2023, 21(10) Column
Atmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental Optics Atomic and Molecular Optics Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Imaging Systems and Image Processing Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Optical Materials Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics Quantum Optics and Quantum Information X-ray Optics Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第21卷 第10期
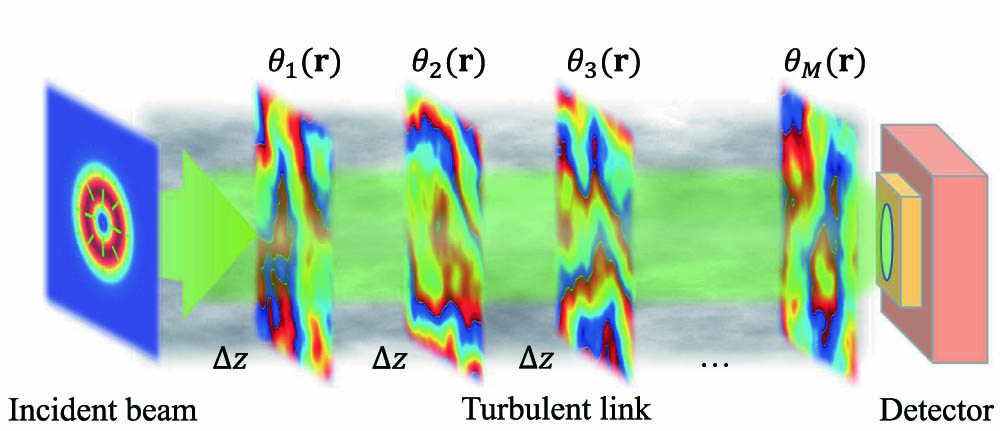
We introduce the Stokes scintillation indices and the corresponding overall Stokes scintillations for quantitatively studying the fluctuations of both the intensity and polarization of an optical vector beam transmitting through the atmospheric turbulence. With the aid of the multiple-phase-screen method, we examine the Stokes fluctuations of a radially polarized beam in Kolmogorov turbulence numerically. The results show that the overall scintillation for the intensity distribution is always larger than the overall scintillation for the polarization-dependent Stokes parameters, which indicates that the polarization state of a vector beam is stabler than its intensity distribution in the turbulence. We interpret the results with the depolarization effect of the vector beam in turbulence. The findings in this work may be useful in free-space optical communications utilizing vector beams.
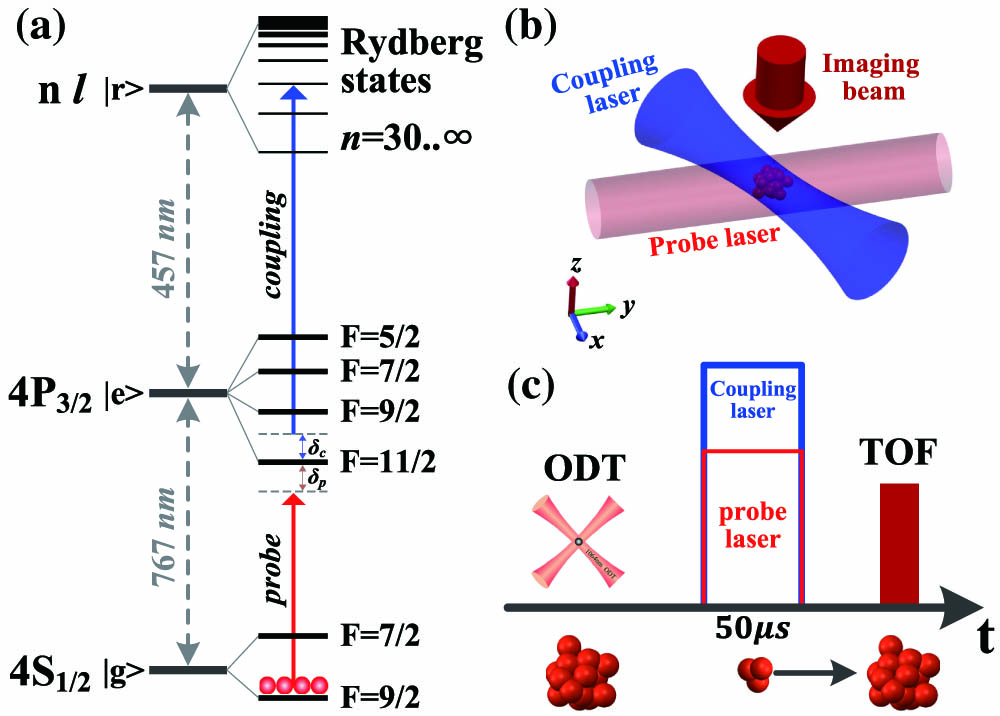
Stokes scintillations atmospheric turbulence vector beams polarization of light We report the measurement of the electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) with Rydberg states in ultracold
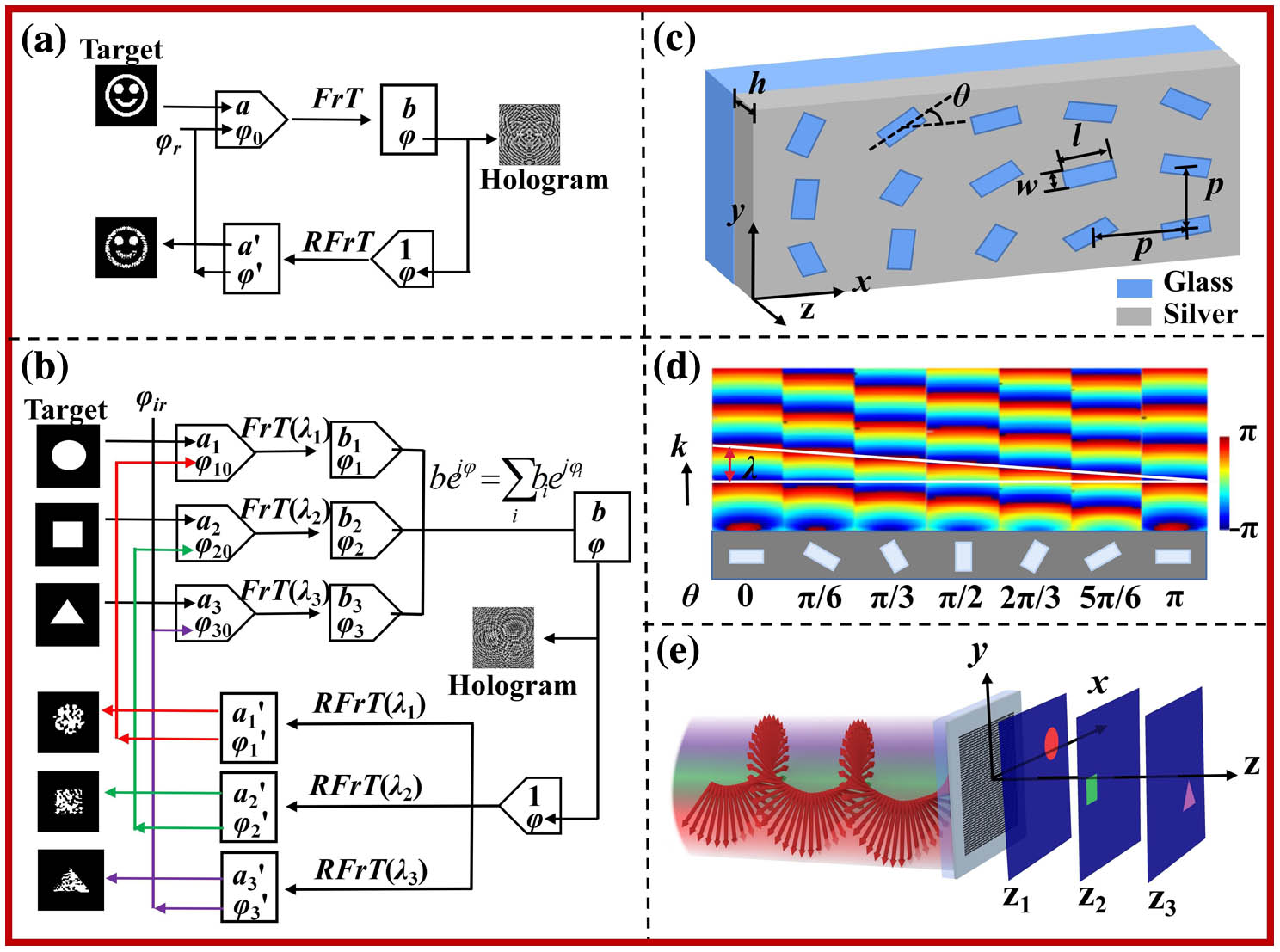
atomic and molecular physics hyperfine structure Rydberg states In light of the powerful light manipulation ability of holographic metasurfaces, optical imaging with wavelength multiplexing and polarization multiplexing is performed in this paper. The metasurface is composed of identical rectangular nanoholes etched in silver film. Three imaging effects, including the in-plane color imaging, three-dimensional wavelength-encrypted imaging, and polarization-multiplexing wavelength-encrypted imaging, are realized. The designed metasurface has compact structure, and the obtained image has lower noise. The simulation and experiment results give the verification. Multiple images, including spatial multiplexing, wavelength multiplexing, and polarization multiplexing, exhibit immense potentialities of metasurfaces, and this work is helpful for expanding the applications of metasurfaces.
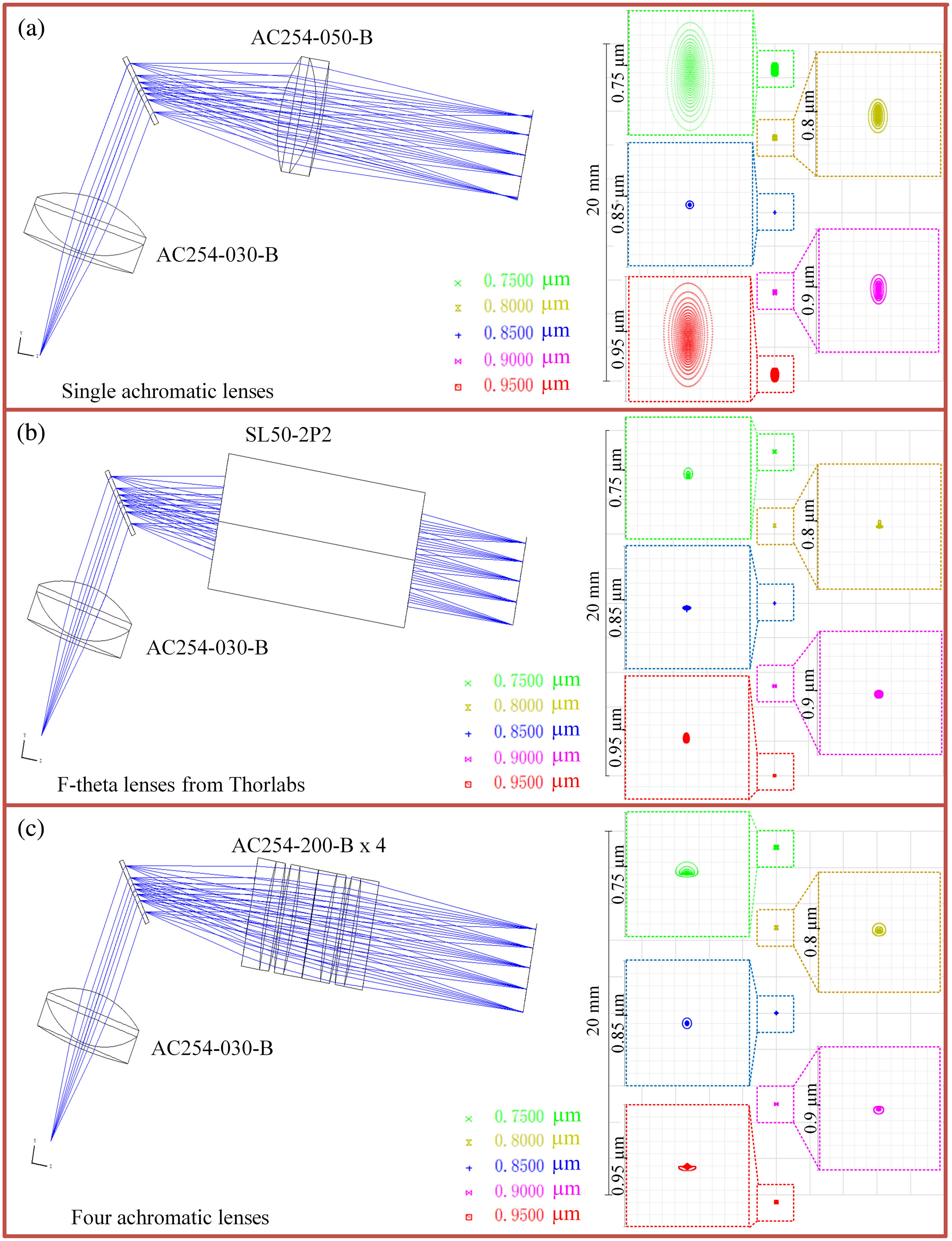
metasurface holography optical encryption color imaging In this Letter, we present a low-cost, high-resolution spectrometer design for ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography (UHR-OCT), in which multiple standard achromatic lenses are combined to replace the expensive F-theta lens to achieve a comparable performance. For UHR-OCT, the spectrometer plays an important role in high-quality 3D image reconstruction. Typically, an F-theta lens is used in spectrometers as the Fourier lens to focus the dispersed light on the sensor array, and this F-theta lens is one of the most expensive components in spectrometers. The advantage of F-theta lens over the most widely used achromatic lens is that the aberrations (mainly spherical aberration, SA) are corrected, so the foci of the dispersed optical beams (at different wavelengths) with different incident angles could be placed on the sensor array simultaneously. For the achromatic lens, the foci of the center part of the spectrum are farther than those on the side in the longitudinal direction, causing degradations of the spectral resolution. Furthermore, in comparison with the achromatic lens with the same focal length, those with smaller diameters have stronger SA, but small lenses are what we need for making spectrometers compact and stable. In this work, we propose a simple method of using multiple long-focal-length achromatic lenses together to replace the F-theta lens, which is
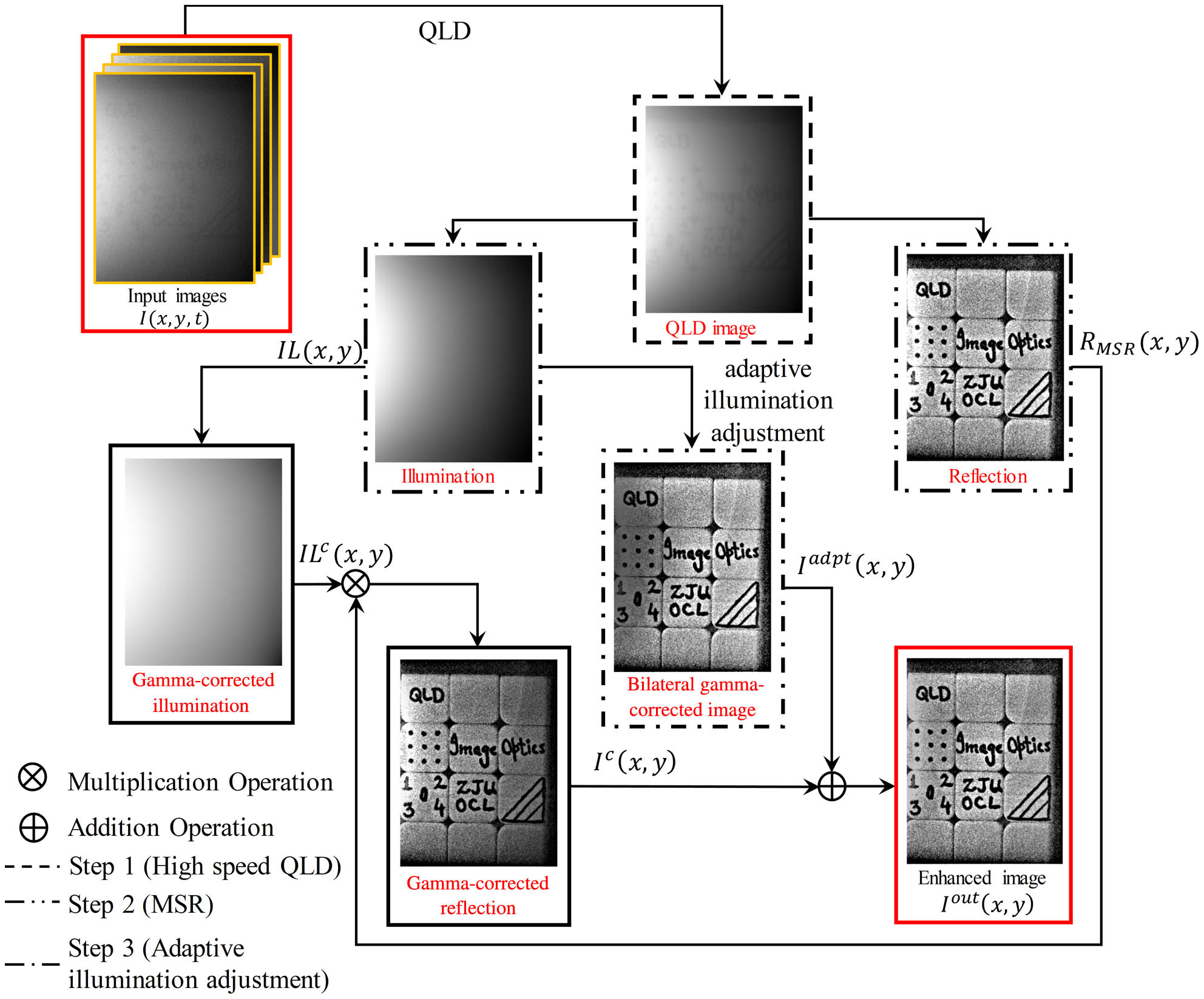
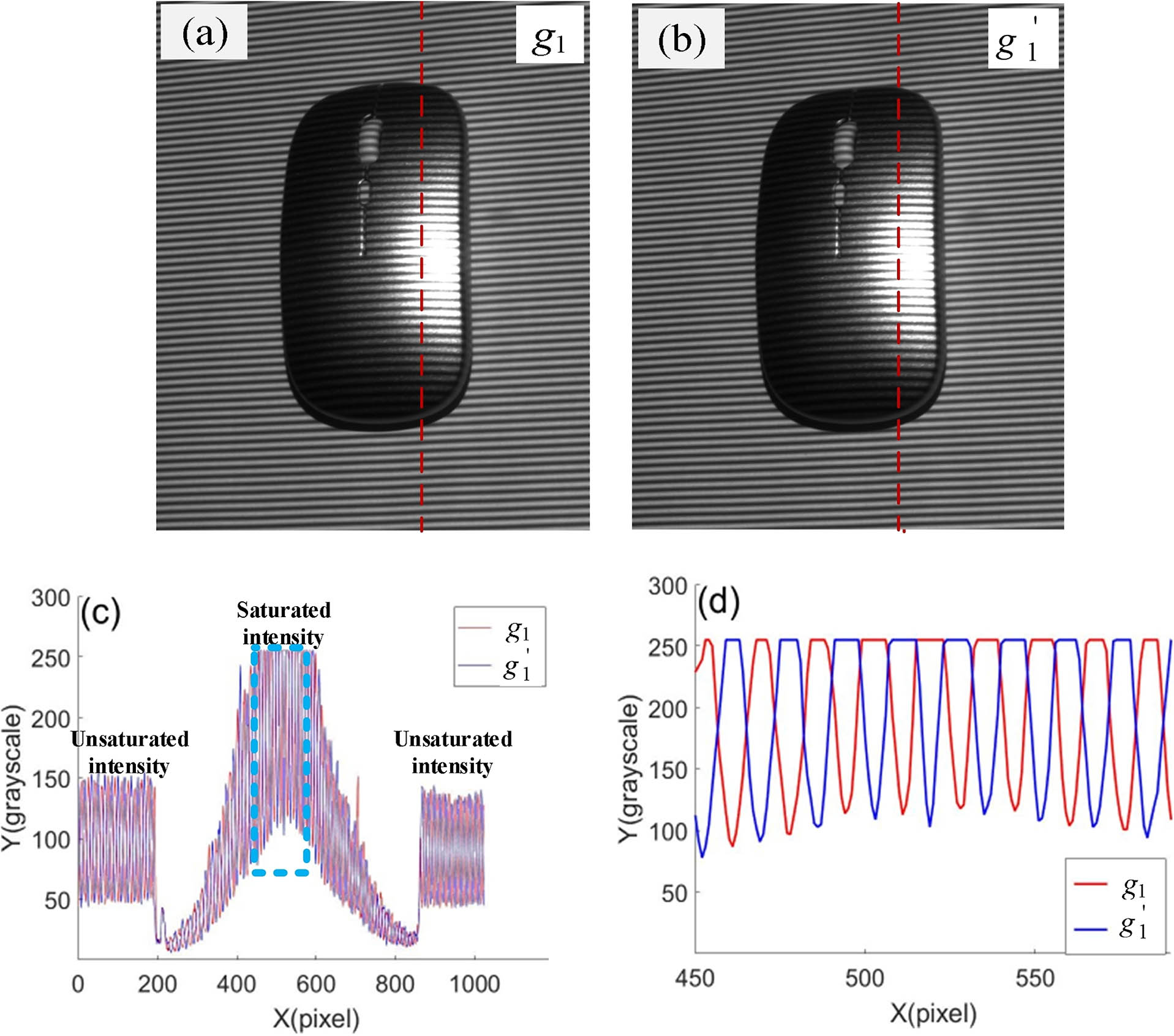
low-cost spectrometer optical coherence tomography spherical aberration suppression ultrahigh-resolution non-invasive imaging This paper presents an improved method for imaging in turbid water by using the individual strengths of the quadrature lock-in discrimination (QLD) method and the retinex method. At first, the high-speed QLD is performed on images, aiming at capturing the ballistic photons. Then, we perform the retinex image enhancement on the QLD-processed images to enhance the contrast of the image. Next, the effect of uneven illumination is suppressed by using the bilateral gamma function for adaptive illumination correction. The experimental results depict that the proposed approach achieves better enhancement than the existing approaches, even in a high-turbidity environment.
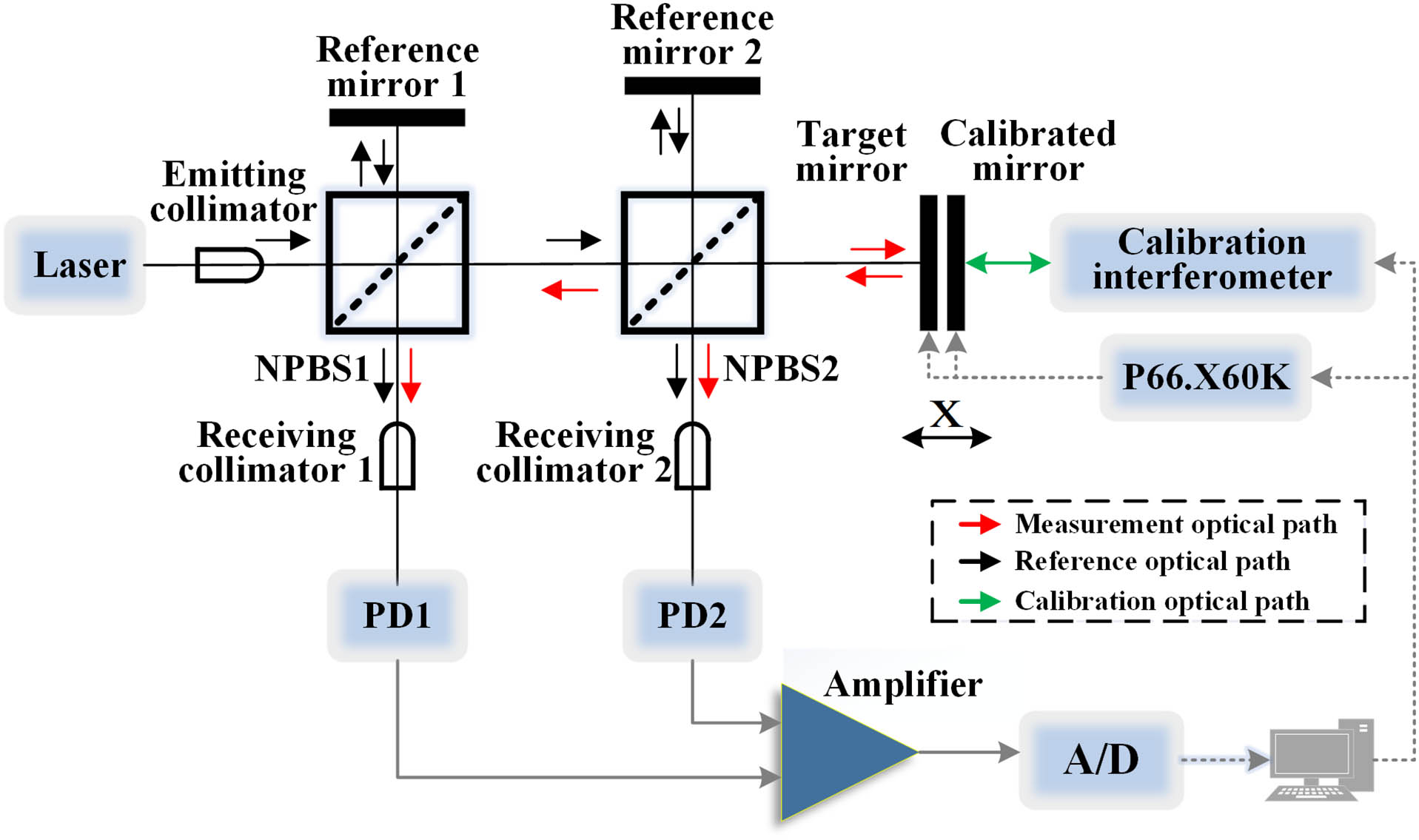
quadrature lock-in discrimination clear vision scattering retinex uneven illumination In this Letter, we propose a simple structure of an orthogonal type double Michelson interferometer. The orthogonal detection method overcomes the problems of uneven ranging sensitivity and the inability of traditional interferometers to determine the displacement direction. The displacement measurement principle and signal processing method of the orthogonal double interferometer are studied. Unlike the arctangent algorithm, the displacement analysis uses the arc cosine algorithm, avoiding any pole limit in the distance analysis process. The minimum step size of the final experimental displacement system is 5 nm, which exhibits good repeatability, and the average error is less than 0.12 nm.
orthogonal detection nanoscale displacement measurement laser interferometer We propose a method for reconstructing non-diffuse surfaces based on the
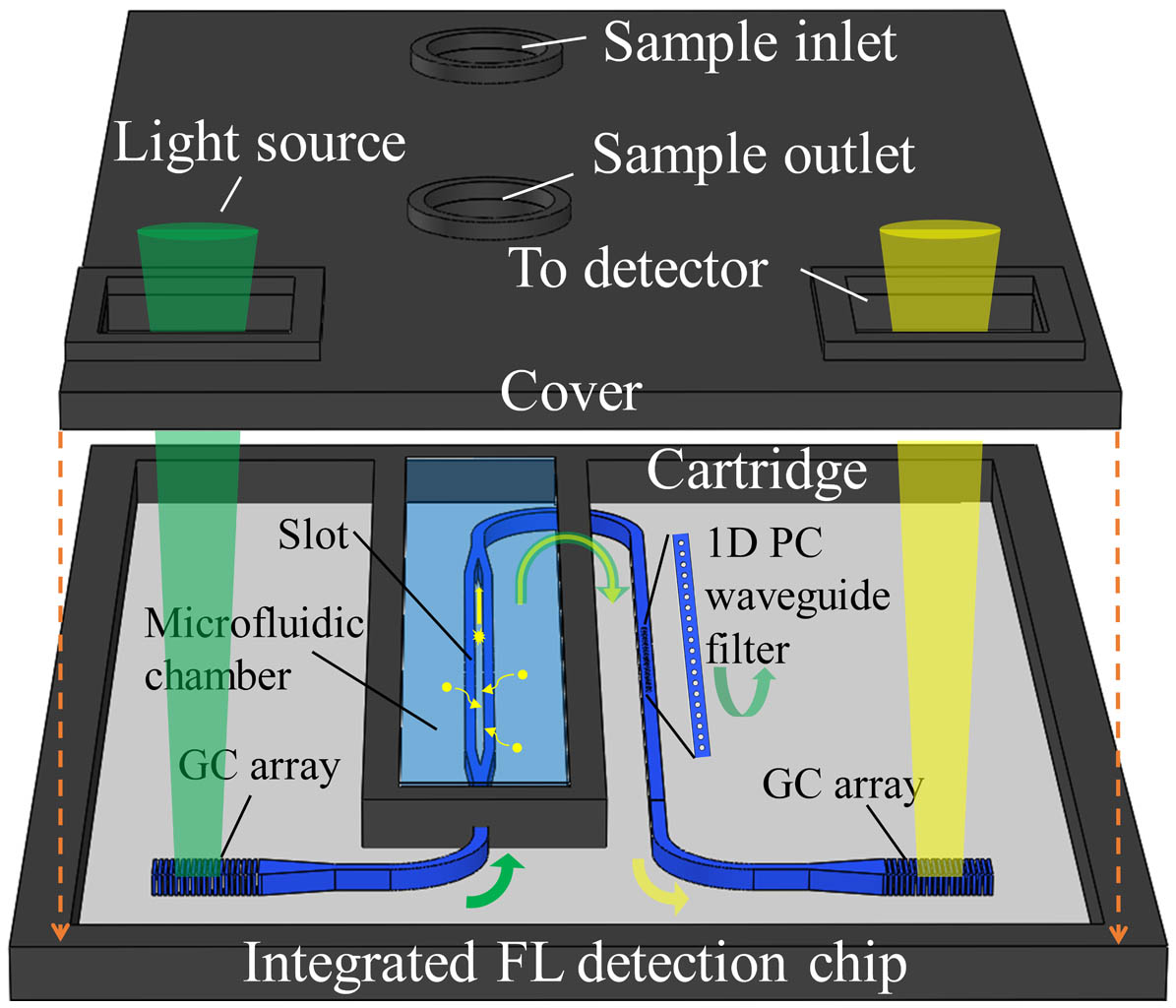
non-diffusion π-phase shift two-plus-one phase shift Fluorescence detection is widely used in biology and medicine, while the realization of on-chip fluorescence detection is vital for the portable and point-of-care test (POCT) application. In this Letter, we propose an efficient fluorescence excitation and collection system using an integrated GaN chip consisting of a slot waveguide and a one-dimensional photonic crystal (1D PC) waveguide. The slot waveguide is used to confine the excitation light for intense light–sample interaction, and the one-trip collection efficiency at the end of slot waveguide is up to 14.65%. More interestingly, due to the introduction of the 1D PC waveguide, the fluorescence signal is directly filtered out, and the excitation light is reflected to the slot waveguide for multiple excitations. Its transmittances for the designed exciting wavelength of 520 nm and the fluorescent wavelength of 612 nm are 0.2% and 85.4%, respectively. Finally, based on numerical analysis, the total fluorescence collection efficiency in our system amounts to 15.93%. It is the first time, to our knowledge, that the concept of an all-in-one-chip fluorescence detection system has been proposed, which paves the way for on-chip fluorescence excitation and collection, and may find potential applications of miniaturized and portable devices for biomedical fluorescence detection.
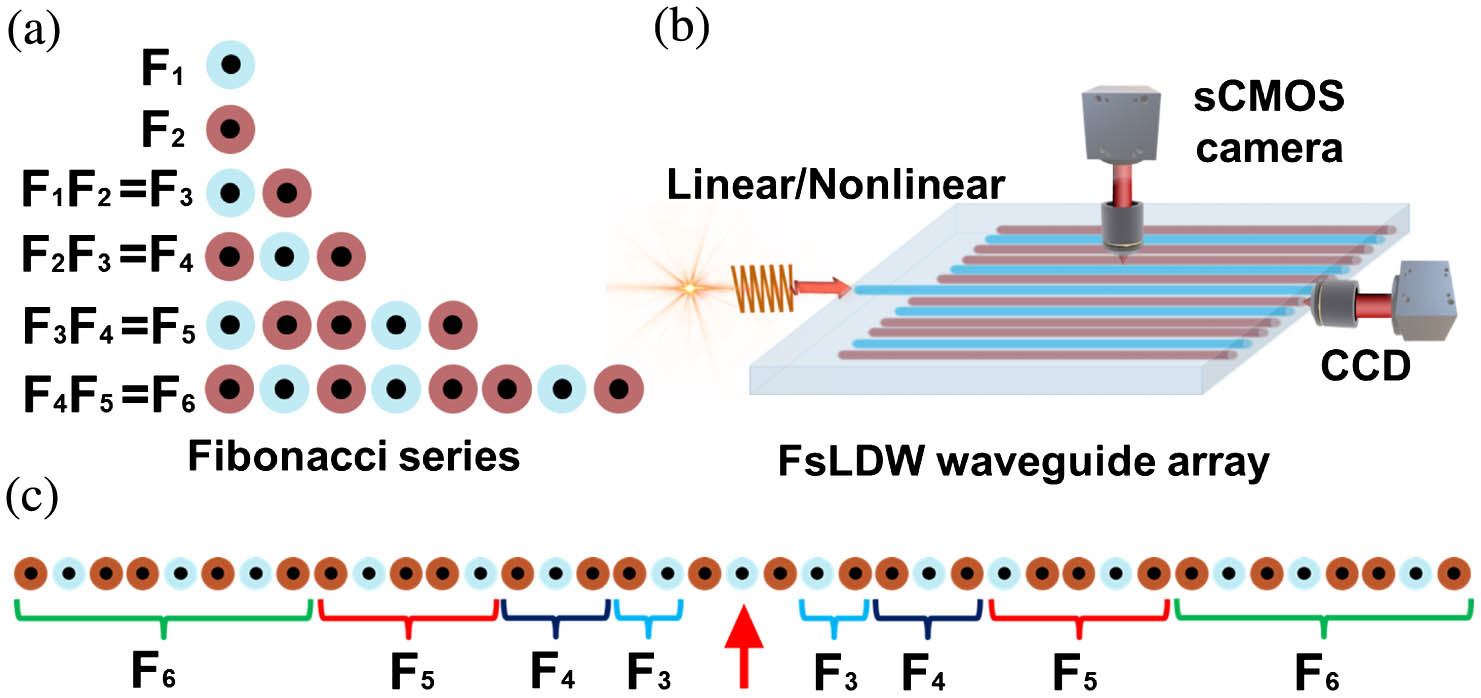
fluorescence slot waveguide photonic crystal on-chip Based on the one-dimensional periodic and Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays, we experimentally investigate localized quantum walks (QWs), both in the linear and nonlinear regimes. Unlike the ballistic transport behavior in conventional random QWs, localization of QWs is obtained in the Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays both theoretically and experimentally. Moreover, we verify the enhancement of the localization through nonlinearity-induced effect. Our work provides a valid way to study localization enhancement in QWs, which might broaden the understanding of nonlinearity-induced behaviors in quasi-periodic systems.
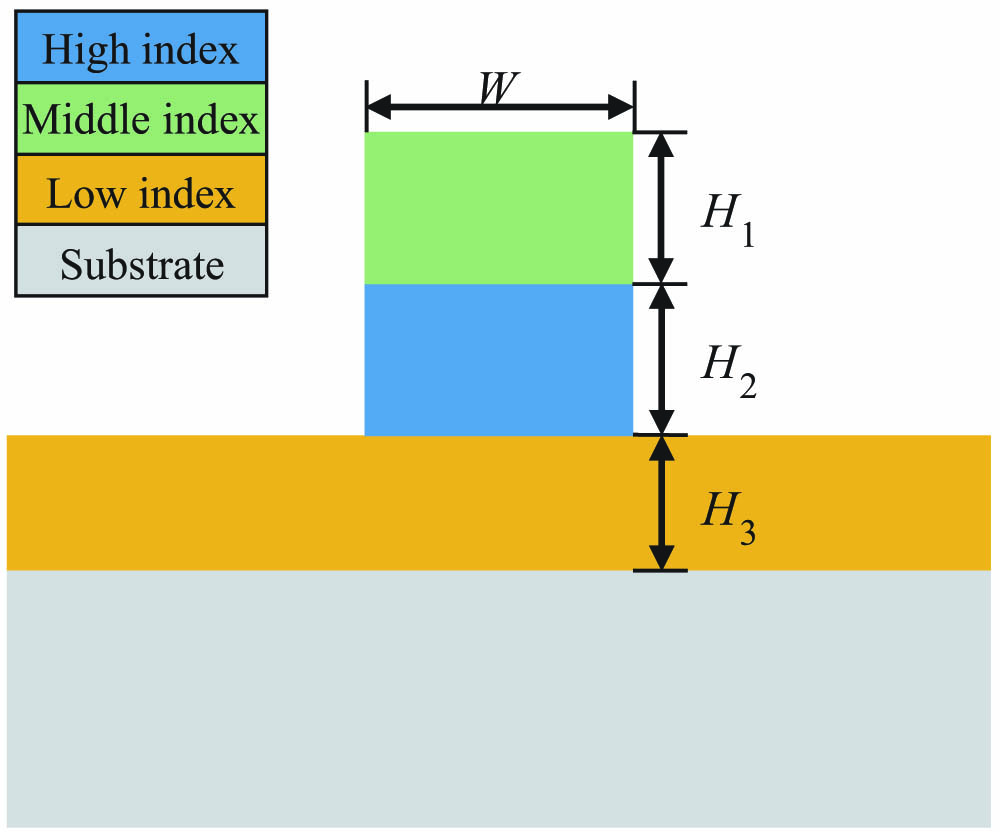
Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays nonlinearity-induced effect localization enhancement We propose a new type of dispersion-flattened waveguide without a slot-assisted structure that can obtain an ultra-flat group velocity dispersion profile with five or six zero-dispersion wavelengths in the mid-infrared region. The dispersion profile becomes less sensitive to the waveguide dimensions due to the absence of the slot-assisted structure, making waveguide fabrication more friendly. The dispersion profile varies between
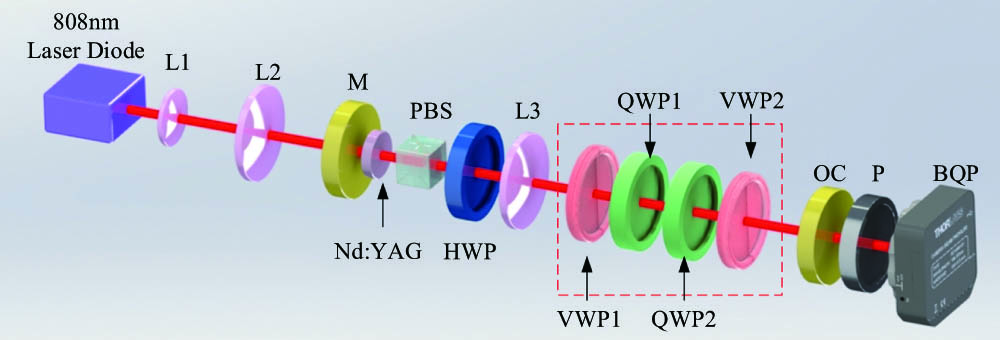
integrated optical devices waveguides dispersion We reporte and demonstrate a solid-state laser to achieve controlled generation of order-switchable cylindrical vector beams (CVBs). In the cavity, a group of vortex wave plates (VWPs) with two quarter-wave plates between the VWPs was utilized to achieve mode conversion and order-switch of CVBs. By utilizing two VWPs of first and third orders, the second and fourth order CVBs were obtained, with mode purities of 96.8% and 94.8%, and sloping efficiencies of 4.45% and 3.06%, respectively. Furthermore, by applying three VWPs of first, second, and third orders, the mode-switchable Gaussian beam, second, fourth, and sixth order CVBs were generated.
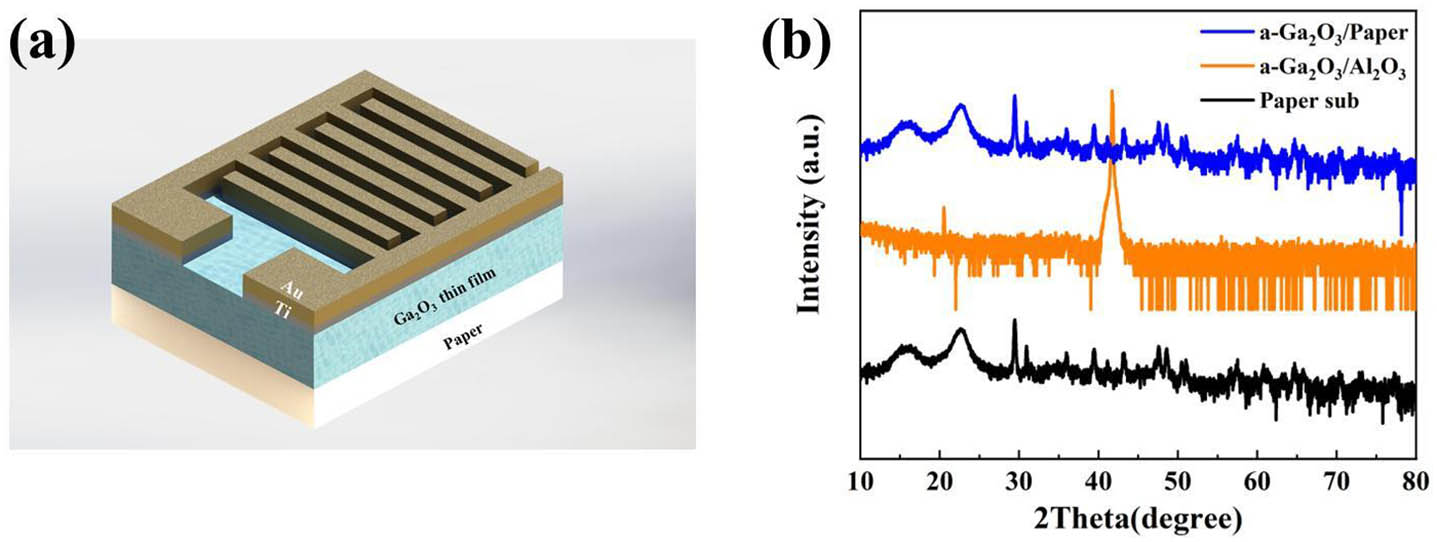
cylindrical vector beams order-switchable beams vortex wave plates solid-state laser Flexible devices provide advantages such as conformability, portability, and low cost. Paper-based electronics offers a number of advantages for many applications. It is lightweight, inexpensive, and biodegradable, making it an ideal choice for disposable electronics. In this work, we propose a novel configuration of photodetectors using paper as flexible substrates and amorphous
amorphous Ga2O3 flexible photodetector solar-blindness paper We developed a general framework for parallel all-optical logic operations with independent phase control of arbitrary orthogonal polarization state enabled by a single-layer metasurface. A pair of orthogonal circular polarized bases are used as two input channels of the logic operator, and their four combinations perfectly match various binary input states. Correspondingly, distinct phase profiles are encoded into the metasurface, which enables parallel operation of the two logic gates by way of polarization switching. It allows for an efficient and compact way to implement multi-channel multiplexed logic gate operations with the capability of fast optical computing at the chip scale.
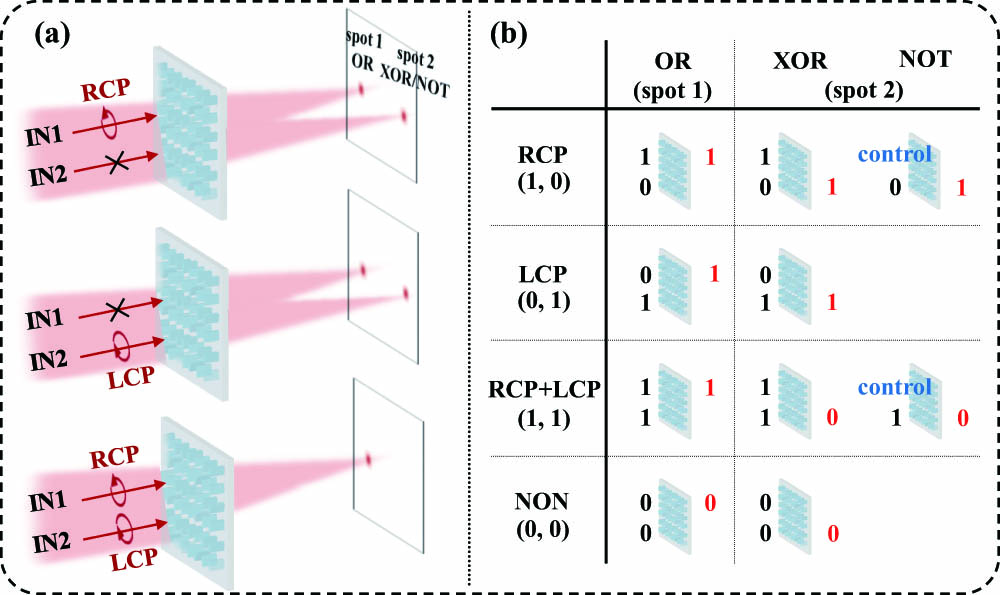
parallel all-optical logic operation metasurface polarization Review of advanced progress of χ2-based all-optical devices on thin-film lithium niobate Download:506次
Download:506次
 Download:506次
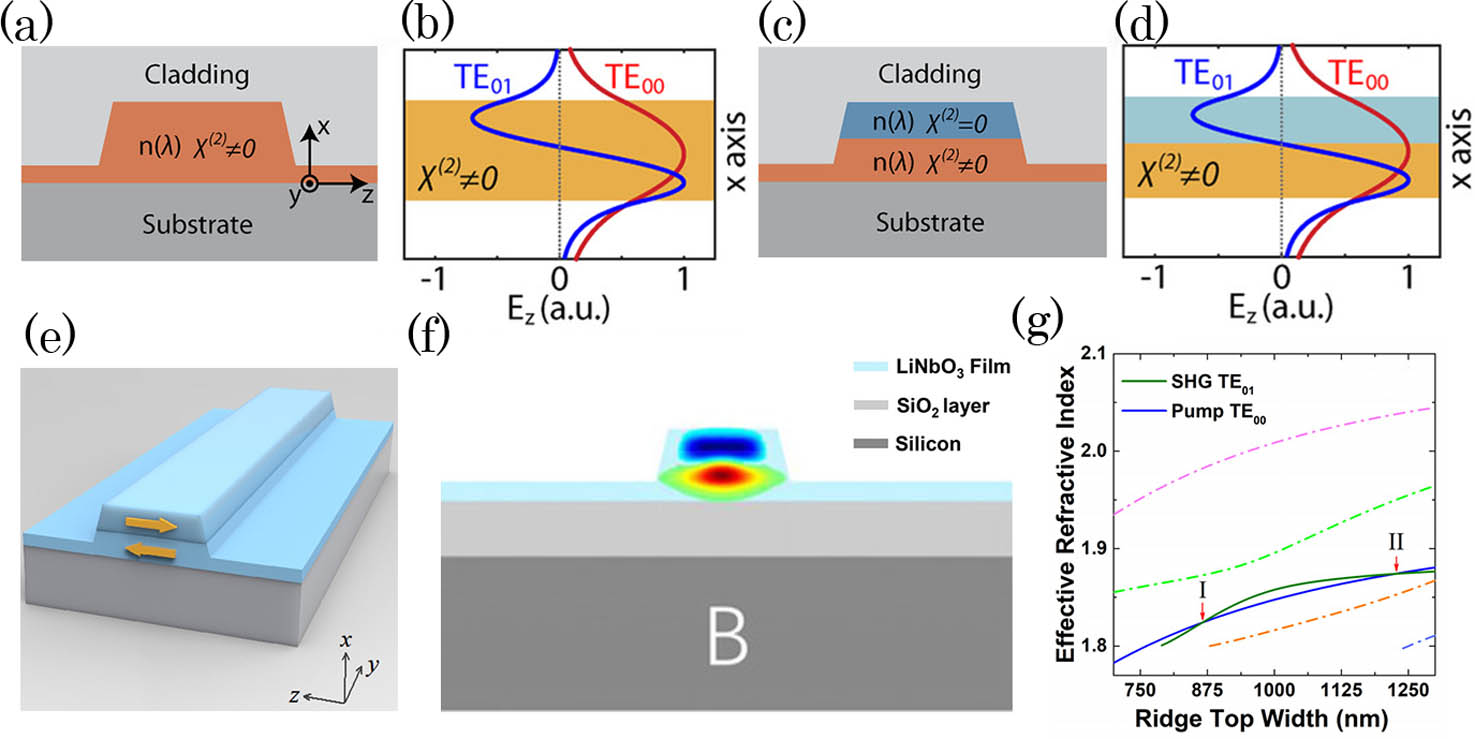
Download:506次The technological innovation of thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) is supplanting the traditional lithium niobate industry and generating a vast array of ultra-compact and low-loss optical waveguide devices, providing an unprecedented prospect for chip-scale integrated optics. Because of its unique strong quadratic nonlinearity, TFLN is widely used to create new coherent light, which significantly promotes all-optical signal processes, especially in terms of speed. Herein, we review recent advances in TFLN, review the thorough optimization strategies of all-optical devices with unique characteristics based on TFLN, and discuss the challenges and perspectives of the developed nonlinear devices.
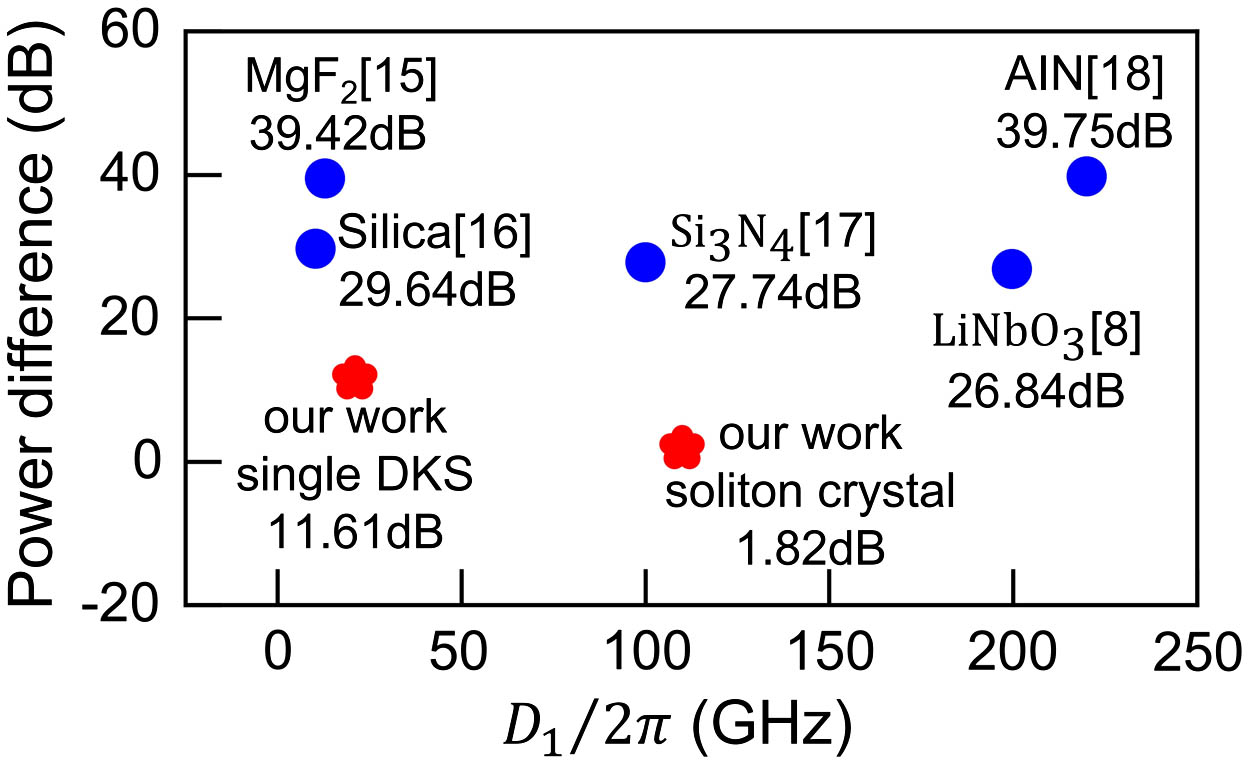
thin-film lithium niobate second-order nonlinearity nonlinear integrated optics The nonlinear physics dynamics of temporal dissipative solitons in a microcavity hinder them from attaining high power from pump lasers with a typical nonlinear energy conversion efficiency of less than 1%. Here, we experimentally demonstrate a straightforward method for improving the output power of soliton combs using a silica microrod cavity with high coupling strength, large mode volume, and high-Q factor, resulting in a low-repetition-rate dissipative soliton (
optical microcavity nonlinear optics temporal soliton Generation of shaping nondiffracting structured caustic beams on the basis of stationary phase principle Download:505次
Download:505次
 Download:505次
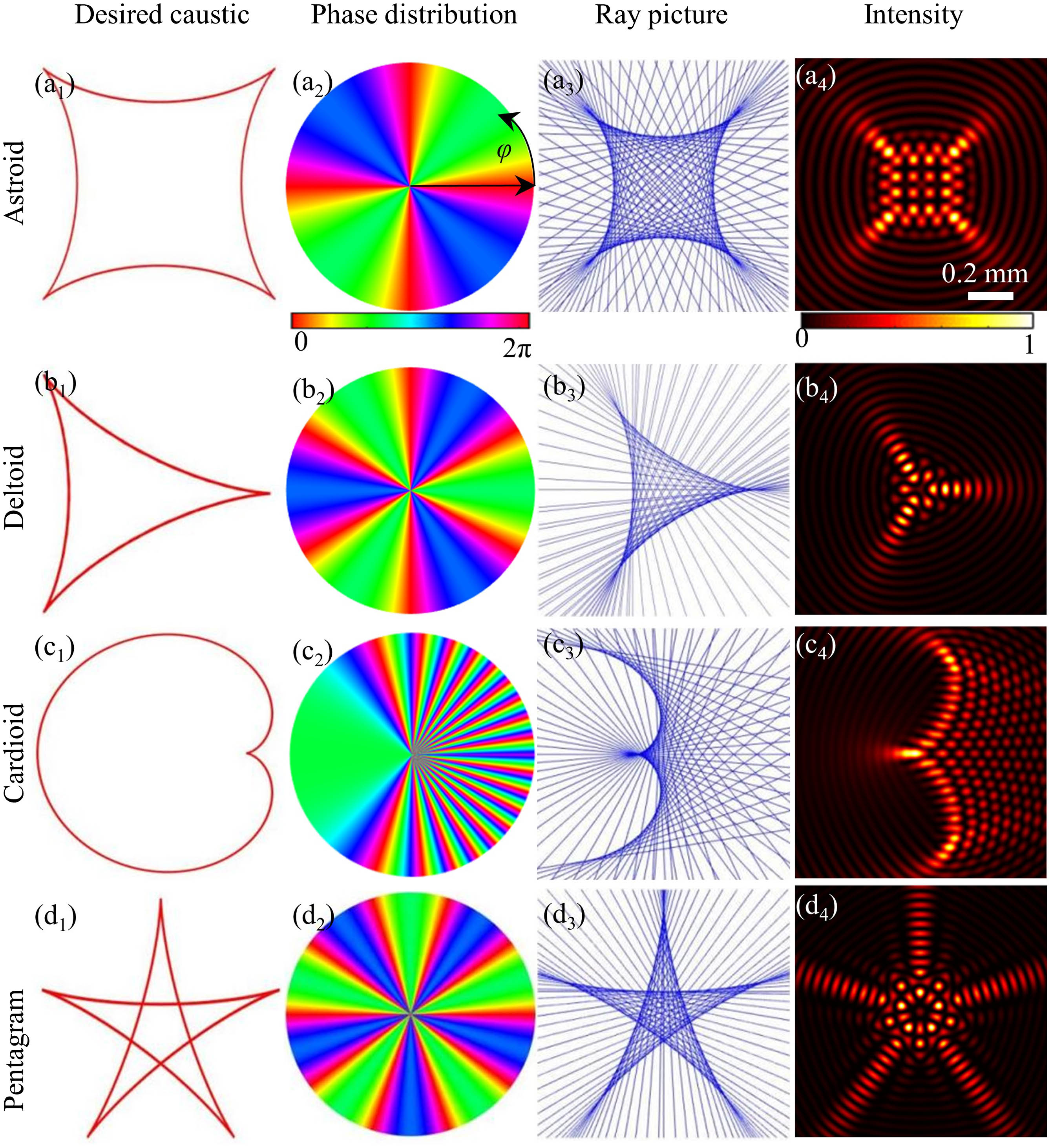
Download:505次On the basis of the stationary phase principle, we construct a family of shaping nondiffracting structured caustic beams with the desired morphology. First, the analytical formula of a nondiffracting astroid caustic is derived theoretically using the stationary phase method. Then, several types of typical desired caustics with different shapes are numerically simulated using the obtained formulas. Hence, the key optical structure and propagation characteristics of nondiffracting caustic beams are investigated. Finally, a designed phase plate and an axicon are used to generate the target light field. The experimental results confirm the theoretical prediction. Compared with the classical method, the introduced method for generating nondiffracting caustic beams is high in light-energy utilization; hence, it is expected to be applied conveniently to scientific experiments.
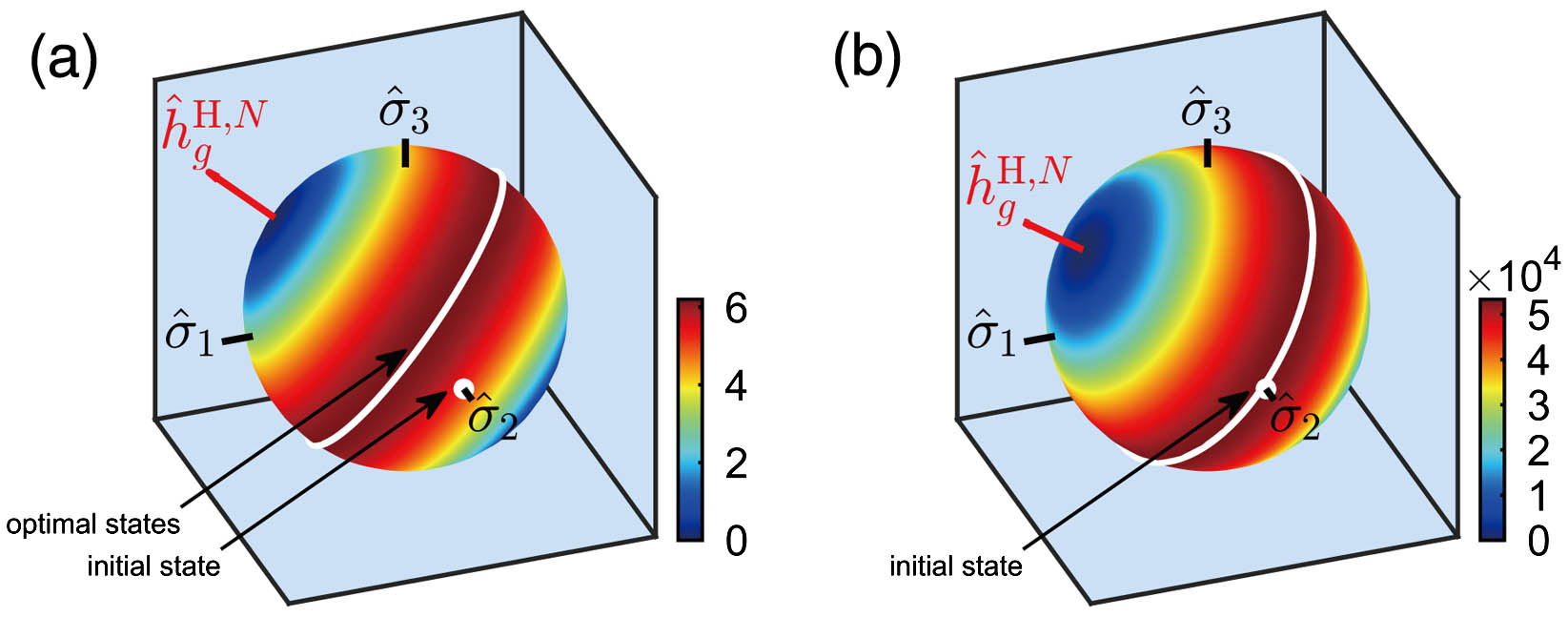
nondiffracting structured caustic beams phase plate stationary phase method axicon Quantum parameter estimation is a crucial tool for inferring unknown parameters in physical models from experimental data. The Jaynes–Cummings model is a widely used model in quantum optics that describes the interaction between an atom and a single-mode quantum optical field. In this Letter, we systematically investigate the problem of estimating the atom-light coupling strength in this model and optimize the initial state in the full Hilbert space. We compare the precision limits achievable for different optical field quantum states, including coherent states, amplitude- and phase-squeezed states, and provide experimental suggestions with an easily prepared substitute for the optimal state. Our results provide valuable insights into optimizing quantum parameter estimation in the Jaynes–Cummings model and can have practical implications for quantum metrology with hybrid quantum systems.
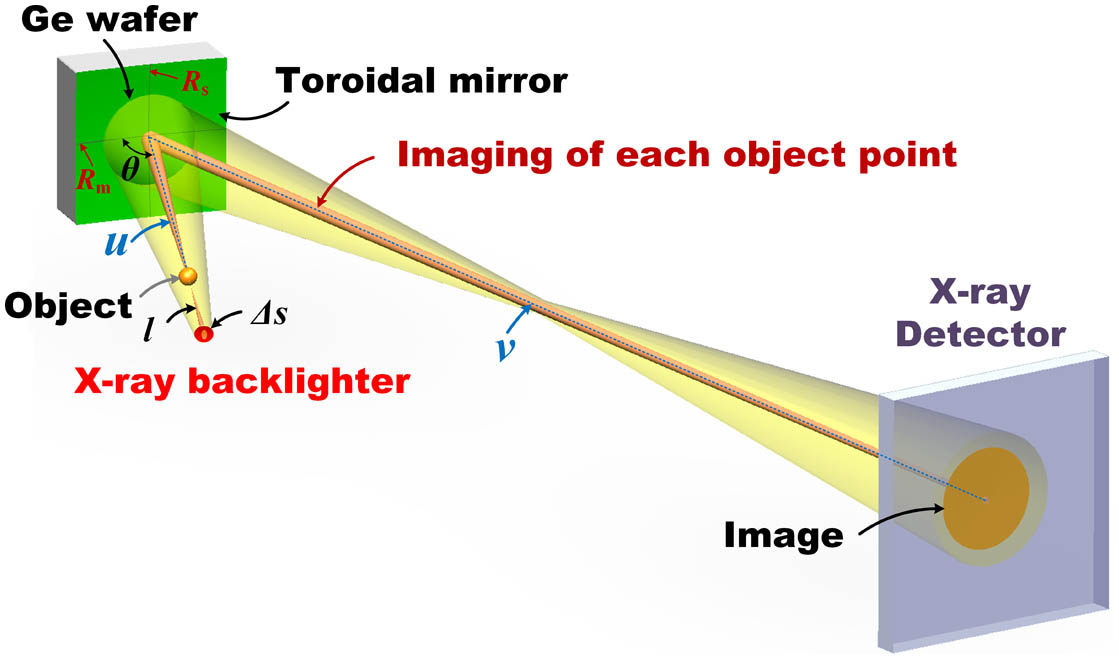
quantum Fisher information Jaynes–Cummings model parameter estimation theory Curved crystal imaging is an important means of plasma diagnosis. Due to the short wavelengths of high-energy X rays and the fixed lattice constant of the spherical crystal, it is difficult to apply the spherical crystal in high-energy X-ray imaging. In this study, we have developed a high-energy, high-resolution X-ray imager based on a toroidal crystal that can effectively correct astigmatism. We prepared a Ge
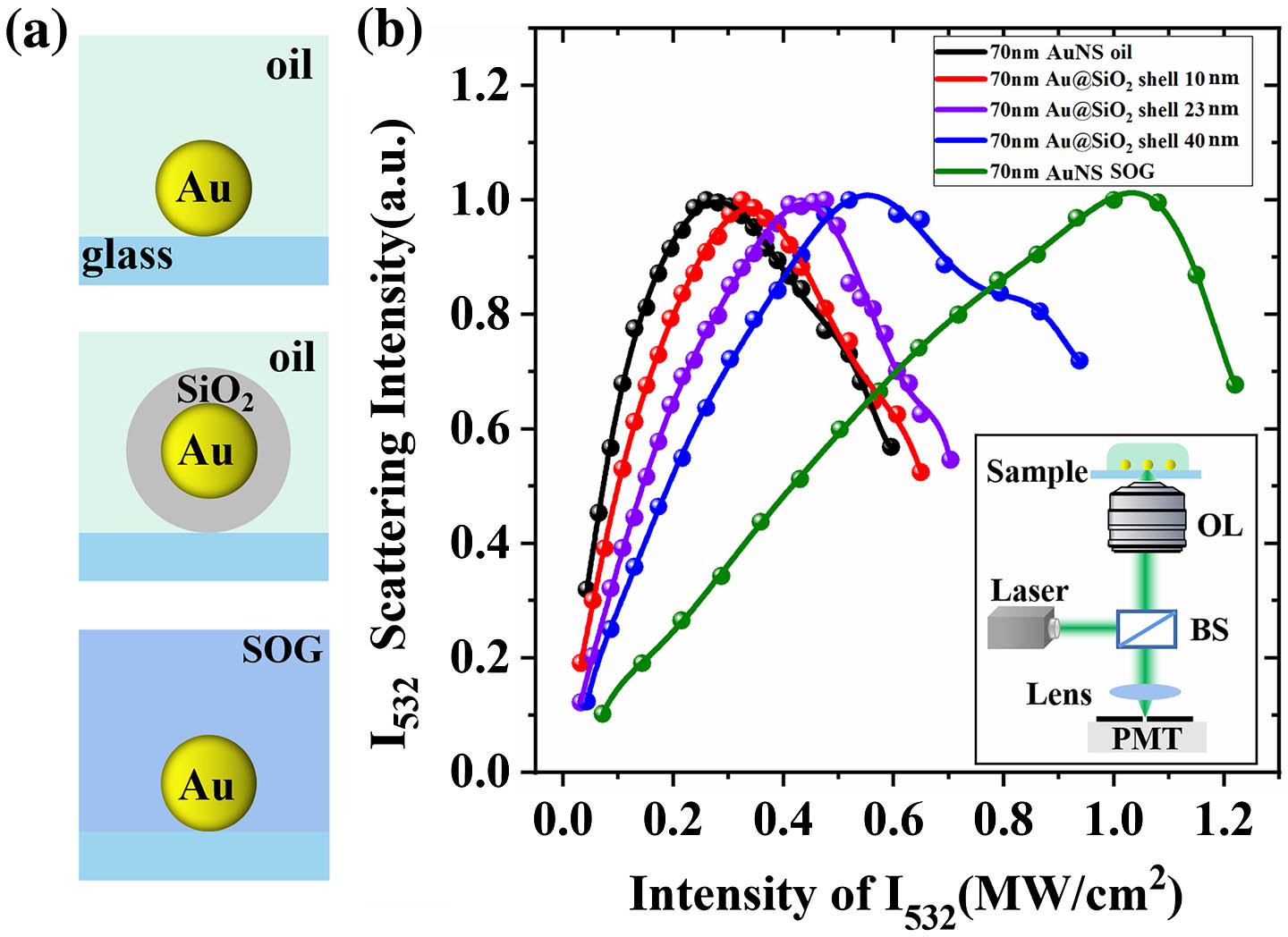
laser plasma diagnostics toroidal crystal monochromatic X-ray imaging In this Letter, we report on the investigations of nonlinear scattering of plasmonic nanoparticles by manipulating ambient environments. We create different local thermal hosts for gold nanospheres that are immersed in oil, encapsulated in silica glass and also coated with silica shells. In terms of regulable effective thermal conductivity, silica coatings are found to contribute significantly to scattering saturation. Benefitting from the enhanced thermal stability and the reduced plasmonic coupling provided by the shell-isolated nanoparticles, we achieve super-resolution imaging with a feature size of 52 nm (
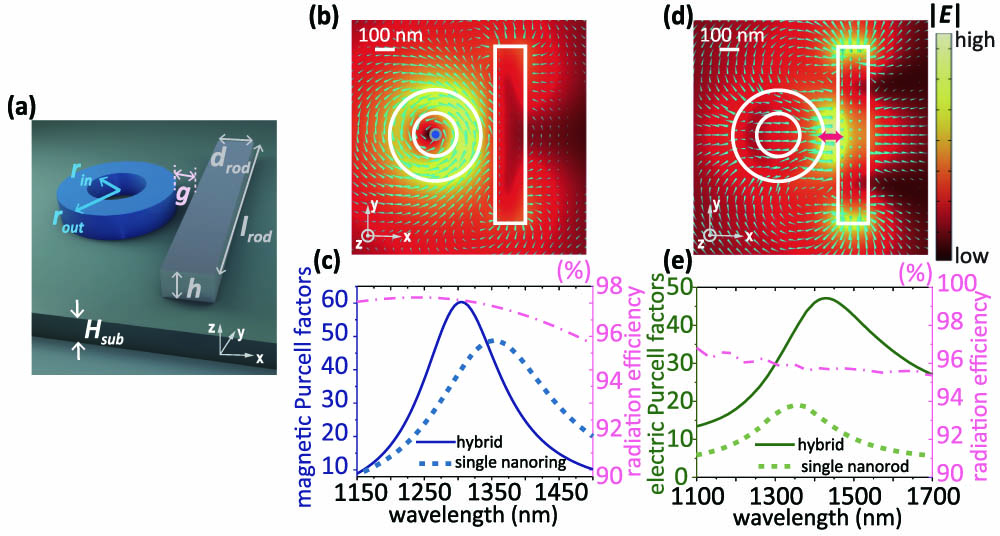
noble metal nanoparticles plasmonic scattering effective thermal conductivity super-resolution Hybrid metal-dielectric structures combine the advantages of both metal and dielectric materials, enabling high-confined but low-loss magnetic and electric resonances through deliberate arrangements. However, their potential for enhancing magnetic emission has yet to be fully explored. Here, we study the magnetic and electric Purcell enhancement supported by a hybrid structure composed of a dielectric nanoring and a silver nanorod. This structure enables low Ohmic loss and highly-confined field under the mode hybridization of magnetic resonances on a nanoring and electric resonances on a nanorod in the optical communication band. Thus, the 60-fold magnetic Purcell enhancement and 45-fold electric Purcell enhancement can be achieved. Over 90% of the radiation can be transmitted to the far field. For the sufficiently large Purcell enhancement, the position of emitter has a tolerance of several tens of nanometers, which brings convenience to experimental fabrications. Moreover, an array formed by this hybrid nanostructure can further enhance the magnetic Purcell factors. The system provides a feasible option to selectively excite magnetic and electric emission in integrated photonic circuits. It may also facilitate brighter magnetic emission sources and light-emitting metasurfaces with a more straightforward design.
Purcell effect magnetic emission hybrid structures 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦