2018, 16(4) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第4期
Long-distance characterization of high-quality laser-wakefield-accelerated electron beams Download:759次
Download:759次
 Download:759次
Download:759次Beam quality degradation during the transition from a laser wakefield accelerator to the vacuum is one of the reasons that cause the beam transport distortion, which hinders the way to compact free-electron-lasers. Here, we performed transition simulation to initialize the beam parameters for beam optics transport. This initialization was crucial in matching the experimental results and the designed evolution of the beamline. We experimentally characterized properties of high-quality laser-wakefield-accelerated electron beams, such as transverse beam profile, divergence, and directionality after long-distance transport. By installing magnetic quadrupole lenses with tailored strength gradients, we successfully collimated the electron beams with tunable energies from 200 to 600 MeV.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 110.2970 Image detection systems Using the classical-trajectory Monte Carlo model, we have theoretically studied the angular momentum distribution of frustrated tunneling ionization (FTI) of atoms in strong laser fields. Our results show that the angular momentum distribution of the FTI events exhibits a double-hump structure. With this classical model, we back traced the tunneling coordinates, i.e., the tunneling time and initial transverse momentum at tunneling ionization. It is shown that for the events tunneling ionized at the rising edge of the electric field, the final angular momentum exhibits a strong dependence on the initial transverse momentum at tunneling. While for the events ionized at the falling edge, there is a relatively harder recollision between the returning electron and the parent ion, leading to the angular momentum losing the correlation with the initial transverse momentum. Our study suggests that the angular momentum of the FTI events could be manipulated by controlling the initial coordinates of the tunneling ionization.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics We investigate the nonadiabatic spectral redshift of high-order harmonic of He
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 320.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics The resonator integrated optic gyros (RIOGs) based on the Sagnac effect have gained extensive attention in navigation and guidance systems due to their predominant advantages: high theoretical accuracy and simple integration. However, the problems of losing lock and low lock-in accuracy are the bottlenecks, which restrict the development of digital RIOGs. Therefore, a multilevel laser frequency lock-in technique has been proposed in this Letter to address these problems. The experimental results show that lock-in accuracy can be improved one order higher and without losing lock in a variable temperature environment. Then, a digital miniaturized RIOG prototype (18 cm × 18 cm × 20 cm
060.2800 Gyroscopes 120.5790 Sagnac effect 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers Simultaneous measurement of axial strain and temperature based on twisted fiber structure Download:555次
Download:555次
 Download:555次
Download:555次In this Letter, an alternative solution is proposed and demonstrated for simultaneous measurement of axial strain and temperature. This sensor consists of two twisted points on a commercial single mode fiber introduced by flame-heated and rotation treatment. The fabrication process modifies the geometrical configuration and refractive index of the fiber. Different cladding modes are excited at the first twisted point, and part of them are coupled back to the fiber core at the second twisted point. Experimental results show distinct sensitivities of 34.9 pm/με with 49.23 pm/°C and 36.19 pm/με with 62.99 pm/°C for the two selected destructive interference wavelengths.
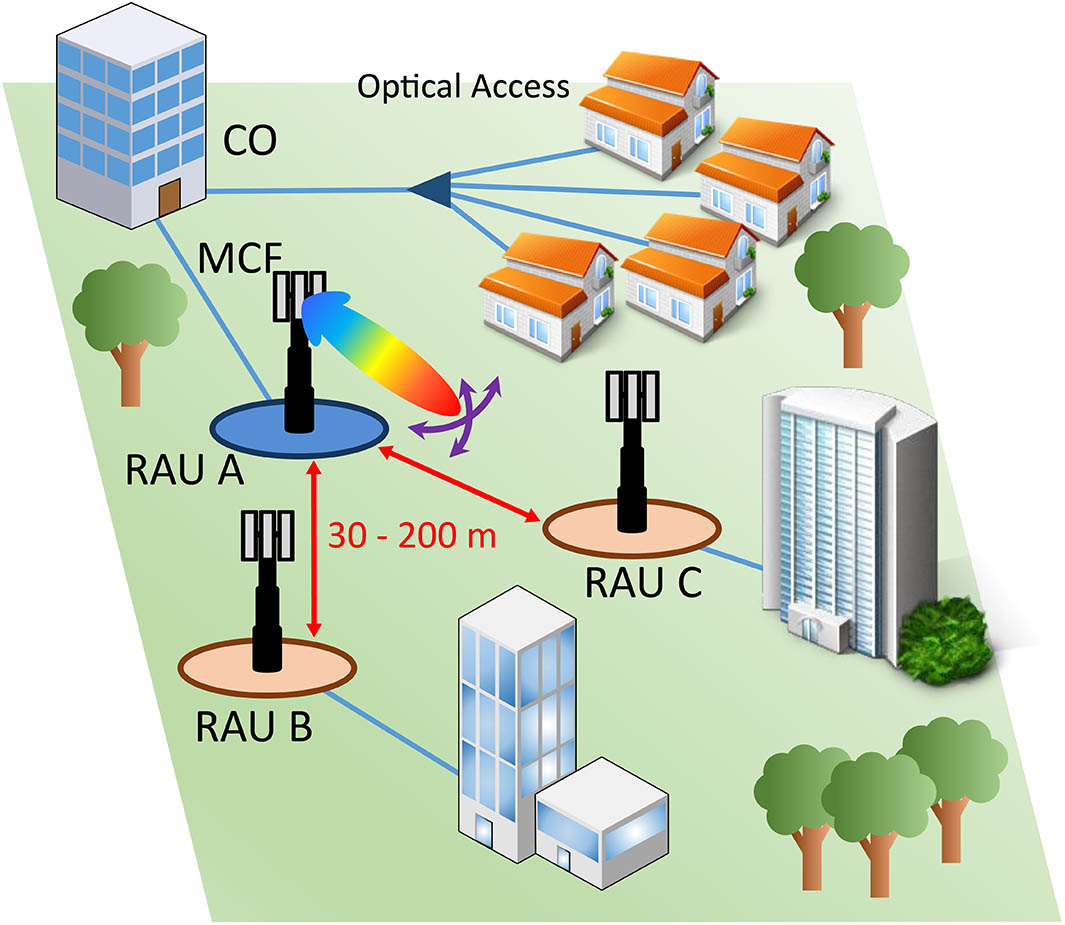
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2430 Fibers, single-mode We propose and experimentally validate an optical true time delay beamforming scheme with straightforward integration into hybrid optical/millimeter (mm)-wave access networks. In the proposed approach, the most complex functions, including the beamforming network, are implemented in a central office, reducing the complexity and cost of remote antenna units. Different cores in a multi-core fiber are used to distribute the modulated signals to high-speed photodetectors acting as heterodyne mixers. The mm-wave carrier frequency is fixed to 50 GHz (V-Band), thereby imposing a progressive delay between antenna elements of a few picoseconds. That true time delay is achieved with an accuracy lower than 1 ps and low phase noise.
060.4510 Optical communications In this Letter, we have proposed a generalized Gaussian probability density function (GGPDF)-based method to estimate the symbol error ratio (SER) for pulse amplitude modulation (PAM-4) in an intensity modulation/direct detection (IM/DD) system. Furthermore, a closed form expression of SER GGD P 1 P 2 P P
060.4510 Optical communications Investigation on an all-optical intensity modulator based on an optical microfiber coupler Download:543次
Download:543次
 Download:543次
Download:543次An all-optical intensity modulator based on an optical microfiber coupler (OMC) is presented. The modulator works at 1550 nm wavelength and is modulated directly by heating the coupling region with 980 nm pump light injected through the coupling port of the OMC. The OMC is controlled to have at least a 30 mm long coupling region with diameter smaller than 8 μm, and the uniform waist region diameter is about 3 μm. This is helpful to ensure the optical modulation function based on the light induced thermal effect in the coupling region, while pump light is injected. The modulation response is measured to show good linearity when the 980 nm pump light has a lower intensity (with power below 2.5 mW), which proves that the OMC acts as an all-optical modulator. The bandwidth of the modulator can be at 0.2–50 kHz with the average power of the intensity-modulated pump light about 2 mW, which can be further improved by optimizing the design of the coupler. The demonstrated modulator may have potential value for the application in an all-optical integration system.
230.4000 Microstructure fabrication Thermally regenerated low-reflectivity fiber Bragg gratings (RFBGs), as one mirror of a resonant cavity, have been introduced as linear-cavity fiber lasers combining with fiber saturable absorbers. The output of lasing presents an optical signal-to-noise ratio of 50 dB and temperature sensitivity coefficient of 15.36 pm / ° C 15.46 pm / ° C
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors We experimentally designed dispersion-managed repeaterless transmission systems with a pre-compensation and post-compensation technique using multi-channel-chirped fiber Bragg gratings. The repeaterless transmission link supports a single channel (1548.51 nm) with a 10 Gbps repeaterless transmission system over 300 km standard single-mode fiber (SSMF). In the system design, two distributed Raman amplifiers (DRAs) were used to improve the signal level propagated along the 300 km SSMF. The co-propagating DRA provided 15 dB on–off gain and the counter-propagating produced 32 dB on–off gain at the signal wavelength. The experiment results show that the post-compensation configuration achieves an optimal performance with a bit error rate at 1 × 10 9
060.2330 Fiber optics communications Coherent pulse stacking (CPS) is a new time-domain coherent addition technique that stacks several optical pulses into a single output pulse, enabling high pulse energy and high average power. A Z
070.2025 Discrete optical signal processing 120.5050 Phase measurement 140.4780 Optical resonators Distortion correction for the elemental images of integral imaging by introducing the directional diffuser Download:733次
Download:733次
 Download:733次
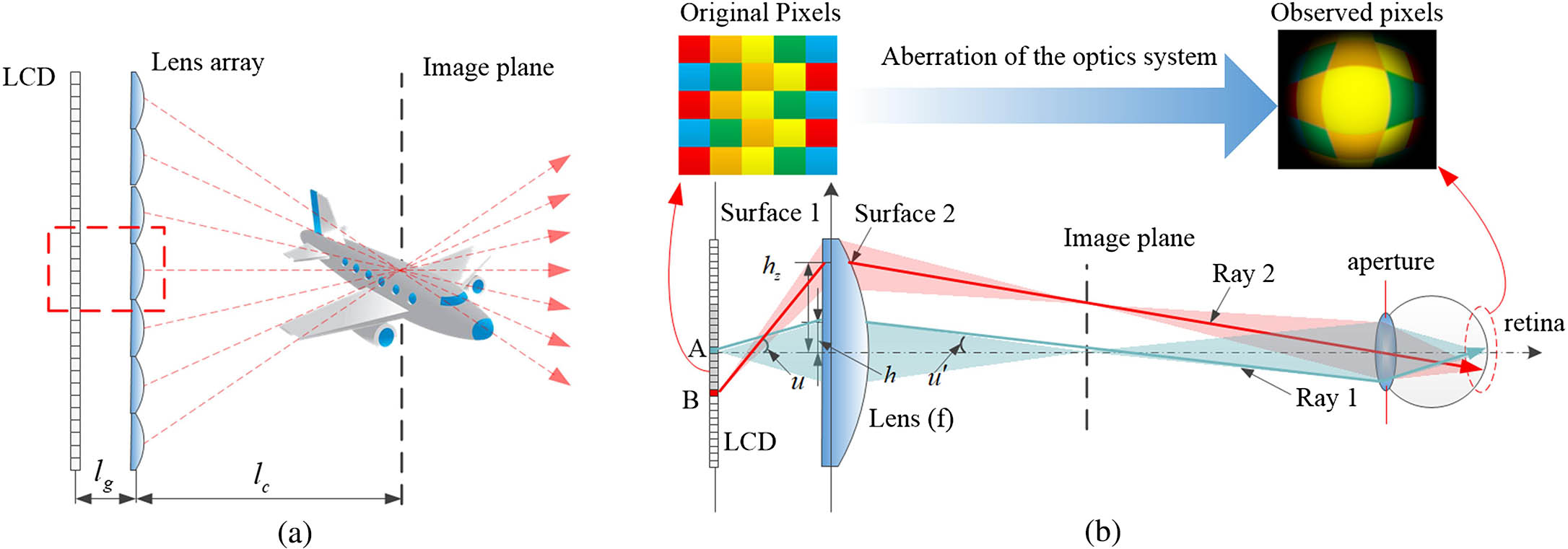
Download:733次A distortion correction method for the elemental images of integral imaging (II) by utilizing the directional diffuser is demonstrated. In the traditional II, the distortion originating from lens aberration wraps elemental images and degrades the image quality severely. According to the theoretical analysis and experiments, it can be proved that the farther the three-dimensional image is displayed from the lens array, the more serious the distortion is. To analyze the process of eliminating lens distortion, one lens and its corresponding elemental image are separated from the traditional II. By introducing the directional diffuser, the aperture stop of the separated optical system changes from the eye’s pupil to the lens. In terms of contrast experiments, the distortion of the improved display system is corrected effectively. In the experiment, when the distance between the reconstructed image and lens array is equal to 120 mm, the largest lens distortion is decreased from 46.6% to 3.3%.
080.1005 Aberration expansions Depth resolution improvement of streak tube imaging lidar system using three laser beams Download:698次
Download:698次
 Download:698次
Download:698次The work proposes a three-laser-beam streak tube imaging lidar system. Besides the main measuring laser beam, the second beam is used to decrease the error of time synchronization. The third beam has n + 0.5 < 2 mm ~ 0.2 pixel
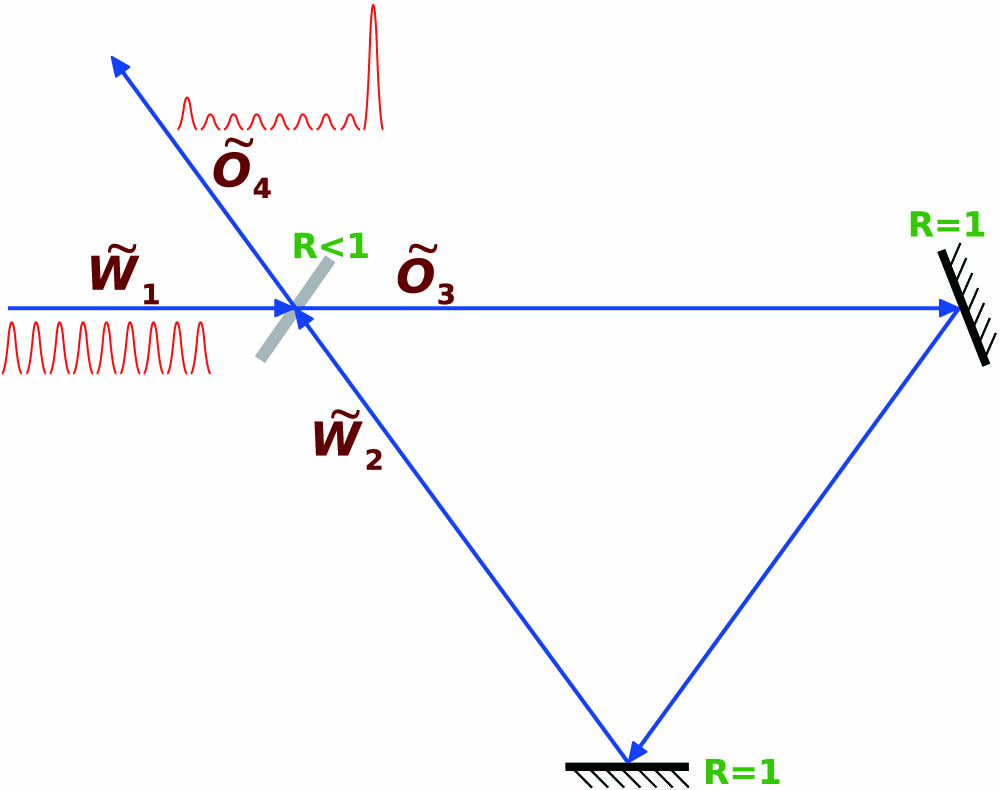
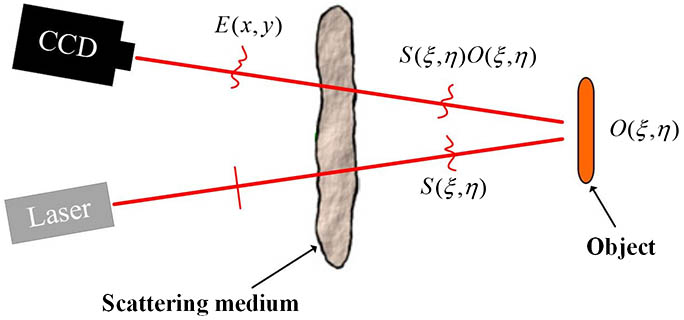
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 280.3640 Lidar Traditional one-way imaging methods become invalid when a target object is completely hidden behind scattering media. In this case, it has been much more challenging, since the light wave is distorted twice. To solve this problem, we propose an imaging method, so-called round-trip imaging, based on the optical transmission matrix of the scattering medium. We show that the object can be recovered directly from the distorted output wave, where no scanning is required during the imaging process. We predict that this method might improve the imaging speed and have potential application for real-time imaging.
110.0113 Imaging through turbid media 110.1650 Coherence imaging 110.1758 Computational imaging To reveal the physical mechanism of laser ablation and establish the prediction model for figuring the surface of fused silica, a multi-physical transient numerical model coupled with heat transfer and fluid flow was developed under pulsed CO 2 CO 2
140.3390 Laser materials processing 140.3470 Lasers, carbon dioxide 220.5450 Polishing 140.3538 Lasers, pulsed We systematically study the optimization of highly efficient terahertz (THz) generation in lithium niobate (LN) crystal pumped by 800 nm laser pulses with 30 fs pulse duration. At room temperature, we obtain a record optical-to-THz energy conversion efficiency of 0.43% by chirping the pump laser pulses. Our method provides a new technique for producing millijoule THz radiation in LN via optical rectification driven by joule-level Ti:sapphire laser systems, which deliver sub-50-fs pulse durations.
190.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics 040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz The confocal microscopy technique was applied for nonlinear optical characterization of single β β c χ ( 2 ) χ ( 2 ) β
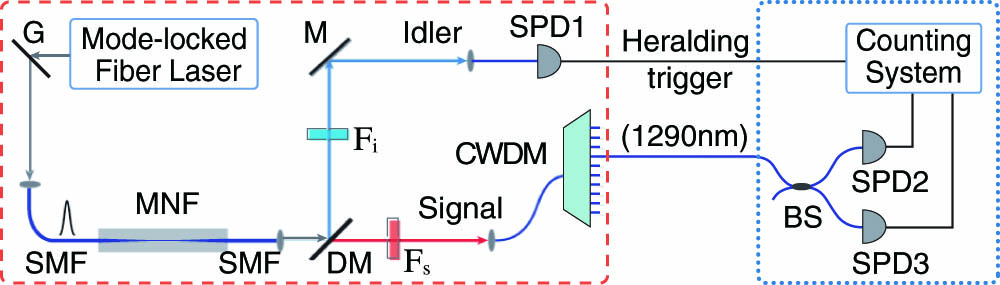
190.3970 Microparticle nonlinear optics 180.4315 Nonlinear microscopy We experimentally demonstrate a heralded single photon source at 1290 nm by exploiting the spontaneous four wave mixing in a taper-drawn micro/nano-fiber (MNF). Because the frequency detuning between the pump and heralded single photons is ~ 58 THz g ( 2 ) ( 0 ) 0.017 ± 0.002
190.4380 Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Variable optical attenuators with ability to independently control two orthogonal linearly polarized light amplitudes Download:543次
Download:543次
 Download:543次
Download:543次New techniques for controlling the amplitudes of two orthogonal linearly polarized light are presented. One is based on adjusting the DC voltage into a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) to alter the amplitude of the light traveling on the slow axis of a fiber into the modulator with little changes in the fast-axis light amplitude. Another is based on adjusting the input DC voltages of a dual-polarization MZM operating in the reverse direction, which enables independent control of the two input orthogonal linearly polarized light amplitudes. Experimental results demonstrate that more than 30 dB difference in slow- and fast-axis light power can be obtained by controlling an MZM input DC voltage, and over 24 dB independent power adjustment for light traveling on the slow and fast axes into a dual-polarization MZM.
230.0250 Optoelectronics 230.5440 Polarization-selective devices 230.2090 Electro-optical devices Supercontinuum generation (SC) of more than one octave spectrum spanning covering from 400 nm to 820 nm was achieved by pumping a piece of aluminum nitride (AIN) single crystal using a nanosecond 355 nm ultraviolet laser. The AlN with a thickness of ~ 0.8 mm
320.6629 Supercontinuum generation 190.2640 Stimulated scattering, modulation,etc. 190.4720 Optical nonlinearities of condensed matter 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦