Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Radiology Technology, College of Health and Medical Technology, Middle Technical University (MTU), Baghdad, Iraq
2 Department of Physics, College of Education for Pure Science (Ibn-AL-Haitham), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
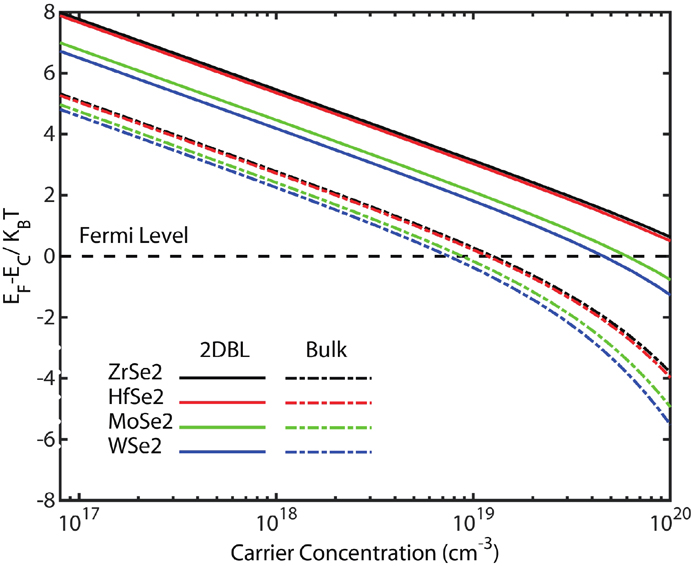
Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.Significant advancements in nanoscale material efficiency optimization have made it feasible to substantially adjust the thermoelectric transport characteristics of materials. Motivated by the prediction and enhanced understanding of the behavior of two-dimensional (2D) bilayers (BL) of zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2), hafnium diselenide (HfSe2), molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), and tungsten diselenide (WSe2), we investigated the thermoelectric transport properties using information generated from experimental measurements to provide inputs to work with the functions of these materials and to determine the critical factor in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials. Based on the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) and Barden-Shockley deformation potential (DP) theory, we carried out a series of investigative calculations related to the thermoelectric properties and characterization of these materials. The calculated dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) values of 2DBL-MSe2 (M = Zr, Hf, Mo, W) at room temperature were 3.007, 3.611, 1.287, and 1.353, respectively, with convenient electronic densities. In addition, the power factor is not critical in the trade-off between thermoelectric materials but it can indicate a good thermoelectric performance. Thus, the overall thermal conductivity and power factor must be considered to determine the preference of thermoelectric materials.
ZT thermoelectric property 2D-bilayer Boltzmann-transport equation TE power factor Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(3): 032001
福建工程学院材料科学与工程学院,福州 350118
窄带隙半导体材料Mg2Sn具有丰度大、密度低、无毒及环境友好等特点,是中低温热电材料的优秀候选者。本文基于密度泛函理论,结合不同形式的电子交换关联能系统分析了Mg2Sn晶体的弹性系数、声子振动谱和电子能带结构,并基于非平衡玻尔兹曼输运理论计算了Mg2Sn的热电性能。结果表明,GGA-PBE作为电子交换关联能可以很好地拟合立方相Mg2Sn的力学性能(声子振动谱无虚频率),其体弹性模量为42.1 GPa且各向同性。同时,当工作温度高于300 K,Mg2Sn的德拜温度开始趋于平缓且不高于315 K,表明Mg2Sn在该温度区域内具有低声子热导率。使用B3LYP作为电子交换关联能可以估算Mg2Sn费米能级附近的电子结构,发现价带顶附近存在三重简并态。同时计算结果表明,Mg2Sn p型掺杂下的热电优值(ZT值)优于n型掺杂,可达1.05。本研究结果为进一步优化Mg2Sn热电性能的研究提供借鉴。
第一性原理 弹性性能 玻尔兹曼输运 热电性能 掺杂 first-principle Mg2Sn Mg2Sn elastic property Boltzmann transport thermoelectric property doped





