
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, College of Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Hunan Key Laboratory of Extreme Matter and Applications (XMAL), Changsha 410073, China
3 Hunan Key Laboratory for Micro-Nano Energy Materials and Devices, School of Physics and Optoelectronics, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105, China
4 Guangxi Key Laboratory of Automatic Detecting Technology and Instrument, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China
Two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals materials have attracted tremendous attention due to their versatile physical properties and flexible manipulation approaches. Among the various types of van der Waals materials, is remarkable for its intrinsic 2D ferroelectricity and high-performance opto-electronic properties. However, the study of the system in terahertz (THz) radiation is scarce, although it is promising for electrically controlled THz field manipulation. We investigate the in different thicknesses and report that the THz generation efficiency induced by femtosecond laser pulses can be largely improved by reducing the thickness from the bulk. Furthermore, we reveal the surge current in thin film coupled with THz emission exhibits a different Auger recombination mode, which is helpful in understanding the mechanism and provides insights into the design of 2D highly efficient THz devices.
van der Waals terahertz carrier dynamics Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(1): 013202
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 New Materials and New Energies, Shen Zhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
2 Analysis and Testing Center, Shen Zhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have intriguing physic properties and offer an exciting platform to explore many features that are important for future devices. In this work, we synthesized monolayer WS2 as an example to study the optical response with hydrostatic pressure. The Raman results show a continuous tuning of the lattice vibrations that is induced by hydrostatic pressure. We further demonstrate an efficient pressure-induced change of the band structure and carrier dynamics via transient absorption measurements. We found that two time constants can be attributed to the capture process of two kinds of defect states, with the pressure increasing from 0.55 GPa to 2.91 GPa, both of capture processes were accelerated, and there is an inflection point within the pressure range of 1.56 GPa to 1.89 GPa. Our findings provide valuable information for the design of future optoelectronic devices.
two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides hydrostatic pressure carrier dynamics band structure ultrafast spectroscopy Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(8): 082001
1 苏州科技大学物理科学与技术学院,江苏省微纳热流技术与能源应用重点实验室,江苏 苏州 215009
2 苏州大学物理科学与技术学院,江苏 苏州 215006
利用多维度的泵浦探测技术来研究Fe掺杂氮化镓(GaN∶Fe)晶体的超快瞬态非线性光学响应和基于Fe缺陷的宽带载流子动力学机制。相位物体(PO)泵浦探测实验结果表明,载流子折射动力学曲线相较于吸收表现出明显的回复,结合超快瞬态吸收光谱实验证明这源于Fe缺陷态的宽带吸收。此外,瞬态吸收响应与载流子俘获速率均可通过Fe含量进行大幅调控,吸收幅值和载流子俘获寿命分别随着Fe含量的增加而增大和缩短。根据瞬态光学非线性结果,提出了基于Fe缺陷不同电荷态下的激发与俘获模型,结合全局分析和速率方程获得了GaN∶Fe的载流子俘获机理与重要的Fe缺陷俘获速率和光吸收截面。GaN∶Fe中可调控的载流子寿命和超宽带的吸收光谱对光开关、光限幅器件、光电探测器等光电器件的设计和开发有着十分重要的意义。
非线性光学 氮化镓 泵浦探测 瞬态吸收光谱 载流子动力学 光学学报
2022, 42(22): 2219001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (IESL), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), Herakleio 70013, Greece
2 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Hellenic Mediterranean University, Herakleio 71004, Greece
3 Department of Materials Science and Technology, University of Crete, Herakleio 70013, Greece
4 Department of Physics, University of Crete, Herakleio 70013, Greece
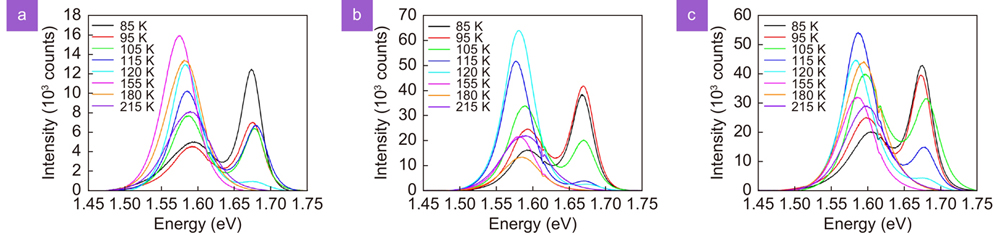
Despite that organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites have attracted enormous scientific attention for energy conversion applications over the recent years, the influence of temperature and the type of the employed hole transport layer (HTL) on the charge carrier dynamics and recombination processes in perovskite photovoltaic devices is still largely unexplored. In particular, significant knowledge is missing on how these crucial parameters for radiative and non-radiative recombinations, as well as for efficient charge extraction vary among different perovskite crystalline phases that are induced by temperature variation. Herein, we perform micro photoluminescence (μPL) and ultrafast time resolved transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) in Glass/Perovskite and two different Glass/ITO/HTL/Perovskite configurations at temperatures below room temperature, in order to probe the charge carrier dynamics of different perovskite crystalline phases, while considering also the effect of the employed HTL polymer. Namely, CH3NH3PbI3 films were deposited on Glass, PEDOT:PSS and PTAA polymers, and the developed Glass/CH3NH3PbI3 and Glass/ITO/HTL/CH3NH3PbI3 architectures were studied from 85 K up to 215 K in order to explore the charge extraction dynamics of the CH3NH3PbI3 orthorhombic and tetragonal crystalline phases. It is observed an unusual blueshift of the bandgap with temperature and the dual emission at temperature below of 100 K and also, that the charge carrier dynamics, as expressed by hole injection times and free carrier recombination rates, are strongly depended on the actual pervoskite crystal phase, as well as, from the selected hole transport material.Despite that organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites have attracted enormous scientific attention for energy conversion applications over the recent years, the influence of temperature and the type of the employed hole transport layer (HTL) on the charge carrier dynamics and recombination processes in perovskite photovoltaic devices is still largely unexplored. In particular, significant knowledge is missing on how these crucial parameters for radiative and non-radiative recombinations, as well as for efficient charge extraction vary among different perovskite crystalline phases that are induced by temperature variation. Herein, we perform micro photoluminescence (μPL) and ultrafast time resolved transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) in Glass/Perovskite and two different Glass/ITO/HTL/Perovskite configurations at temperatures below room temperature, in order to probe the charge carrier dynamics of different perovskite crystalline phases, while considering also the effect of the employed HTL polymer. Namely, CH3NH3PbI3 films were deposited on Glass, PEDOT:PSS and PTAA polymers, and the developed Glass/CH3NH3PbI3 and Glass/ITO/HTL/CH3NH3PbI3 architectures were studied from 85 K up to 215 K in order to explore the charge extraction dynamics of the CH3NH3PbI3 orthorhombic and tetragonal crystalline phases. It is observed an unusual blueshift of the bandgap with temperature and the dual emission at temperature below of 100 K and also, that the charge carrier dynamics, as expressed by hole injection times and free carrier recombination rates, are strongly depended on the actual pervoskite crystal phase, as well as, from the selected hole transport material.
transient absorption spectroscopy μ-photoluminescence variable temperature perovskite crystalline phases hole transport layer charge carrier dynamics Opto-Electronic Science
2022, 1(4): 210005
利用带间激发的超快瞬态吸收光谱,研究了导电(n型)氮(N)掺杂和半绝缘(SI)钒(V)掺杂6H-SiC晶片的超快载流子复合动力学过程。N杂质和/或固有缺陷的间接复合主导了n型6H-SiC的载流子弛豫,其寿命超过了10 ns。与n型6H-SiC相比,V掺杂对SI-6H-SiC的瞬态吸收具有显著的调制作用,这源于由V深能级的载流子俘获引起的一个额外的载流复合过程。载流子俘获(寿命约为160 ps)比间接复合快2个数量级以上。通过简化能级模型并进行全局分析,研究了6H-SiC的载流子复合机制,准确地获得了6H-SiC的载流子寿命。
超快光学 载流子动力学 瞬态吸收光谱 n型SiC 半绝缘SiC 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(6): 063201





