Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Biomedical Engineering (Suzhou), Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China Hefei 230041, P. R. China
2 Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou, Jiangsu 215163, P. R. China
Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) has been widely used to image the three-dimensional (3D) structures and functions of various millimeter-size bio-specimen such as zebrafish. However, the sample adsorption and scattering cause shading of the light-sheet illumination, preventing the even 3D image of thick samples. Herein, we report a continuous-rotational light-sheet microscope (CR-LSM) that enables simultaneous 3D bright-field and fluorescence imaging. With a high-accuracy rotational stage, CR-LSM records the outline projections and the fluorescent images of the sample at multiple rotation angles. Then, 3D morphology and fluorescent structure were reconstructed with a developed algorithm. Using CR-LSM, zebrafish’s whole-fish contour and blood vessel structures were obtained simultaneously.
Light-sheet microscope zebrafish blood vessels morphology Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(2): 2350022
1 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2 湖北省高端生物医学成像重大科技基础设施,湖北 武汉 430074
近几十年来,光片荧光显微镜作为荧光显微技术的一种革新,显著提升了生命科学研究中对组织与细胞结构和功能的高时空分辨率成像能力。相较于传统的落射荧光显微技术,光片显微镜通过选择性逐层照明生物样本,大大提高了光子利用效率,降低了光毒性,并显著提升了成像速度。光片显微镜问世以来,其在生命科学研究中的应用范围逐渐拓宽,从胚胎学、神经科学到肿瘤研究等多个领域均有所涉及,不仅可用于观察细胞和组织的基本结构,还可用于实时监测生物过程中的动态变化。同时,其跨尺度的特点使其适用于从宏观到微观的多个尺度上的观察。本文综述了光片显微镜在高通量成像、超分辨成像以及易用性方面的应用及发展,旨在为生命科学研究人员提供全面的了解和参考,推动光片显微镜在更多领域的应用和发展。
荧光显微成像 光片荧光显微镜 高通量成像 超分辨成像 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(6): 0618019
1 中国科学技术大学生物医学工程学院,江苏 苏州 215163
2 中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所江苏省医用光学重点实验室,江苏 苏州 215163
光片显微镜由于具有强大的光学层切能力、较快的成像速度和较低的光损伤,成为三维成像的重要工具。光片显微镜通常利用两个垂直放置的物镜分别进行照明和成像,这带来了对样品的空间限制并禁用了高数值孔径的成像物镜。以倾斜平面照明和微镜微器件反射技术为代表的单物镜光片显微技术突破上述限制,展示出在高分辨率和体积高速成像方面的优势,并且可与超分辨显微术等多种技术结合,在近年来取得了巨大发展。介绍单物镜光片显微成像技术的原理、关键性能的提升和其在生物医学的应用。
生物光学成像 光片显微镜 三维成像 荧光显微镜 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(6): 0618014
1 南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院智能计算成像实验室(SCILab),江苏 南京 210094
2 南京理工大学江苏省光谱成像与智能感知重点实验室,江苏 南京 210094
3 南京理工大学智能计算成像研究院(SCIRI),江苏 南京 210019
随着生物医学研究对复杂组织结构和功能的深入探索,高分辨率、高信噪比的深组织成像技术变得愈加重要。传统的显微镜技术往往局限于二维、透明的生物薄样本的观测,这在很大程度上无法满足当前生物医学领域对三维深组织体成像的研究需求。光片荧光显微镜凭借其低光损伤、高采集速率、大视场、体成像等优点被生物学家广泛使用。然而,生物组织固有的高散射特性仍然为深层成像带来了巨大的挑战。本文重点介绍了光片荧光显微成像技术在深组织成像领域的最新进展,特别是应对高散射样本挑战的解决策略,旨在为相关领域的研究人员提供有价值的参考,助力其对该前沿技术的最新进展和应用前景的理解。首先,阐述了光片荧光显微镜的基本原理和高散射吸收特性的形成原因及影响;然后,进一步阐明了增加组织穿透深度、应对光散射和吸收等问题的最新进展;最后,探讨了具有大穿透深度和强抗散射能力的光片荧光显微成像技术的发展前景以及潜在应用。
荧光显微 光片照明 深组织成像 三维成像 光学散射 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(2): 0211010
1 华中科技大学 光学与电子信息学院, 武汉 430000
2 华中科技大学 武汉光电国家研究中心, 武汉 430000
光片荧光显微镜具有光毒性低和3D成像容易等特点, 逐渐成为生物医学领域的关键设备。运用ZEMAX设计了一款光片荧光大数值孔径显微镜物镜, 该物镜具有针对常用荧光波长(460nm/509nm/590nm/620nm)成像优化﹑引入光阑结构来使物镜景深可调等特点, 从而能提高对光片厚度的适应性, 减少杂散光干扰, 增加系统信噪比。系统末端设计了微透镜阵列, 参考CMOS传感器像素尺寸调节, 提高了系统能量利用率。物镜总长小于45mm, 数值孔径为0.7, 放大倍率为40x, 工作距离为0.4mm, 性能指标均满足国家标准。
应用光学 显微镜物镜 光片 光阑结构 微透镜阵列 applied optics microscope objectives light sheet diaphragm structure microlens-arrays
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Technische Universität Ilmenau, Fachgebiet Technische Optik, Postfach 100565, 98684 Ilmenau, Germany
2 Iba Heiligenstadt, 37308 Heilbad Heiligenstadt, Germany
Light sheet fluorescence microscope with single light sheet illumination enables rapid 3D imaging of living cells. In this paper we show the design, fabrication and characterization of a diffractive optical element producing several light sheets along a 45° inclined tube. The element, which is based on a multi-focal diffractive lens and a linear grating, generates five thin light sheets with equal intensities when combined with a refractive cylindrical lens. The generated uniform light sheets can be applied for the scanning of samples in tubes enabling flow-driven 3-dimensional imaging.
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy Diffractive optical elements Multi-plane imaging 3D imaging Multi-focal lens Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2023022

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of Freiburg, Department of Microsystems Engineering, Laboratory for Micro-Optics, Freiburg, Germany
2 GRINTECH GmbH, Jena, Germany
3 University of Freiburg, Department of Microsystems Engineering, Microsystems for Biomedical Imaging Laboratory, Freiburg, Germany
One-dimensional Airy beams allow the generation of thin light-sheets without scanning, simplifying the complex optical arrangements of light-sheet microscopes (LSMs) with an extended field of view (FOV). However, their uniaxial acceleration limits the maximum numerical aperture of the detection objective in order to keep both the active and inactive axes within the depth of field. This problem is particularly pronounced in miniaturized LSM implementations, such as those for endomicroscopy or multi-photon neural imaging in freely moving animals using head-mounted miniscopes. We propose a new method to generate a static Airy light-sheet with biaxial acceleration, based on a novel phase profile. This light-sheet has the geometry of a spherical shell whose radius of curvature can be designed to match the field curvature of the micro-objective. We present an analytical model for the analysis of the light-sheet parameters and verify it by numerical simulations in the paraxial regime. We also discuss a micro-optical experimental implementation combining gradient-index optics with a 3D-nanoprinted, fully refractive phase plate. The results confirm that we are able to match detection curvatures with radii in the range of 1.5 to 2 mm.
light-sheet microscopy Airy beam accelerating beams field curvature two-photon polymerization Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 UTS-SUSTech Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
2 Institute for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Faculty of Science, University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, New South Wales 2007, Australia
3 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Biomaterials, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
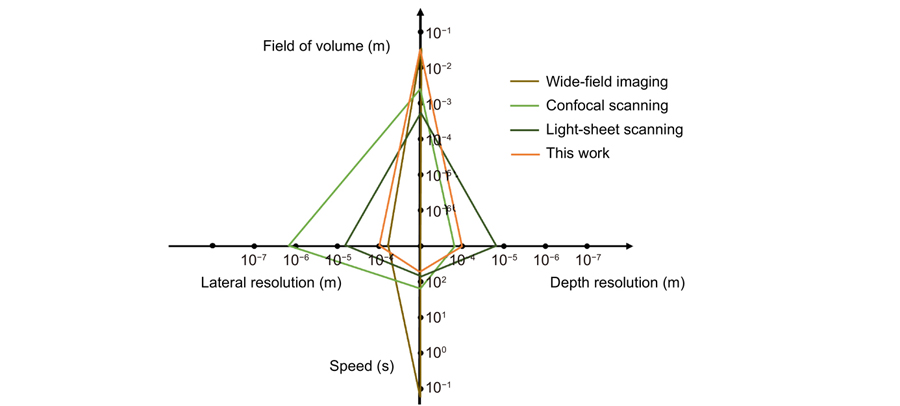
Fluorescence imaging through the second near-infrared window (NIR-II,1000–1700 nm) allows in-depth imaging. However, current imaging systems use wide-field illumination and can only provide low-contrast 2D information, without depth resolution. Here, we systematically apply a light-sheet illumination, a time-gated detection, and a deep-learning algorithm to yield high-contrast high-resolution volumetric images. To achieve a large FoV (field of view) and minimize the scattering effect, we generate a light sheet as thin as 100.5 μm with a Rayleigh length of 8 mm to yield an axial resolution of 220 μm. To further suppress the background, we time-gate to only detect long lifetime luminescence achieving a high contrast of up to 0.45 Ιcontrast. To enhance the resolution, we develop an algorithm based on profile protrusions detection and a deep neural network and distinguish vasculature from a low-contrast area of 0.07 Ιcontrast to resolve the 100 μm small vessels. The system can rapidly scan a volume of view of 75 × 55 × 20 mm3 and collect 750 images within 6 mins. By adding a scattering-based modality to acquire the 3D surface profile of the mice skin, we reveal the whole volumetric vasculature network with clear depth resolution within more than 1 mm from the skin. High-contrast large-scale 3D animal imaging helps us expand a new dimension in NIR-II imaging.
NIR-II fluorescence time-gated light sheet illumination deep learning vessel enhancement 3D imaging Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(4): 220105
1 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300000
2 北京信息科技大学现代测控技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100192
搭建了一种基于液体变焦透镜和振镜的三维光片显微成像系统,设计了振镜、液体变焦透镜、相机的同步控制采集成像系统,通过调谐振镜和液体变焦透镜,使得光片激发样品和成像同步,获得样品不同切面的图像堆栈并实现样品的三维重建。当采用数值孔径为0.3、放大倍率为10的成像物镜时,该系统的轴向扫描范围为507 μm,横向视场达到1970 μm×1300 μm,横向分辨率为1.32 μm,轴向分辨率可达12.75 μm。在轴向扫描过程中,系统的放大倍率保持恒定,可以用于对一定尺寸生物样品的成像实验和相关研究,并通过对斑马鱼胚胎进行成像验证所提系统对厚生物样品成像的可行性。
成像系统 光片显微成像 液体变焦透镜 振镜 三维成像





