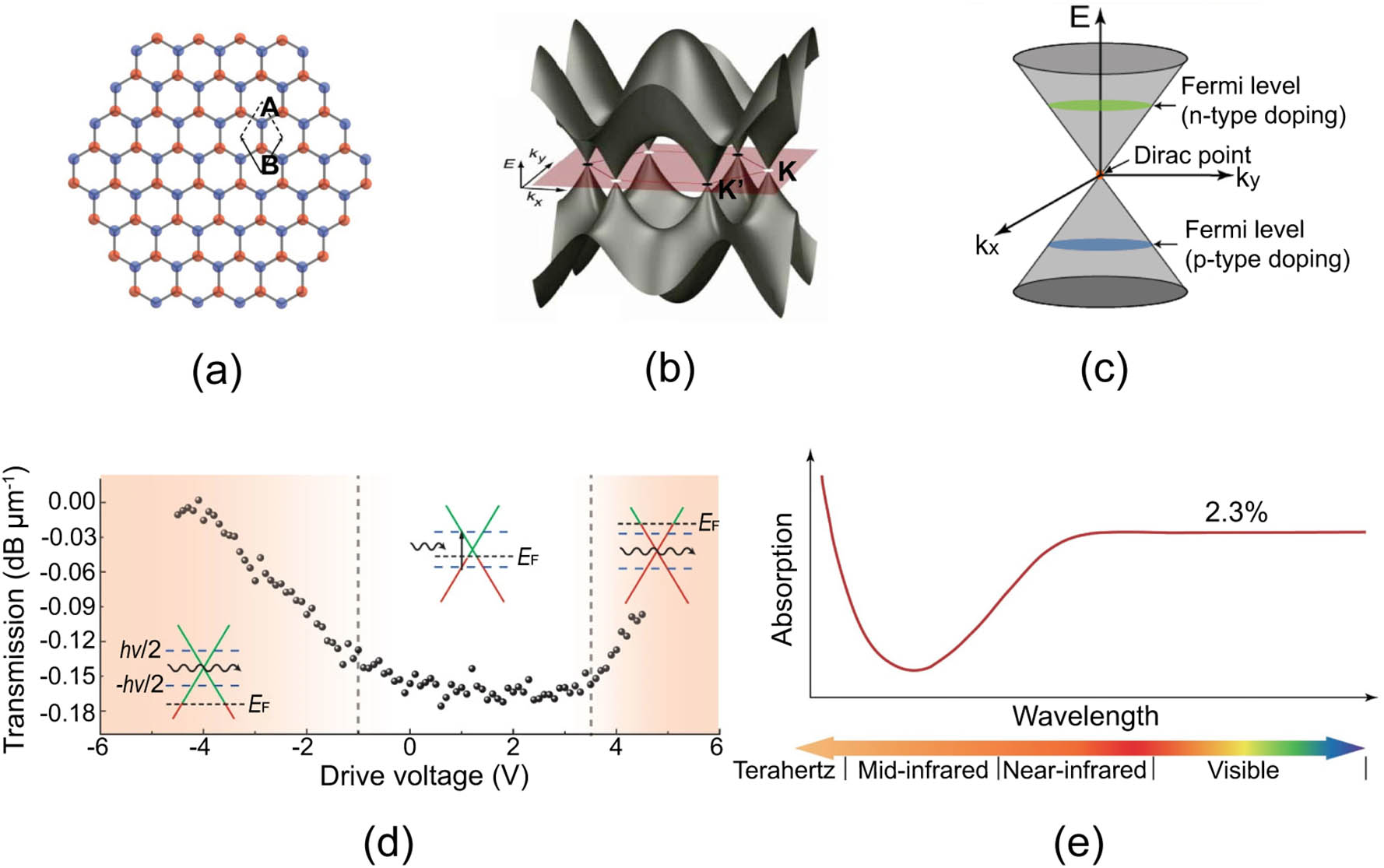
The heterogeneous integration of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) with a diverse range of optoelectronic materials has emerged as a transformative approach, propelling photonic chips toward larger scales, superior performance, and advanced integration levels. Notably, two-dimensional (2D) materials, such as graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), black phosphorus (BP), and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), exhibit remarkable device performance and integration capabilities, offering promising potential for large-scale implementation in PICs. In this paper, we first present a comprehensive review of recent progress, systematically categorizing the integration of photonic circuits with 2D materials based on their types while also emphasizing their unique advantages. Then, we discuss the integration approaches of 2D materials with PICs. We also summarize the technical challenges in the heterogeneous integration of 2D materials in photonics and envision their immense potential for future applications in PICs.
two-dimensional materials silicon photonics heterogeneous integration photonic integrated circuits Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
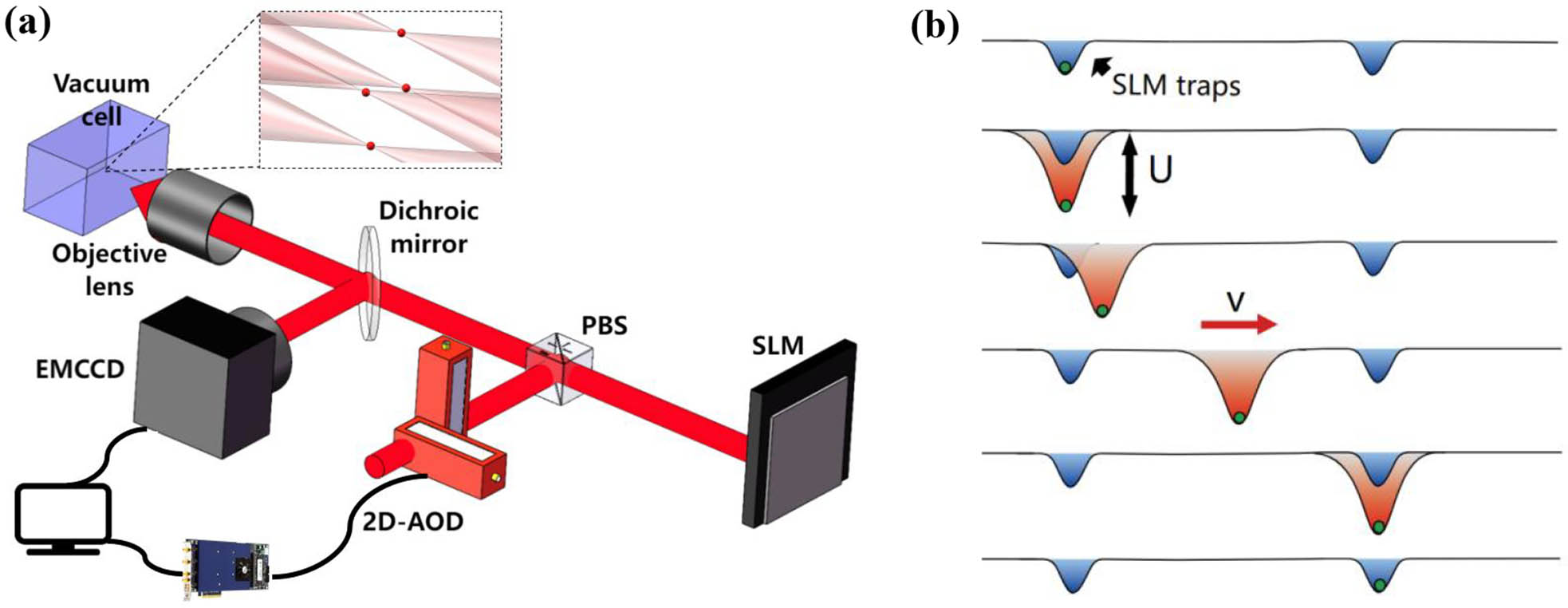
The defect-free neutral atom array has emerged as an ideal platform to investigate complex many-body physics of interacting quantum particles, offering the opportunities for quantum simulation and quantum-enhanced metrology. To fast build a large-scale quantum system, we design a sorting-atom algorithm with maximum parallelisms. Compared with previous protocols, our method saves the rearrangement time by sorting row-by-row and is also universal to arbitrary periodic patterns with no need to change the hardware. We present the generation of a defect-free square and other periodic geometries and demonstrate the potential to scale up a defect-free array to 2500 atoms with only about 180 steps of rearrangement.
optical tweezer defect-free atomic array Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110010
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
Broadband mode converters are essential devices for space-division and wavelength-division multiplexing systems. There are great challenges in the generation of higher-order modes above the third order with low loss and high mode purity employing all-fiber devices. In this paper, an all-fiber LP41 mode converter is proposed and fabricated by tapering a nine-core single-mode fiber bundle. Experimental results indicate that this all-fiber LP41 mode converter is low-loss, high-purity, and ultrabroadband. The insertion loss is less than 0.4 dB. The purity of odd LP41 at 1310 nm is 95.09%, and the operating bandwidth exceeds 280 nm.
photonic lantern mode converter space-division multiplexing Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110008
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
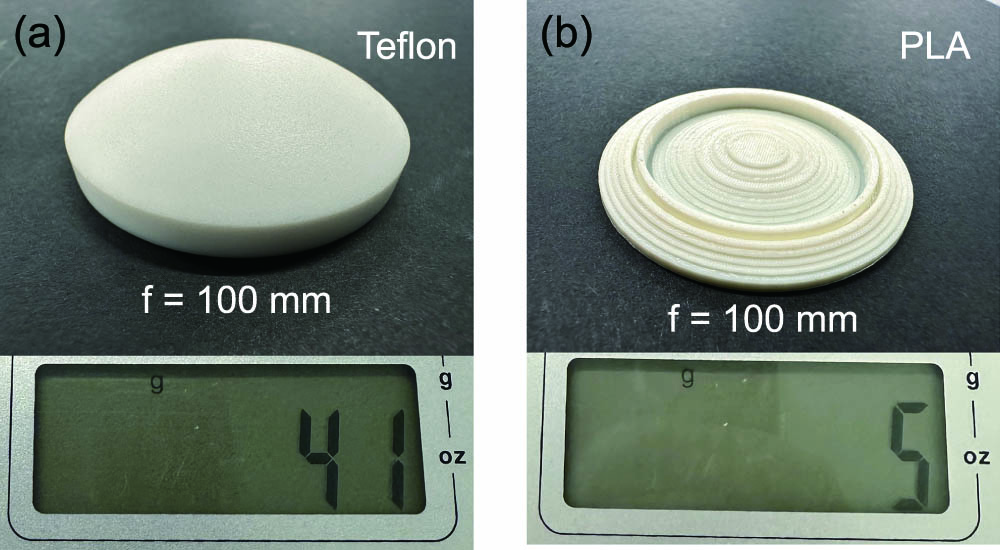
Terahertz (THz) lenses have numerous applications in imaging and communication systems. Currently, the common THz lenses are still based on the traditional design of a circular convex lens. In this work, we present a method for the design of a 3D-printed multilevel THz lens, taking advantage of the benefits offered by 3D printing technology, including compact size, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness. The approach utilizes an inverse design methodology, employing optimization methods to promise accurate performance. To reduce simulation time, we employ the finite-difference time-domain method in cylindrical coordinates for near-field computation and couple it with the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld diffraction theory to address far-field calculations. This technology holds great potential for various applications in the field of THz imaging, sensing, and communications, offering a novel approach to the design and development of functional devices operating in the THz frequency range.
THz lens 3D printing achromatic lens THz communication Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110006
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Terahertz Technology Innovation Research Institute, Terahertz Spectrum and Imaging Technology Cooperative Innovation Center, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Tera Aurora Electro-optics Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200093, China
4 Shanghai Institute of Intelligent Science and Technology, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
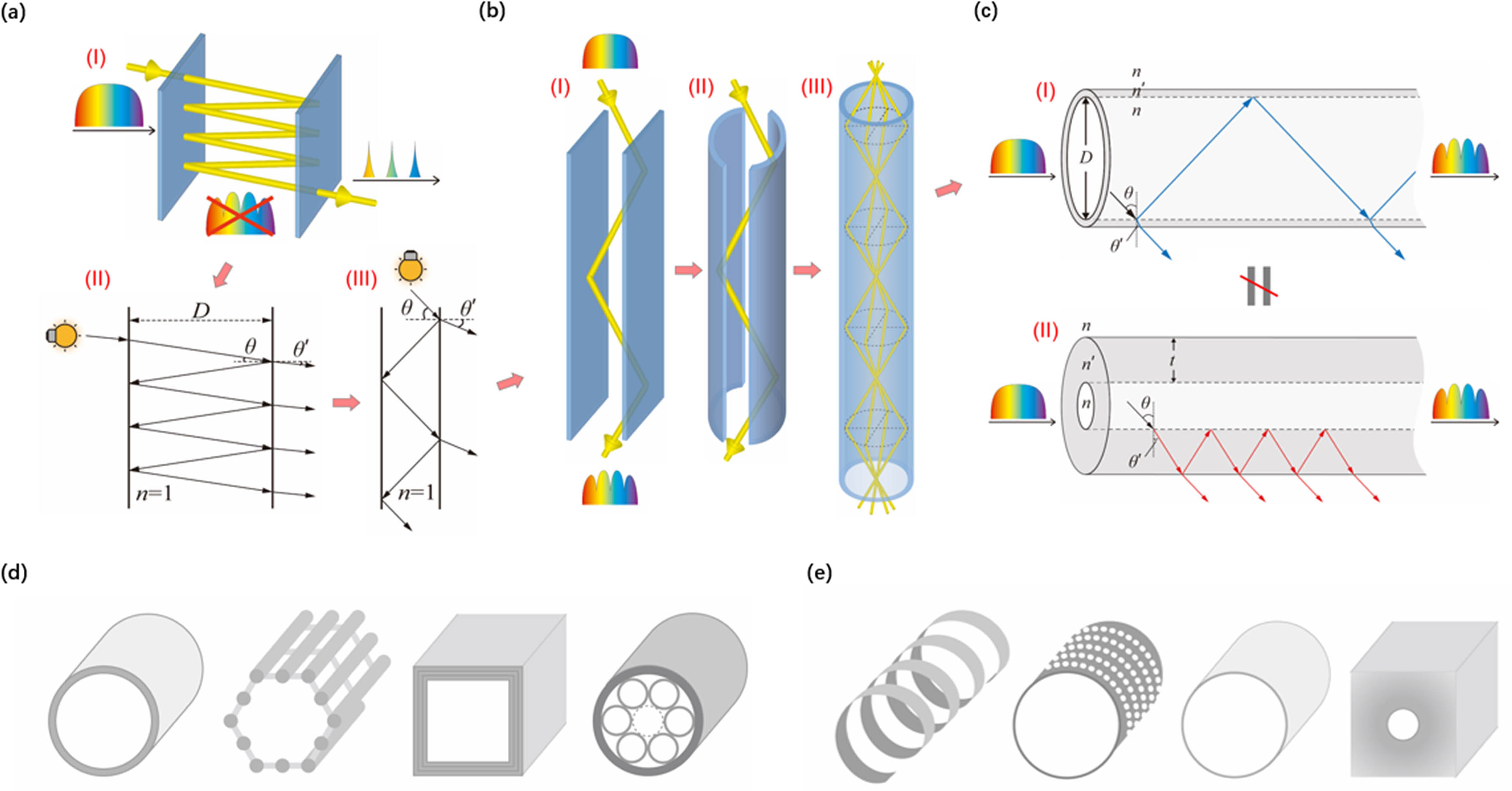
This work presents a brief review of our recent research on an antiresonant mechanism named core antiresonant reflection (CARR), which leads to a broadband terahertz (THz) spectrum output with periodic dips at resonant frequencies after its transmission along a hollow-core tubular structure (e.g., a paper tube). The CARR theory relies only on parameters of the tube core (e.g., the inner diameter) rather than the cladding, thus being distinct from existing principles such as the traditional antiresonant reflection inside optical waveguides (ARROWs). We demonstrate that diverse tubular structures, including cylindrical, polyhedral, spiral, meshy, and notched hollow tubes with either transparent or opaque cladding materials, as well as a thick-walled hole, could indeed become CARR-type resonators. Based on this CARR effect, we also perform various applications, such as pressure sensing with paper-folded THz cavities, force/magnetism-driven chiral polarization modulations, and single-pulse measurements of the angular dispersion of THz beams. In future studies, the proposed CARR method promises to support breakthroughs in multiple fields by means of being extended to more kinds of tubular entities for enhancing their interactions with light waves in an antiresonance manner.
antiresonance core cladding tubular structure application Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Eye Institute, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
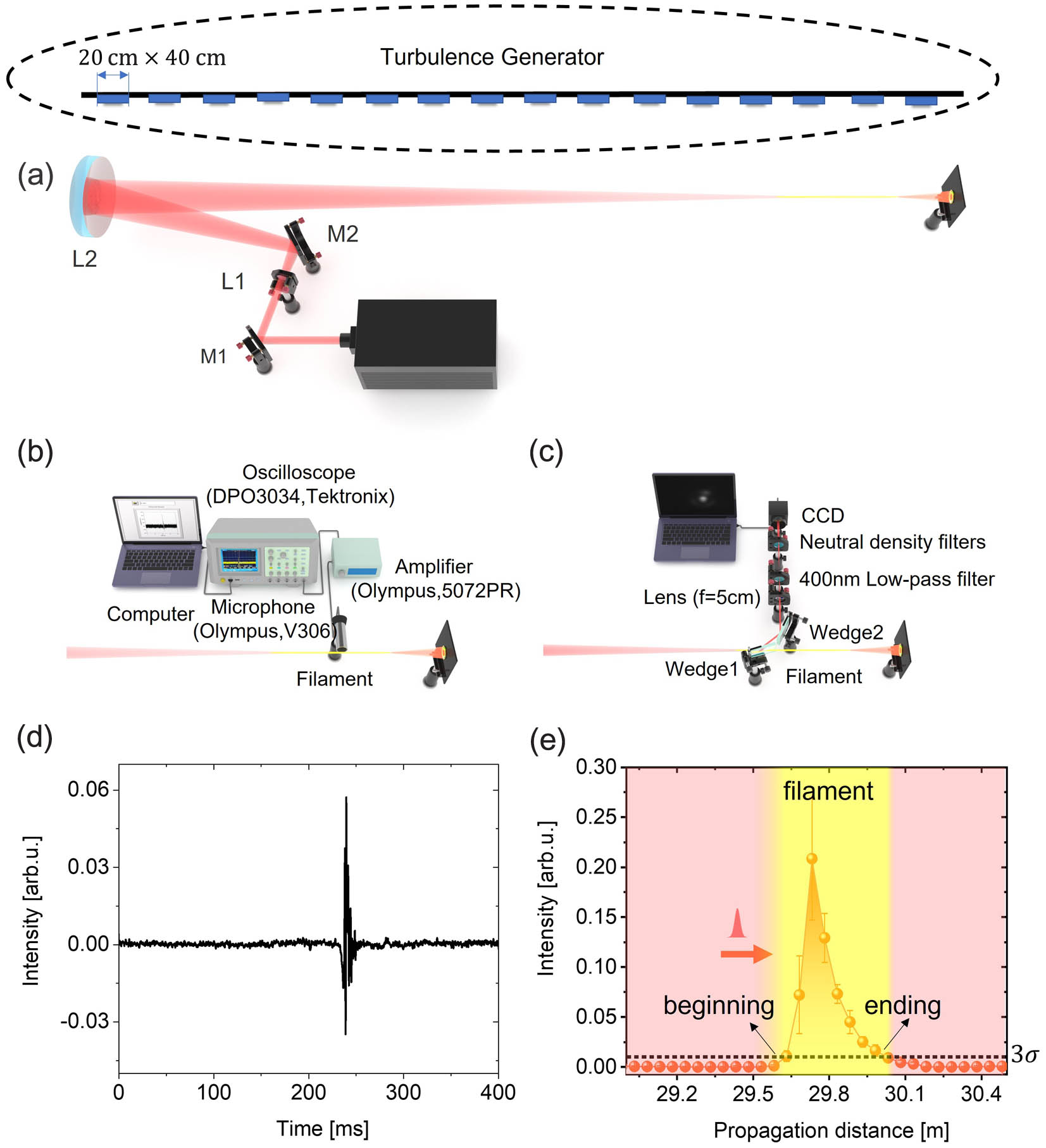
The effects of turbulence intensity and turbulence region on the distribution of femtosecond laser filaments are experimentally elaborated. Through the ultrasonic signals emitted by the filaments, it is observed that increasing turbulence intensity and an expanding turbulence active region cause an increase in the start position of the filament and a decrease in filament length, which can be well explained by theoretical calculation. It is also observed that the random perturbation of the air refractive index caused by atmospheric turbulence expands the spot size of the filament. Additionally, when the turbulence refractive index structure constant reaches , multiple filaments are formed. Furthermore, the standard deviation of the transverse displacement of filament is found to be proportional to the square root of the turbulent structure constant under the experimental turbulence parameters in this paper. These results contribute to the study of femtosecond laser propagation mechanisms in complex atmospheric turbulence conditions.
femtosecond laser filamentation turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Ultrafast Laser Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Technical Science of Ministry of Education, School of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
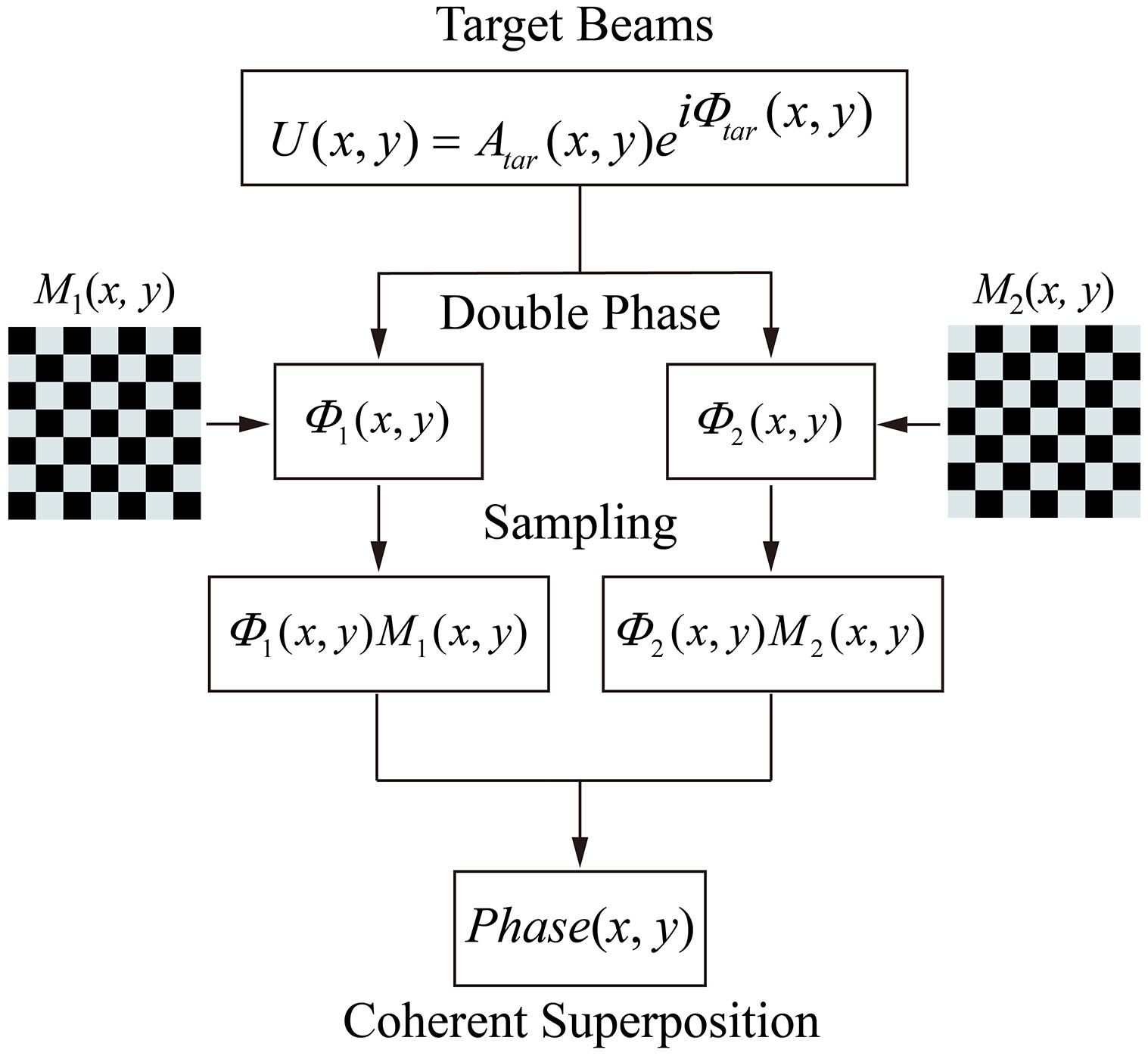
The manipulation of structured light beams requires simultaneous spatial modulation of amplitude and phase. Based on the double-phase holography (DPH) algorithm, we demonstrate an efficient reconstruction of Bessel beams with arbitrary on-axis intensity. Also, the off-axis DPH method enables more than doubled laser energy utilization compared with the widely-used off-axis phase wrapping modulation method. The DPH algorithm is also used in two-photon polymerization to enable the rapid fabrication of microtube arrays, ortho-hexagonal scaffolds, and 2D patterned microstructures. This work gives experimental proof to show the powerful feasibility of the DPH method in constructing economic adaptive laser processing systems.
double-phase hologram structured beam two-photon polymerization Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110002





