
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong University, Center for Optics Research and Engineering, Qingdao, China
2 Shandong University, Key Laboratory of Laser and Infrared System of the Ministry of Education, Qingdao, China
3 Shandong University, School of Information Science and Engineering, Qingdao, China
4 National Research Council Canada, Ottawa, Canada
5 University of Ottawa, Physics Department, Ottawa, Canada
The optical rogue wave (RW), known as a short-lived extraordinarily high amplitude dynamics phenomenon with small appearing probabilities, plays an important role in revealing and understanding the fundamental physics of nonlinear wave propagations in optical systems. The random fiber laser (RFL), featured with cavity-free and “modeless” structure, has opened up new avenues for fundamental physics research and potential practical applications combining nonlinear optics and laser physics. Here, the extreme event of optical RW induced by noise-driven modulation instability that interacts with the cascaded stimulated Brillouin scattering, the quasi-phase-matched four-wave mixing as well as the random mode resonance process is observed in a Brillouin random fiber laser comb (BRFLC). Temporal and statistical characteristics of the RWs concerning their emergence and evolution are experimentally explored and analyzed. Specifically, temporally localized structures with high intensities including chair-like pulses with a sharp leading edge followed by a trailing plateau appear frequently in the BRFLC output, which can evolve to chair-like RW pulses with adjustable pulse duration and amplitude under controlled conditions. This investigation provides a deep insight into the extreme event of RWs and paves the way for RW manipulation for its generation and elimination in RFLs through adapted laser configuration.
optical rogue wave modulation instability random fiber laser cascaded stimulated Brillouin scattering four-wave mixing temporally localized structure Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(2): 026008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronics Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
2 Institute for Advanced Study, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
3 Fiber Optics Research Centre, School of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
4 Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife-PE, Brazil
5 Email: hejingsong@szu.edu.cn
High-intensity vortex beams with tunable topological charges and low coherence are highly demanded in applications such as inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and optical communication. However, traditional optical vortices featuring nonuniform intensity distributions are dramatically restricted in application scenarios that require a high-intensity vortex beam owing to their ineffective amplification resulting from the intensity-dependent nonlinear effect. Here, a low-coherence perfect vortex beam (PVB) with a topological charge as high as 140 is realized based on the super-pixel wavefront-shaping technique. More importantly, a globally adaptive feedback algorithm (GAFA) is proposed to efficiently suppress the original intensity fluctuation and achieve a flat-top PVB with dramatically reduced beam speckle contrast. The GAFA-based flat-top PVB generation method can pave the way for high-intensity vortex beam generation, which is crucial for potential applications in ICF, laser processing, optical communication and optical trapping.
digital micromirror device flat-top beam orbital angular momentum perfect vortex beam random fiber laser High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2024, 12(1): 010000e5
1 北京信息科技大学 光电测试技术及仪器教育部重点实验室
2 北京信息科技大学 光纤传感与系统北京实验室,北京 100016
提出了一种基于M-Z结构的可调谐掺铒光纤随机激光器,并对随机激光输出过程、随机激光的波长可调谐输出以及随机激光的稳定性进行了实验研究。通过采用光纤熔接手段将两个2×2光纤耦合器进行熔接,构成全光纤M-Z滤波结构。实验结果表明,激光器的阈值功率为120 mW,调整可调谐衰减器改变增益损耗,实现波长可调谐输出,其中单波长输出分别为1 554.4,1 555.2和1 556.3 nm,信噪比达到31.65 dB;双波长输出分别为1 525.9,1 556.2和1 531.6,1 556.2 nm,信噪比优于21.92 dB;三波长输出分别为1 527.4,1 546.9,1 551.6和1 526.9,1 530.0,1 549.8 nm,信噪比优于20.10 dB;四波长输出为1 525.9,1 530.1,1 547.9和1 552.3 nm,信噪比优于18.95 dB;其中单波长和双波长的功率波动分别优于1.65和1.99 dB;激光器斜率效率为0.627%。
光纤随机激光 掺铒光纤 波长可调谐 random fiber laser erbium doped fiber M-Z M-Z wavelength tunable

Li Jiang 1,2,3Jinming Wu 1,2,3Rui Song 1,2,3,*Zilun Chen 1,2,3[ ... ]Jing Hou 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China
2 Nanhu Laser Laboratory, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China
3 Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Energy Laser Technology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China
The random distributed-feedback fiber laser (RFL) is a new approach to obtain a high-power stable supercontinuum (SC) source. To consider both structure simplification and high-power SC output, an innovative structure achieving a kilowatt-level SC output in a single-stage RFL with a half-open cavity is demonstrated in this paper. It consists of a fiber oscillator, a piece of long passive fiber and a broadband coupler, among which the broadband coupler acting as a feedback device is crucial in SC generation. When the system has no feedback, the backward output power is up to 298 W under the pump power of 1185 W. When the feedback is introduced before the pump laser, the backward power loss can be reduced and the pump can be fully utilized, which could promote forward output power and conversion efficiency significantly. Under the maximum pump power of 1847 W, a 1300 W SC with spectrum ranging from 887 to 1920 nm and SC conversion efficiency of 66% is obtained. To the best of our knowledge, it is the simplest structure used for high-power SC generation, and both the generated SC output power and the conversion efficiency are highest in the scheme of the half-opened RFL output SC.
high conversion efficiency high-power supercontinuum random fiber laser single-stage structure High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(6): 06000e80
1 深圳大学微纳光电子学研究院二维材料光电科技国际合作联合实验室,广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳技术大学工程物理学院,广东 深圳 518118
3 深圳大学物理与光电工程学院光纤传感技术粤港联合研究中心,广东 深圳 518060
1.7 μm激光处于眼安全波段并位于许多重要气体分子的指纹吸收峰,在生物医疗、气体传感等领域具有重要应用价值。而涡旋光束作为一种新兴的结构光场,其具有环形光强分布和螺旋相位波前,并携带轨道角动量,在光通信、微粒操控等领域应用广泛。因此发展1.7 μm高能涡旋激光器具有重要的研究价值和应用前景。但传统稀土离子掺杂光纤或晶体的发射谱,或难以覆盖该波段,或在该波段激光增益较小,且涡旋光产生主要基于空间光结构,导致1.7 μm波段涡旋光激光系统复杂、集成度低,难以实现高功率输出。本文利用螺旋长周期光纤光栅作为涡旋模式转换器,在基于受激拉曼散射效应的1.7 μm波段光纤随机激光半开放腔中实现了全光纤结构的高功率涡旋激光输出,最大输出功率为2.09 W,中心波长为1690 nm。得益于涡旋光纤随机激光器的全光纤结构,该装置具有良好的时域稳定性,短时时域波动低至2.8%。该研究结果不仅为实现兼具高功率输出和良好时域稳定性的紧凑型1.7 μm波段涡旋激光器提供有效方案,还能进一步拓展其在激光医疗、气体检测、光镊和生物成像等领域的应用。
1.7 μm波段 涡旋光束 光纤随机激光器 螺旋长周期光纤光栅 涡旋光纤随机激光器 光学学报
2023, 43(22): 2214003
江丽 1,2,3宋锐 1,2,3,*侯静 1,2,3,**陈胜平 1,2,3[ ... ]韩凯 1,2
1 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学南湖之光实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
3 国防科技大学高能激光技术湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
高功率可见光至近红外波段的超连续谱光源在光电对抗、光学相干层析成像和高光谱激光雷达等方面具有广泛的应用前景。最近几年,涌现了一些用于产生高功率超连续谱光源的新方法,推动了高功率超连续谱光源的进一步发展。本文从主振荡功率放大结构、随机光纤激光器结构以及多路非相干合成这三种用于高功率超连续谱产生的主流方案出发,着重介绍了近年来有代表性的高功率可见光至近红外波段超连续谱光源的研究进展,并综合分析了这三种方案的优缺点以及未来的发展潜力。
非线性光学 高功率光纤超连续谱 渐变折射率多模光纤 光子晶体光纤 随机光纤激光器 多路非相干合成 光学学报
2023, 43(17): 1719001
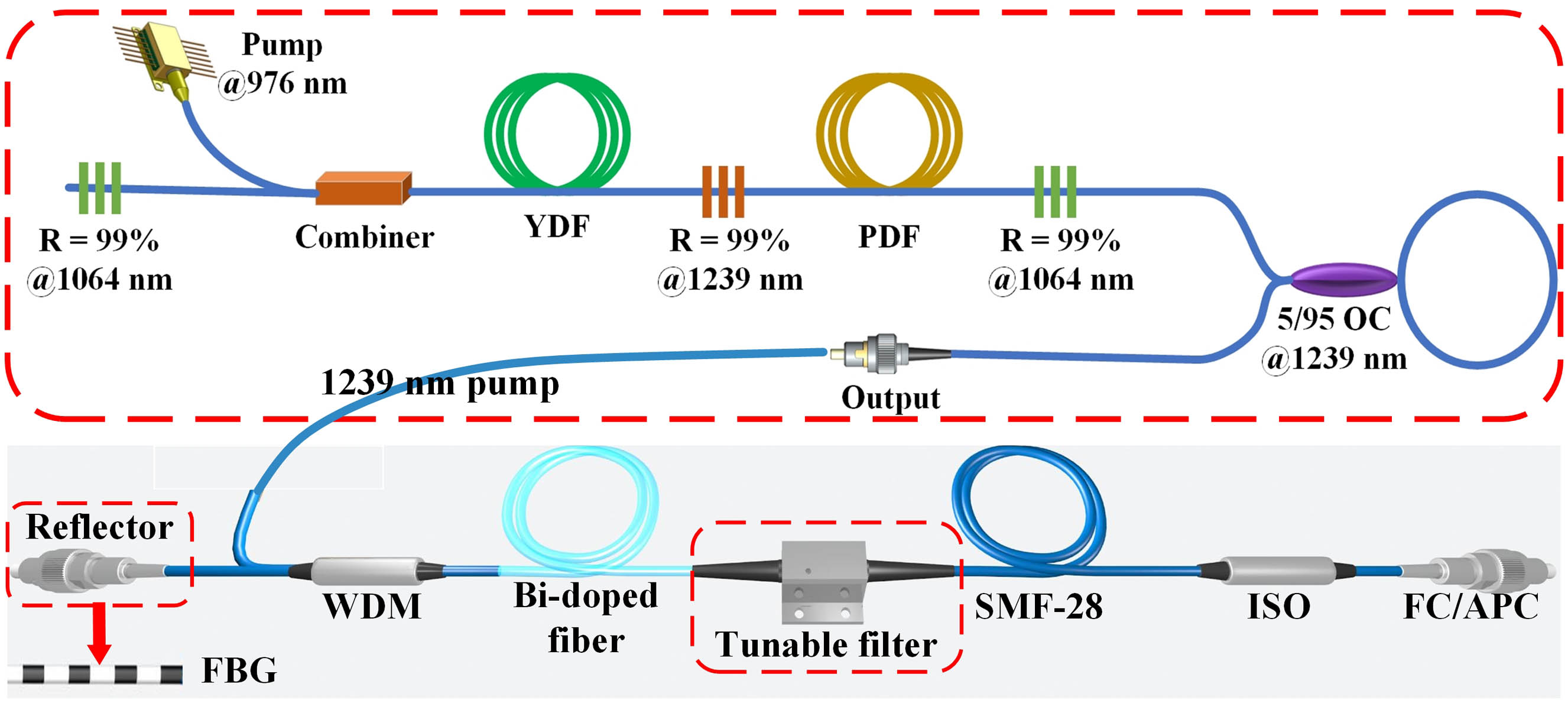
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fujian Key Laboratory of Ultrafast Laser Technology and Applications, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Innovation Laboratory for Sciences and Technologies of Energy Materials of Fujian Province (IKKEM), Xiamen 361005, China
3 Prokhorov General Physics Institute, Dianov Fiber Optics Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119333, Russia
4 Devyatykh Institute of Chemistry of High-Purity Substances, Russian Academy of Sciences, Nizhny Novgorod 603951, Russia
We have successfully generated a 1.3/1.4 µm random fiber laser (RFL) using bismuth (Bi)-doped phosphosilicate fiber. The Bi-doped RFL has shown excellent long-term operational stability with a standard deviation of approximately 0.34% over 1 h at a maximum output power of 549.30 mW, with a slope efficiency of approximately 29.21%. The Bi-doped phosphosilicate fiber offers an emission spectrum ranging from 1.28 to 1.57 µm, indicating that it can be tuned within this band. Here, we demonstrated a wavelength-tuning fiber laser with a wavelength of 1.3/1.4 µm, achieved through the using of a fiber Bragg grating or a tunable filter. Compared to traditional laser sources, the RFL reduces the speckle contrast of images by 11.16%. Due to its high stability, compact size, and high efficiency, this RFL is highly promising for use in biomedical imaging, communication, and sensor applications.
random fiber laser bismuth-doped fiber wavelength tuning fiber laser Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(7): 071401
电子科技大学光纤传感与通信教育部重点实验室,四川 成都 611731
拉曼光纤随机激光结合无源传感单元可以实现超长距离的准分布式传感。然而,受限于光谱探测速度,该传感方案通常只适用于静态传感领域。针对该问题,将拉曼光纤随机激光与拍频光谱探测技术相结合,提出了一种新型的拉曼光纤随机激光长距离动态传感技术。首先,基于含时光谱稳态模型论证了光谱快速测量对长距离动态传感的适用性。随后,在原理性验证实验中通过处理本振光与光纤随机激光拍频后的时域信号,实现了对光纤随机激光光谱的快速测量,并突破了光波往返时间对传感带宽的限制。同时,利用去噪卷积神经网络对光谱的中心波长变化进行标定,大幅提高了扰动信号探测的信号质量,实现了对不同频率、不同波形的扰动信息的准确测量。该研究为进一步拓展光纤随机激光的应用领域提供了新的思路。
光纤传感 光纤随机激光 拉曼散射 瑞利散射 去噪卷积神经网络 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(11): 1106027
1 上海大学通信与信息工程学院,上海 200444
2 特种光纤与光接入网重点实验室,上海 200444
布里渊随机光纤激光器(BRFL)是基于受激布里渊散射(SBS)效应和随机分布式反馈谐振腔组成的新型激光器。笔者基于保偏光纤(PMF)中SBS的非线性轴向偏振牵引效应,提出并实现了一种可实现正交偏振嵌位的受激布里渊随机光纤激光器(PMF-BRFL)。首先对PMF-BRFL系统的偏振工作分区进行了理论分析,接着讨论了系统偏振嵌位的动态范围与系统参数之间的关系,最后采用3 km长PMF实现了PMF-BRFL系统。该系统可以实现偏振态稳定正交嵌位的窄带激光输出,实验结果与理论分析结果一致。
激光器 受激布里渊散射 随机光纤激光器 偏振牵引效应 正交偏振嵌位 保偏光纤 中国激光
2023, 50(10): 1001002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing & Communications (Ministry of Education), University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
Cascaded random Raman fiber lasers (CRRFLs) have been used as a new platform for designing high power and wavelength-agile laser sources. Recently, CRRFL pumped by ytterbium-doped random fiber laser (YRFL) has shown both high power output and low relative intensity noise (RIN). Here, by using a wavelength- and bandwidth-tunable point reflector in YRFL, we experimentally investigate the impacts of YRFL on the spectral and RIN properties of the CRRFL. We verify that the bandwidth of the point reflector in YRFL determines the bandwidth and temporal stability of YRFL. It is found that with an increase in the bandwidth of the point reflector in YRFL from 0.2 nm to 1.4 nm, CRRFL with higher spectral purity and lower RIN can be achieved due to better temporal stability of YRFL pump. By broadening the point reflector’s bandwidth to 1.4 nm, the lasing power, spectral purity, and RIN of the 4th-order random lasing at 1 349 nm can reach 3.03 W, 96.34%, and –115.19 dB/Hz, respectively. For comparison, the spectral purity and RIN of the 4th-order random lasing with the point reflector’s bandwidth of 0.2 nm are only 91.20% and –107.99 dB/Hz, respectively. Also, we realize a wavelength widely tunable CRRFL pumped by a wavelength-tunable YRFL. This work provides a new platform for the development of ideal distributed Raman amplification pump sources based on CRRFLs with both good temporal stability and wide wavelength tunability, which is of great importance in applications of optical fiber communication and distributed sensing.
Random fiber laser Raman fiber laser relative intensity noise distributed Raman amplification Photonic Sensors
2022, 12(4): 220414





