Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Key Laboratory for Biomedical Measurements and Ultrasound Imaging, National-Regional Key Technology Engineering Laboratory for Medical Ultrasound, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, US
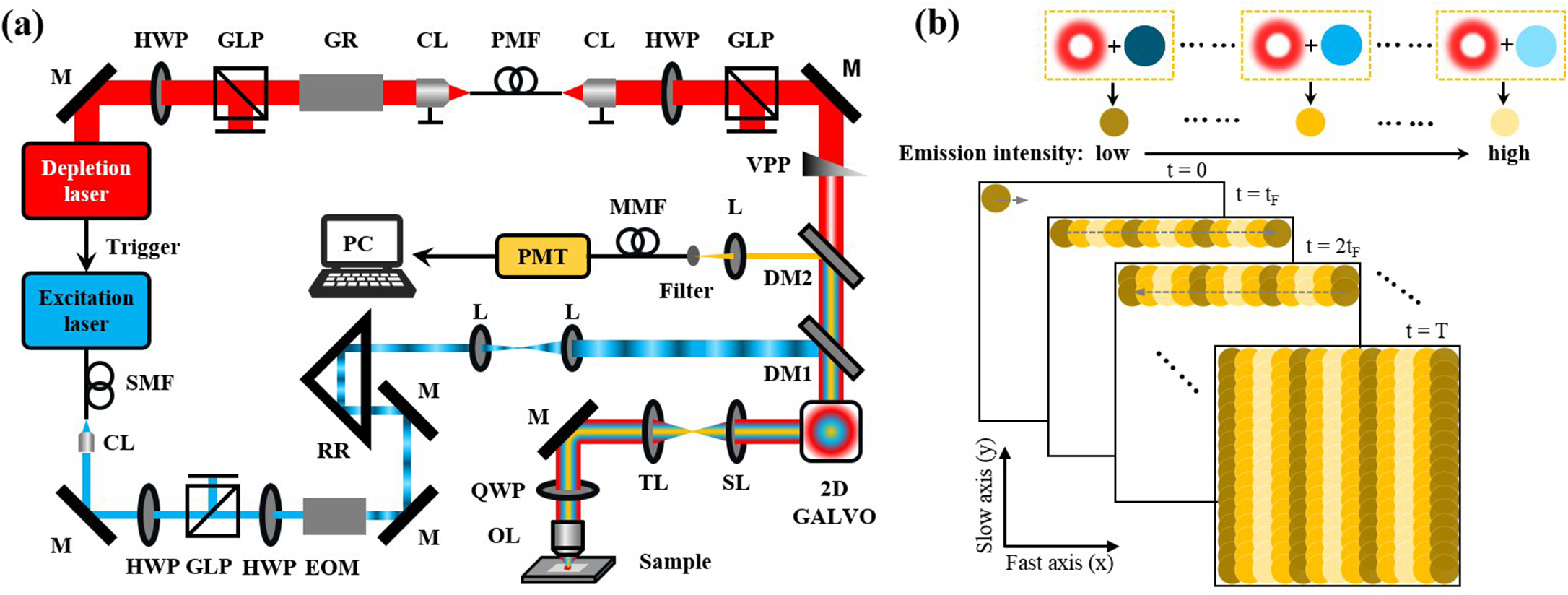
Wide-field linear structured illumination microscopy (LSIM) extends resolution beyond the diffraction limit by moving unresolvable high-frequency information into the passband of the microscopy in the form of moiré fringes. However, due to the diffraction limit, the spatial frequency of the structured illumination pattern cannot be larger than the microscopy cutoff frequency, which results in a twofold resolution improvement over wide-field microscopes. This Letter presents a novel approach in point-scanning LSIM, aimed at achieving higher-resolution improvement by combining stimulated emission depletion (STED) with point-scanning structured illumination microscopy (psSIM) (STED-psSIM). The according structured illumination pattern whose frequency exceeds the microscopy cutoff frequency is produced by scanning the focus of the sinusoidally modulated excitation beam of STED microscopy. The experimental results showed a 1.58-fold resolution improvement over conventional STED microscopy with the same depletion laser power.
stimulated emission depletion structured illumination microscopy superresolution microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031701
戴太强 1,2,3,4高晔 1,2,3,4马英 5蔡卜磊 1,2,3,4[ ... ]孔亮 1,2,3,4,*
1 军事口腔医学国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710032
2 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,陕西 西安 710032
3 陕西省口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,陕西 西安 710032
4 第四军医大学口腔医院 颌面外科,陕西 西安 710032
5 西安电子科技大学 物理学院,陕西 西安 710171
观察细胞器间动态相互作用,深入分析作用规律,对于揭示生理病理过程现象背后的机制具有十分重要的意义。传统光学显微镜受到由光波波长和孔径造成的衍射极限的限制,无法观测细胞器纳米级精细结构及细胞器间相互作用的动态变化规律。超分辨显微成像技术的出现为细胞器相互作用研究提供了重要手段,在深入揭示细胞器相互作用规律,阐明生理病理现象深层的机制研究中发挥了重要的作用。文中介绍了受激发射损耗(Stimulated emission depletion, STED)显微成像、结构光照明显微成像(Structured illumination microscopy, SIM)、单分子定位显微成像(Single molecule localization microscopy, SMLM)技术,并总结了这三类超分辨显微成像技术在细胞器相互作用中的应用与现状,为超分辨显微成像技术在细胞器相互作用研究中的应用提供思路拓展。最后,对超分辨显微成像技术在细胞器相互作用研究中的优势与不足进行分析总结,展望了超分辨显微成像技术在活细胞内细胞器相互作用成像中的需求发展趋势,为光学与医学及生物学的交叉融合发展提供一定的参考。
超分辨显微成像 细胞器间相互作用 受激发射损耗显微成像 结构光照明显微成像 单分子定位显微成像 super-resolution microscopy organelle interaction stimulated emission depletion microscopy structured illumination microscopy single molecule localization microscopy 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(11): 20220622
超分辨显微成像技术是生物医学领域的重要成像工具,它通过突破光学衍射的极限,以纳米级尺度解析大脑神经元的结构,其在活体大脑成像中的应用对于神经科学的发展具有重要影响。由于组织光散射、生物相容性、成像系统兼容性等因素,超分辨显微成像技术在活体大脑成像的深度、速度、时间等方面都受到限制。基于传统的双光子显微成像策略,本文介绍了目前应用于活体大脑成像的受激发射损耗显微成像和结构光照明显微成像的研究进展,分析了它们存在的困难和挑战,最后总结了应对挑战的思路并对未来的发展进行了展望。
中国激光
2022, 49(20): 2007301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, Shanghai 200120, China
4 Engineering Research Center of Optical Instrument and Systems, Ministry of Education and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
A stimulated emission depletion is capable of breaking the diffraction limit by exciting fluorescent molecules with a solid Gaussian beam and quenching the excited molecules with another donut beam through stimulated emission. The coincidence degree of these two beams in three dimensions will significantly influence the spatial resolution of the microscope. However, the conventional alignment approach based on raster scanning of gold nanoparticles by the two laser beams separately suffers from a mismatch between fluorescence and scattering modes. To circumvent the above problems, we demonstrate a fast alignment design by scanning the second beam over the fabricated sample, which is made of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) dye resin. The relative positions of solid and donut laser beams can be represented by the fluorescent AIE from the labeled spots in the dye resin. This design achieves ultra-high resolutions of 22 nm in the x/y relative displacement and 27 nm in the z relative displacement for fast spatial matching of the two laser beams. This study has potential applications in scenarios that require the spatial matching of multiple laser beams, and the field of views of different objectives, for example, in a microscope with high precision.
nanophotonics stimulated emission depletion microscope aggregation-induced emission dual-beam alignment Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(11): 113601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Hematology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China
2 Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering of Hainan Province, School of Biomedical Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
Hematologic malignancies are one of the most common malignant tumors caused by the clonal proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic and lymphoid stem cells. The examination of bone marrow cells combined with immunodeflciency typing is of great signiflcance to the diagnostic type, treatment and prognosis of hematologic malignancies. Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy (SRM) is a special kind of optical microscopy technology, which breaks the resolution limit and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2014. With the development of SRM, many related technologies have been applied to the diagnosis and treatment of clinical diseases. It was reported that a major type of SRM technique, single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM), is more sensitive than flow cytometry (FC) in detecting cell membrane antigens' expression, thus enabling better chances in detecting antigens on hematopoietic cells than traditional analytic tools. Furthermore, SRM may be applied to clinical pathology and may guide precision medicine and personalized medicine for clone hematopoietic cell diseases. In this paper, we mainly discuss the application of SRM in clone hematological malignancies.
Hematologic malignancies super-resolution fluorescence microscopy structured illumination microscopy stimulated emission depletion microscopy single molecule localization microscopy Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2022, 15(2): 2230005
1 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院现代光学仪器国家重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310027
2 之江实验室超级感知研究中心,浙江 杭州 310023
3 暨南大学光子技术研究院广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 510000
利用边缘光抑制技术,设计并研制了一套双光束激光三维直写光刻系统。该系统含有高速扫描振镜和三维纳米压电平台两组扫描机构,可以根据不同加工需求完成多种扫描模式下的微纳结构制造。分析了光刻光束中激发光与抑制光的能量变化对加工精度的影响,通过对光刻光束能量的精确控制,实现了基板表面最小线宽为64 nm的均匀线条和线宽为30 nm的悬浮线的稳定加工,加工结构的线宽变化符合理论预期。该系统在进行实用器件加工时,最高加工产率可达到0.6 mm2/min。使用该系统加工制造了多种微纳结构,证实了其具备加工大深宽比周期结构、复杂曲线结构和不规则三维结构的能力。
激光技术 光学制造 受激发射损耗 激光直写 微纳光学器件
1 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院现代光学仪器国家重点实验室, 浙江 杭州310027
2 浙江大学宁波技术研究所, 浙江 宁波315100
3 之江实验室, 浙江 杭州311121
超分辨显微成像技术是细胞生物学中研究细胞器结构、相互作用和蛋白质功能的强大工具,其具有突破光学衍射极限的分辨能力,从纳米尺度上为细胞生物学提供了新的分析手段,对生命科学相关领域具有重大意义。然而,受衍射极限的影响,超分辨显微镜的轴向分辨率相比于横向分辨率要更难以提高,这导致实现细胞结构亚百纳米分辨率的三维成像更为困难。从受激辐射损耗显微术和单分子定位显微术这两种主流技术出发,对目前存在的多种三维成像技术进行了原理介绍和特点分析,最后对其未来发展方向进行了展望。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(22): 2200001
北京工业大学生命科学与生物医学工程学院, 智能化生理测量与临床转化北京市国际科技合作基地, 北京 100024
并行受激发射损耗(STED)显微术采用周期性排列的光学格子作为荧光抑制图案并行实现多点荧光擦除,可以有效地提升显微成像的时间分辨率。本文建立了并行STED显微成像系统的简化光学系统模型,在此基础上推导出受光学参数影响的并行荧光擦除图案周期公式,来阐明辅助物镜及显微物镜对该周期的影响机理。由该公式,解出了能产生更小周期并行荧光擦除图案的最优光学参数。数值仿真结果显示,本文方法能产生出周期小至276 nm×276 nm的正方形网格状并行荧光擦除图案。
显微 荧光显微镜 并行受激发射损耗 荧光擦除图案 光学系统参数 数值仿真 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(9): 091801





