1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所精密仪器与装备研发中心,吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
多光谱重建技术在生物医学领域有着巨大的应用潜力。在传统的皮肤和口腔细菌评估中,目视检查仍然是最广泛使用的方法。这种方法依靠肉眼观察,主观性很强。即使是有经验的临床医生,对细菌感染的确定和评估也经常存在不确定性。为了提供客观和更准确的细菌评估,提出一种基于Wiener估计的荧光多光谱重建方法。该方法基于智能手机平台,用紫色光源激发,采集了皮肤和牙齿的自发荧光图像,使用Wiener估计算法将获取的自发荧光图像重建为具有31个波段(范围为400~700 nm)的多光谱数据立方体,提取并比较细菌产生的卟啉和内源性背景组织发射的光谱强度。基于提取的自发荧光光谱,应用加权减法来实现对皮肤表面细菌的高对比度和高信噪比识别。实验结果表明,所提方法不仅能够准确重建荧光多光谱图像,而且能够实现细菌的定位,应用加权减法后,对比度增强了12~46倍,信噪比提高了1.63~2倍。
光谱、荧光和发光 多光谱重建 快照式 智能手机 维纳估计 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(2): 0230002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centro de Investigaciones en Óptica, A.C., 37150 Guanajuato, México
2 División de Ciencias e Ingenierías, Universidad de Guanajuato, 37150 Guanajuato, México
The fluorescence evolution along Tm3+-doped ––––NaF (ZBLAN) optical fibers, as well as amplified spontaneous emission in the UV-IR region with emphasis on 350 nm, 365 nm, and 450 nm, is studied, estimating optimal fiber lengths for amplification within the region. The fibers were diode-pumped with single and double lines (687 and/or 645 nm). Double-line pumping presents a quite superior efficiency for producing UV-blue signals with the benefit of requiring very short fibers, around 20 cm, compared to single-line pumping requiring more than 50 cm. A virtual cycle in which the pumps enhance each other’s absorption is the key to these systems.
nonlinear optics fiber up-conversion fluorescence and luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(7): 071901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia
2 Faculty of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, 86400 Bt. Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
3 Industrial Biotechnology Research Centre, SIRIM Berhad, 40200 Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
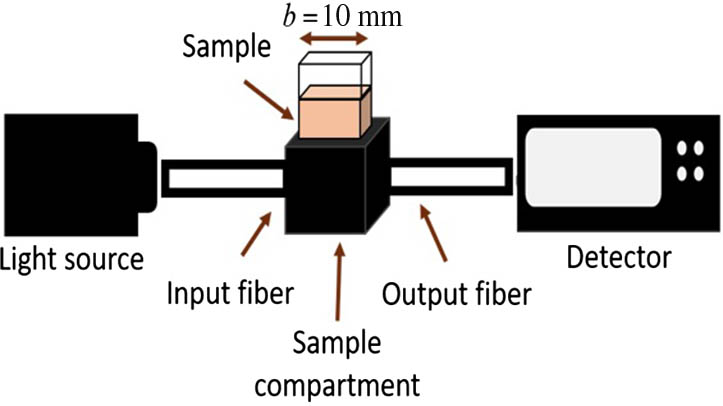
A spectrophotometer with an LED as the light source for uric acid detection is proposed in this work. The mechanism of uric acid detection is based on energy absorbed by sodium urate, which is a chemical product of uric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. For the performance validation, comparison between the spectrophotometer with an LED and halogen lamp is carried out. Measurement results suggest that the spectrophotometer system with LED light has better sensitivity than that with halogen light. At a 460 nm wavelength, the sensitivity for the spectrophotometer with an LED is 0.0046 dL/mg, which is 73% higher than that with halogen light that records 0.0012 dL/mg. This enhanced sensitivity is attributed to the higher luminous efficacy of the LED light beam. As a result, a larger amount of flux interacts with the sample, leading to the sensitivity enhancement. The spectrophotometer with an LED is also applied for the detection of uric acid in a real human urine sample. Based on the experimental data at a 460 nm wavelength, the method manages to achieve the sensitivity of 0.0016 dL/mg, accuracy of 96.01%, limit of detection of 4.79 mg/dL, and limit of quantification of 14.52 mg/dL. These findings show that the use of LED as the input light source is promising for the spectrophotometer.
170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6190 Spectrometers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Hefei University, Hefei 230601, China
2 State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Optical Monitoring Technology, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
Using a measurement system based on fluorescence induced by variable pulse light, photosynthesis parameters of
chlorella pyrenoidosa are obtained, employing single-turnover and multiple-turnover protocols under dark-adapted and light-adapted conditions. Under the light-adapted condition,
σPSII′ is larger, and
Fv′/Fm(ST)′ and
Fv′/Fm(MT)′ are smaller than those of the dark-adapted condition, but the corresponding parameters possess good linear correlations.
Fm(MT),
Fm(MT)′,
Fv/Fm(MT), and
Fv′/Fm(MT)′, which are measured using the multiple-turnover protocol, are larger than those of the single-turnover protocol. The linear correlation coefficient between
Fm(ST) and
300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 013001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
We demonstrate that the filamentation process is strongly influenced by the polarization state of the driver laser. When the laser polarization changes from linear to circular, the critical power for the self-focusing of a Ti:Sapphire laser (800 nm, 40 fs) in air increases from about 9.6±1.0 to 14.9±1.5 GW, while the second nonlinear refractive index n2 of air decreases from 9.9 × 10 20 to 6.4 × 10 20 cm2/W. We also demonstrate that the luminescence from the neutral nitrogen molecules at 337 nm is dependent on both the laser intensity and plasma density inside the filament.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 260.5950 Self-focusing 260.5210 Photoionization Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(12): 120201
1 Department of Chemistry, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Med-X Research Institute, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200031, China
4 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles 90095, USA
5 Japan Science and Technology Agency, Tokyo 102-0076, Japan
Mid-infrared (mid-IR) (2 – 20 μm) photonics has numerous chemical and biologic “fingerprint” sensing applications due to characteristic vibrational transitions of molecules in the mid-IR spectral region. Unfortunately, compared to visible light and telecommunication band wavelengths, photonic devices and applications have been difficult to develop at mid-IR wavelengths because of the intrinsic limitation of conventional materials. Breaking a new ground in the mid-IR science and technology calls for revolutionary materials. Graphene, a single atom layer of carbon arranged in a honey-comb lattice, has various promising optical and electrical properties because of its linear dispersion band structure and zero band gap features. In this review article, we discuss recent research developments on mid-IR graphene photonics, in particular ultrafast lasers and photodetectors. Graphene-photonics-based biochemical applications, such as plasmonic sensing, photodynamic therapy, and florescence imaging are also reviewed.
mid-infrared (mid-IR) mid-infrared (mid-IR) graphene graphene lasers lasers photodetectors photodetectors optical sensing and sensors optical sensing and sensors photodynamic therapy photodynamic therapy spectroscopy spectroscopy fluorescence and luminescence fluorescence and luminescence Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2016, 9(2): 259

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Depauw University, Greencastle, Indiana 46135, USA
2 Department of Physics, Virginia Tech, Virginia 24061, USA
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York 14260, USA
4 Department of Physics, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York 14260, USA
Intramolecular vibrations of large macromolecules reside in the terahertz range. In particular, protein vibrations are closely spaced in frequency, resulting in a nearly continuous vibrational density of states. This density of vibrations interferes with the identification of specific absorption lines and their subsequent association with specific functional motions. This challenge is compounded with the absorption being dominated by the solvent and local relaxational motions. A strategy for removing the isotropic relaxational loss and isolating specific vibrations is to use aligned samples and polarization-sensitive measurements. Here, we demonstrate a technique to rapidlyattain the anisotropic resonant absorbance using terahertz time domain spectroscopy and a spinning sample. The technique, modulated orientation-sensitive terahertz spectroscopy (MOSTS), has a nonzero signal only for anisotropic samples, as demonstrated by a comparison between a silicon wafer and a wire grid polarizer. For sucroseand oxalic acid molecular crystals, the MOSTS response is in agreement with modeled results for the intermolecular vibrations. Further, we demonstrate that, even in the presence of a large relaxational background, MOSTS isolates underlying vibrational resonances.
Instrumentation Instrumentation measurement measurement and metrology and metrology Ellipsometry and polarimetry Ellipsometry and polarimetry Spectroscopy Spectroscopy fluorescence and luminescence fluorescence and luminescence Spectroscopy Spectroscopy modulation modulation Spectroscopy Spectroscopy molecular molecular Spectroscopy Spectroscopy terahertz terahertz Photonics Research
2016, 4(3): 030000A1
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optical Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai Ultra-Precision Optical Manufacturing Engineering Center, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education), Shanghai 200433, China
3 College of Physical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
4 Department of Medical Physics, Weifang Medical University, Shandong 261053, China
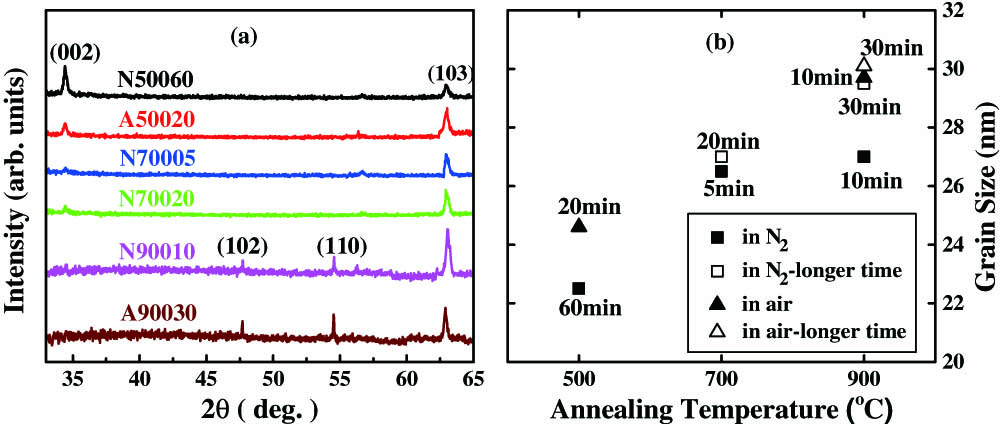
A number of zinc oxide (ZnO) films are deposited on silicon substrates using the magnetron sputtering method. After undergoing thermal treatment under different conditions, those films exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structures and different photoluminescent characteristics. Besides the notable ultraviolet emission, which is related to the free exciton effect, a distinct blue fluorescence around 475 nm is found in some special samples. The blue photoluminescence emission of the ZnO film is believed to be caused by oxygen vacancies.
310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 310.1860 Deposition and fabrication 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 260.3800 Luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 103101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We establish a system to measure the functional absorption cross section of photosystem II (PSII) (\sigma PSII) and maximum quantum yield of photochemistry in PSII (Fv/Fm). The system utilizes a sequence of high-frequency excitation flashes at microsecond intervals to induce a microsecond-level fluorescence yield curve. Parameters \sigma PSII and Fv/Fm are calculated by fitting the curve using nonlinear regression. Experimental results show that the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the system is less than 3%, and the correlation coefficient of Fv/Fm values measured by this system and those measured by pulse amplitude modulation method is 0.950.
010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(8): 080101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Monovalent ions Li+, Na+, and K+, as charge compensators, are introduced into CaYAl3O7: M (M=Eu3+, Ce3+) in this letter. Their crystal phases and photoluminescence properties of different alkali metal ions doped in CaYAl3O7 are investigated. In addition, the influence of charge compensation ion Li+ which has a more obvious role in improving luminescence intensity on CaYAl3O7: Eu3+ phosphor is intentionally discussed in detail and a possible mechanism of charge compensation is given. The enhancement of red emission centered at 618 nm belonging to Eu3+ is achieved by adding alkali metal ion Li+ under 393-nm excitation.
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(5): 051602





