1 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,吉林长春3002
2 中国科学院 苏州生物医学工程技术研究所,江苏苏州15163
针对高光谱遥感图像分类时有标注的源域训练数据与无标注目标域数据分布不一致的问题,提出基于部分最优传输的无监督领域自适应方法,实现对处于不同数据分布的高光谱遥感地物像素级分类。利用深度卷积神经网络将样本映射到潜在高维空间,根据部分最优传输理论建立样本传输方案,最小化域间分布差异,构建适配模型。采用类感知采样技术和质量分数因子自适应调整策略,促进域间类别对齐,建立全局最优传输。在两组公开高光谱遥感图像数据集上进行实验,从总体分类精度OA(%)、类别平均分类精度AA(%)、分类一致性检验Kappa(×100)等3个评价指标对像素分类结果量化比较。实验结果显示,在两组迁移任务上,相较于仅使用源域数据的基线模型,总体分类准确率分别提升2.21%和2.75%,相较于原始最优传输策略提升1.71%和2.01%,表明模型能够有效提升高光谱遥感影像中像素级地物的分类精度。
计算机视觉 神经网络 领域自适应 最优传输 高光谱图像 computer vision neural network domain adaptation optimal transport hyperspectral image 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(17): 2555
1 哈尔滨理工大学 测控技术与通信工程学院 黑龙江省激光光谱技术及应用重点实验室, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 50080
2 国网黑龙江省电力有限公司 综合信息中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150010
3 中部大学 计算机科学学院,日本 爱知 487-8501
针对跨场景高光谱遥感图像分类中源域和目标域的频谱偏移问题,提出一种结合空谱域适应与极度梯度提升树(eXtreme Gradient Boosting, XGBoost)的跨场景高光谱图像分类模型。将深度超参数卷积模型(Depthwise Over-parameterized Convolution Model,DOCM)和大核注意力(Large Kernel Attention,LKA)结合,构成空谱注意力模型,提取源域空谱特征。利用相同的空谱注意力模型对目标域进行特征提取,并与鉴别器完成对抗域适应,减少源域与目标域之间的频谱偏移;通过目标域中少量有标签数据对目标域特征提取器进行有监督域适应,使目标域特征提取器进一步学习目标域的真实分布,并对源域和目标域的特征进行映射,形成相似的空间分布,完成聚类域适应。最后,使用集成分类器XGBoost进行高光谱图像分类,进一步提高模型的训练速度与置信度。在Pavia和Indiana高光谱数据集上的实验结果表明,本文算法的总体分类精度分别达到了91.62%和 65.98%。相比较于其他跨场景高光谱图像分类模型,本文所提模型具有更高的地物分类精度。
高光谱图像 域适应 大核注意力 XGBoost hyperspectral images domain adaptation large kernel attention XGBoost 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(13): 1950
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学电子电气与通信工程学院,北京 100049
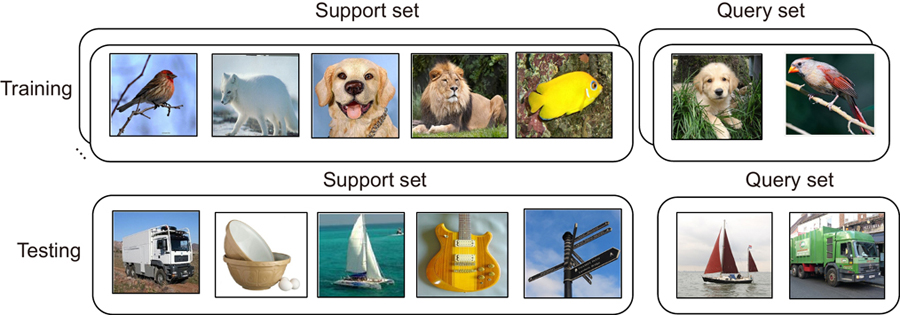
To improve the performance of few-shot classification, we present a general and flexible method named Multi-Scale Attention and Domain Adaptation Network (MADA). Firstly, to tackle the problem of limited samples, a masked autoencoder is used to image augmentation. Moreover, it can be inserted as a plug-and-play module into a few-shot classification. Secondly, the multi-scale attention module can adapt feature vectors extracted by embedding function to the current classification task. Multi-scale attention machine strengthens the discriminative image region by focusing on relating samples in both base class and novel class, which makes prototypes more accurate. In addition, the embedding function pays attention to the task-specific feature. Thirdly, the domain adaptation module is used to address the domain shift caused by the difference in data distributions of the two domains. The domain adaptation module consists of the metric module and the margin loss function. The margin loss pushes different prototypes away from each other in the feature space. Sufficient margin space in feature space improves the generalization performance of the method. The experimental results show the classification accuracy of the proposed method is 67.45% for 5-way 1-shot and 82.77% for 5-way 5-shot on the miniImageNet dataset. The classification accuracy is 70.57% for 5-way 1-shot and 85.10% for 5-way 5-shot on the tieredImageNet dataset. The classification accuracy of our method is better than most previous methods. After dimension reduction and visualization of features by using t-SNE, it can be concluded that domain drift is alleviated, and prototypes are more accurate. The multi-scale attention module enhanced feature representations are more discriminative for the target classification task. In addition, the domain adaptation module improves the generalization ability of the model.
小样本图像识别 注意力机制 领域自适应 相似性度量 few-shot image classification attention mechanism domain adaptation similarity metric
1 天津大学 电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072
2 天津津航技术物理研究所,天津 300308
近年来,基于深度学习的目标检测技术在机器人、自动驾驶和交通监控等领域有着广泛的应用。然而,由于训练集和测试集样本分布偏差的原因,将现成的预训练检测器应用到实际开放场景时通常会出现明显性能下降。针对该问题提出了一种频域内的领域自适应方法,利用离散余弦变换的频域能量集中特性,通过在频域内对少数重要频率系数进行处理,实现了面向目标检测的领域自适应,降低了对存储和计算资源的要求并减少了领域差异。该方法可以分为两个阶段:第一阶段使用无监督图像转换方式,将源域已标注的训练数据向目标域作转换;第二阶段采用基于对抗的领域自适应方法训练目标检测模型,对转换后的训练数据与目标域内的数据作特征适配。针对不同天气场景的目标识别实验表明:所提的频域内领域自适应方法在4种领域自适应对比算法中排名第一,与仅用源域数据训练的模型相比,mAP值提升了33.9%。
领域自适应 目标检测 图像转换 频域 domain adaptation object detection image translation frequency domain 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(7): 20210638
提出一种基于无监督域适应的低空海面红外目标检测方法。首先利用图像翻译网络将源域图像翻译为目标域图像并共享标签。其次在YOLOv5s目标检测网络中使用梯度反转层优化网络提取特征的域间适应性。此外利用最大均值差异损失进一步缩小从网络中提取的不同红外探测器图像的特征分布。最后采用AdamW异步更新优化算法进一步提高模型在训练过程中的稳定性与检测精度。将所提方法在不同红外探测器采集的低空海面红外船只与无人机数据集中进行实验。实验结果表明,相较于传统有监督学习方法,所提方法有效降低了人工标注成本,且源域检测精度提高6.56个百分点,目标域检测精度提高2.62个百分点,有效提升目标检测模型在不同红外探测器间的泛化能力。
机器视觉 红外探测器 无监督域适应 梯度反转层 稳定训练 目标检测
1 南京林业大学林学院, 江苏 南京 210037
2 滁州学院地理信息与旅游学院, 安徽 滁州 239000
3 安徽省地理信息智能感知与服务工程实验室, 安徽 滁州 239000
4 河海大学地球科学与工程学院, 江苏 南京210098
提出一种基于深度对抗域适应的高分辨率遥感影像跨域分类方法。利用深度卷积神经网络VGG16(Visual Geometry Group)学习场景影像的深度特征,然后利用对抗学习方法最小化源域和目标域特征分布差异。利用RSI-CB256(Remote Sensing Image Classification Benchmark)、NWPU-RESISC45(Northwestern Polytechnical University Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification)和AID(Aerial Image data set)数据集构建源域数据集,并将UC-Merced(University of California, Merced)和WHU-RS 19(Wuhan University Remote Sensing)两个数据集作为目标域数据集进行实验,实验结果表明,所提方法在目标域数据集没有标签的情况下,能够提高模型对目标域数据集的泛化能力。
遥感 场景分类 无监督域适应 卷积神经网络 生成对抗网络 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(11): 112801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Ricoh Institute of Information and Communication Technology, Research and Development Division, Ricoh Company, 2-7-1 Izumi, Ebina 243-0460, Japan
2 Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University, 6-6-05 Aoba, Sendai 980-8579, Japan
3 Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, Tohoku University, 6-6-05 Aoba, Sendai 980-8579, Japan
Noninvasive, glucose-monitoring technologies using infrared spectroscopy that have been studied typically require a calibration process that involves blood collection, which renders the methods somewhat invasive. We develop a truly noninvasive, glucose-monitoring technique using midinfrared spectroscopy that does not require blood collection for calibration by applying domain adaptation (DA) using deep neural networks to train a model that associates blood glucose concentration with mid-infrared spectral data without requiring a training dataset labeled with invasive blood sample measurements. For realizing DA, the distribution of unlabeled spectral data for calibration is considered through adversarial update during training networks for regression to blood glucose concentration. This calibration improved the correlation coe±cient between the true blood glucose concentrations and predicted blood glucose concentrations from 0.38 to 0.47. The result indicates that this calibration technique improves prediction accuracy for mid-infrared glucose measurements without any invasively acquired data.
Noninvasive glucose monitoring calibration mid-infrared spectroscopy domain adaptation neural network Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(6): 1850038





