1 中南大学物理与电子学院纳米光子学与器件湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410083
2 中南大学高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410083
海水淡化技术在解决水资源短缺的问题上起着重要的作用,其中太阳能海水技术的研究#更是备受关注。激光微纳制造技术作为一种先进、便捷的加工方法,近年来在制备海水淡化材料领域取得了一定的研究成果。本文以太阳能海水淡化技术以及激光加工技术作为研究背景,根据研究材料的多样性,从材料的构成本质出发,将近年来关于激光微纳制造海水淡化材料的研究分为碳基类、金属基类和复合基类材料三个部分来进行阐述,最后结合当前研究,阐明该方向面临的挑战并对其前景进行展望。

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hunan Key Laboratory of Nanophotonics and Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance and Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Infrared (IR) thermal imaging has aroused great interest due to its wide application in medical, scientific, and military fields. Most reported approaches for regulating thermal radiation are aimed to realize IR camouflage and are not applicable to enhance thermal imaging. Here, we introduce a simple and effective method to process porous glass by femtosecond laser scanning, where distributed nanocavities and nanowires were produced, which caused improvement of the treated glass emissivity. The as-prepared sample possessed better IR thermal radiation performance but lower transmittance to visible light. We also demonstrated its applicability by placing it in different backgrounds, where the IR image temperature of laser-treated glass was closer to the actual environment, and this strategy may provide a new vision for enhanced thermal imaging.
femtosecond laser thermal radiation texture micro/nanostructures glass Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(3): 033801
1 中南大学物理与电子学院超微结构与超快过程湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 中南大学高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
水下气体浸润性表面在许多领域都具有重要的作用,近年来受到了各国研究人员的密切关注。飞秒激光微纳制造技术作为一种全新的非接触式加工手段,近年来在调控材料表面水下气体浸润性方面进行了许多探索性研究。总结飞秒激光微纳制造技术在水下气体浸润性表面的最新研究进展,从水下超疏气表面、水下超亲气表面、水下超疏气-超亲气转换以及水下气体运输四个方面进行阐述,最后结合当前的研究状况指出该领域目前所存在的问题以及对前景的展望。
激光光学 飞秒激光 微纳制造 水下气体浸润性 超疏气 超亲气 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(11): 111418
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hunan Key Laboratory of Super Microstructure and Ultrafast Process, School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2 The State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
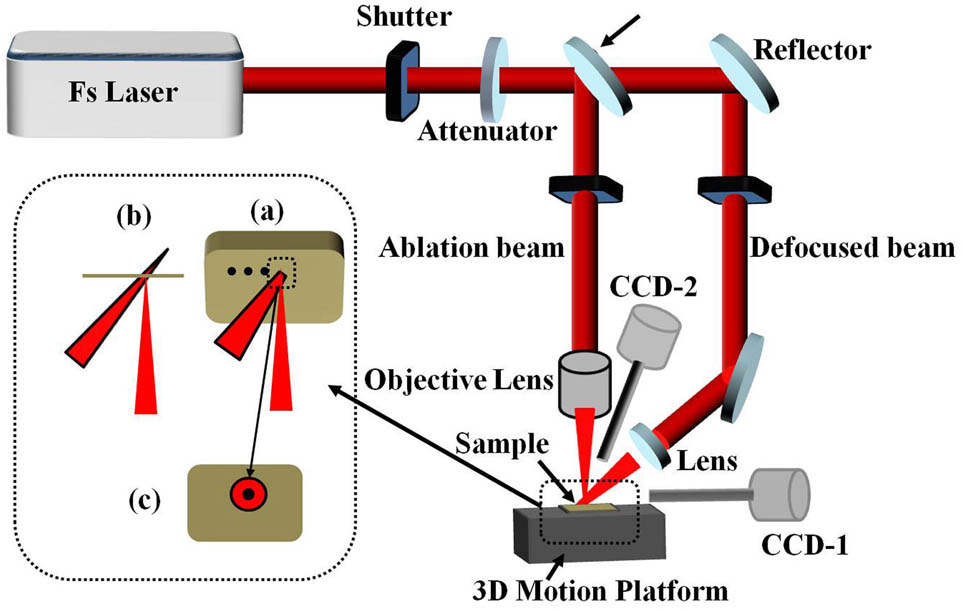
We evaluate the effects of the holes geometry drilled by a femtosecond laser on a stainless alloy with various defocused irradiation time, which ranges from 0 min to 1 h. The laser ablation efficiency is increased by a factor of 3 when the irradiation time is elevated from 0 to 30 min. Also, the morphology of the hole is observed by a scanning electron microscope, where the result indicates that the defocused irradiation time has a significant influence on the morphology changes. The reason for such changes is discussed based on the pretreatment effect and the confined plasma plume. As an application example, the microchannel is fabricated by a femtosecond laser combined with the defocused irradiation to demonstrate the advantage of the proposed method in fabricating functional structures.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 011401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of High Performance and Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
A constant elastic alloy is a widely used material with a high elastic modulus and an excellent wave velocity consistency. Different morphologies on the constant elastic alloy surface are observed through femtosecond laser irradiation. When the laser average fluence is set to 0.58 J/cm2 and 200 laser pulses, with the increasing depth of distilled water, the period of the laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) becomes shorter accordingly. The higher the ethanol concentration is, the more spot-shaped structures will be formed among the surface structures when the depth of the coverage of ethanol is 2 mm. The period of the LIPSS reaches its maximum when the concentration of ethanol is 80%.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 100.0118 Imaging ultrafast phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 021404
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
A fused silica glass micro-channel can be formed by chemical etching after femtosecond laser irradiation, and the successful etching probability is only 48%. In order to improve the micro-channel fabrication success probability, the method of processing a high-temperature lattice by a femtosecond laser pulse train is provided. With the same pulse energy and scanning speed, the success probability can be increased to 98% by optimizing pulse delay. The enhancement is mainly caused by the nanostructure, which changes from a periodic slabs structure to some intensive and loose pore structures. In this Letter, the optimum pulse energy distribution ratio to the etching is also investigated.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 230.7380 Waveguides, channeled Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(7): 071403
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
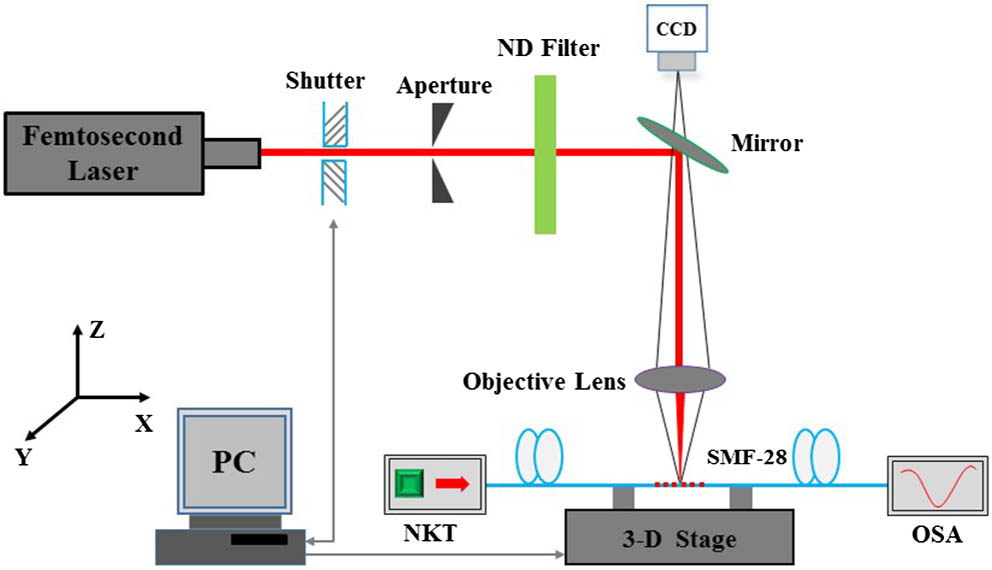
We propose a high temperature-sensitive long period fiber grating (LPFG) sensor fabricated by using the femtosecond laser transversal-scanning method. The femtosecond pulses scan over the whole fiber core and some part of the cladding region; the modified regions are more extended. It is found that the LPFG-I fabricated by the transversal-scanning method shows higher temperature sensitivity and better temperature uniformity than that of LPFG-II written by the femtosecond laser point-by-point method. The LPFG-I with a temperature sensitivity of 75.96 pm/°C in the range of 25°C–400°C is measured. Moreover, in the range from 400°C to 800°C, a higher temperature sensitivity of 148.64 pm/°C and good linearity of 0.99 are achieved, while the temperature sensitivity of LPFG-II is only 95.55 pm/°C. LPFG-I exhibits better temperature characteristics, which, to the best of our knowledge, has the highest sensitivity in silica fiber temperature sensors.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(9): 090602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of High Performance and Complex Manufacturing, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
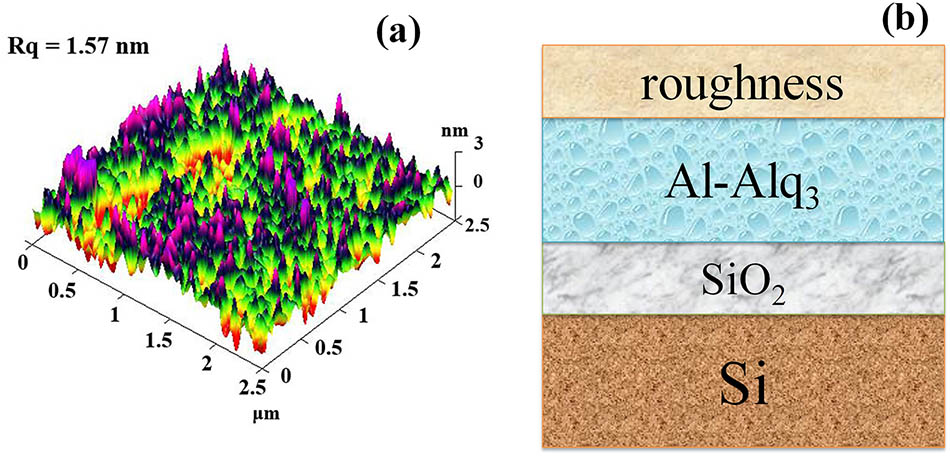
The optical constants, photoluminescence properties, and resistivity of Al-Alq3 thin films prepared by the thermal co-evaporation method on a silicon substrate are studied with various Al fractions. A variable angle spectroscopic ellipsometry is employed to determine the optical constants in the wavelength from 300 to 1200 nm at incidence angles of 65°, 70°, and 75°, respectively. Both the refractive indices and extinction coefficient apparently increase with increasing Al fractions. The intensity of photoluminescence spectra gradually increases with decreasing Al fractions due to intrinsic energy level transition of Alq3 organic semiconductor in the ultraviolet wave band. The resistivity decreases from 42.1 to 3.36 Ω·cm with increasing Al fraction from 40% to 70%, resulting in a larger emission intensity in photoluminescence spectra for the 40% Al fraction sample.
160.4890 Organic materials 120.2130 Ellipsometry and polarimetry Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111602
1 中南大学 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 罗彻斯特大学光学研究所, 纽约 14627
与传统传感器相比, 全光纤马赫泽德尔干涉仪(MZI)传感器, 具有结构简单、分辨率高、稳定性好等优点, 在石油化工、健康监测、生物化学等领域有广泛应用。介绍了MZI全光纤传感器的传感机理,对比了其他的加工方法, 如电弧放电、加热拉伸、CO2激光诱导微变形等的优缺点, 详细介绍了飞秒激光加工得到的MZI传感器的结构形式、折射率和温度等传感性能。重点阐述了飞秒激光加工MZI的研究现状和优点, 并对运用飞秒激光方法加工的MZI进行了总结和展望。
飞秒激光 全光纤MZI传感器 传感特性 Femtosecond laser All fiber MZI sensors Sensing performances
1 中南大学 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 中南大学机电工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410083
ZnS材料具有良好的光学和电学性能, 是一种重要的半导体材料, 在电学, 光学和催化领域有巨大的应用前景。研究了飞秒激光能量和扫描速度对ZnS表面形貌及其疏水性能的影响规律。研究发现, 随着激光能量增加沟槽深度和宽度增加, 同时沟槽深度变化更为显著; 扫描速度减小时, 沟槽深度和宽度增加, 沟槽边缘质量更好。在此基础上, 研究了扫描速度对ZnS表面湿润特性的影响。实验结果表明, 扫描速度越小, 沟槽形貌越粗糙, 其表面疏水性能更强, 实验获得的最大疏水角为140°。
飞秒激光 激光能量 扫描速度 表面形貌 疏水性能 ZnS ZnS femtosecond pulse laser laser energy scanning speed surface morphology hydrophobic property





