2017, 15(5) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第15卷 第5期
The environmental perturbation on atoms is a key factor restricting the performance of atomic frequency standards, especially in the long-term scale. In this Letter, we perform a real-time noise distinguish (RTND) to an atomic clock to decrease the uncertainty of the atomic clock beyond the level that is attained by the current controlling method. In RTND, the related parameters of the clock are monitored in real time by using the calibrated sensors, and their effects on the clock frequency are calculated. By subtracting the effects from the error signal, the local oscillator is treated as equivalently locked to the unperturbed atomic levels. In order to perform quantitative tests, we engineer time-varying noise much larger than the intrinsic noise in our fountain atomic clock. By using RTND, the influences of the added noises are detected and subtracted precisely from the error signals before feeding back to the reference oscillator. The result shows that the statistical uncertainty of our fountain clock is improved by an order of magnitude to 2×10?15. Besides, the frequency offset introduced by the noise is also corrected, while the systematic uncertainty is unaffected.
020.1335 Atom optics 120.3940 Metrology Parity chain and parity chain breaking in the two-level cavity quantum electrodynamics system Download:927次
Download:927次
 Download:927次
Download:927次We investigate the transitions between energy levels and parity symmetry in an effective two-level polar molecule system strongly coupled with a quantized harmonic oscillator. By the dressed-state perturbation theory, the transition diagrams between the dressed-state energy levels are presented clearly and show that the odd (even) parity symmetry is broken by the permanent dipole moment (PDM) of the polar molecules. By the analytical and numerical methods, we find that when the coupling strength and the PDM increase, the more frequency components are induced by the counter-rotating terms and PDM.
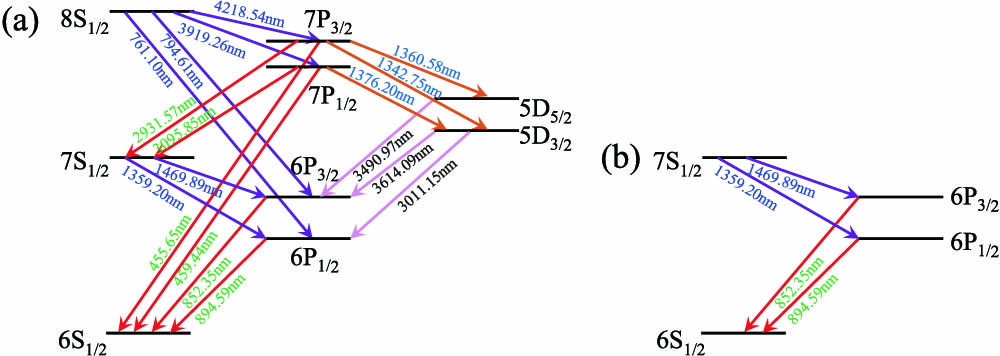
020.5580 Quantum electrodynamics 140.3945 Microcavities 270.0270 Quantum optics A 1470 nm + 852 nm 6 S 1 / 2 - 6 P 3 / 2 - 7 S 1 / 2 1470 nm + 852 nm 6 P 3 / 2 F ′ = 5 7 S 1 / 2 F ′ ′ = 4
020.3320 Laser cooling 270.4180 Multiphoton processes 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Artificial neural-network-based visible light positioning algorithm with a diffuse optical channel Download:1175次
Download:1175次
 Download:1175次
Download:1175次Visible light positioning becomes popular recently. However, its performance is degraded by the indoor diffuse optical channel. An artificial neural-network-based visible light positioning algorithm is proposed in this Letter, and a trained neural network is used to achieve positioning with a diffuse channel. Simulations are made to evaluate the proposed positioning algorithm. Results show that the average positioning error is reduced about 13 times, and the positioning time is reduced about two magnitudes. Moreover, the proposed algorithm is robust with a different field-of-view of the receiver and the reflectivity of the wall, which is suitable for various positioning applications.
060.4510 Optical communications 200.4260 Neural networks 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes The symbol error rate (SER) performance of a multipulse pulse-position modulation (MPPM) free space optical (FSO) system under the combined effect of turbulence-induced fading modeled by exponentiated Weibull (EW) distribution and pointing errors with a soft-decision detector is investigated systematically. Particularly, the theoretical conditional SER (CSER) of soft-decision decoded MPPM is derived. The corresponding closed-form CSER is obtained via curve fitting with the Levenberg–Marquardt method. The analytical SER expression over the aggregated fading channels is then achieved in terms of Laguerre integration. Monte Carlo simulation results are also offered to corroborate the validity of the proposed SER model.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence Highly linear W-band receiver front-end based on higher-order optical sideband processing Download:719次
Download:719次
 Download:719次
Download:719次A highly linear W-band receiver front-end based on higher-order optical sideband (OSB) processing is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. Two-tone analysis shows that by manipulating higher-order OSBs, the third-order intermodulation distortion (IMD3) introduced by optoelectronic components (mainly modulators) in the receiver front-end can be further suppressed, and a 9 dB improvement of the ratio of the fundamental and IMD3 can be attained. In the experiment, the spurious-free dynamic range of the W-band receiver front-end is up to 122.1 dB · Hz 2 / 3
060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 130.4310 Nonlinear Multipath interference induced power fading occurs when the transmission path lengths from the light emitting diodes to a single receiver are different in a visible light communication system. To solve this problem, we apply a QR-decomposition-based channel equalizer (QR-CE) to achieve successive interference cancellation for a discrete Fourier transform spreading (DFT-S) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signal. We experimentally demonstrate a 200 Mb/s DFT-S OFDM over a 2 m free-space transmission. The experimental results show that a DFT-S OFDM with QR-CE attains much better bit error rate performance than a DFT-S OFDM with conventional CEs. The impacts of several parameters on a QR-CE are also investigated.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 200.2605 Free-space optical communication 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes We develop an improved region growing method to realize automatic retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell segmentation for photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) imaging. The minimum bounding rectangle of the segmented region is used in this method to dynamically update the growing threshold for optimal segmentation. Phantom images and PAM imaging results of normal porcine RPE are applied to demonstrate the effectiveness of the segmentation. The method realizes accurate segmentation of RPE cells and also provides the basis for quantitative analysis of cell features such as cell area and component content, which can have potential applications in studying RPE cell functions for PAM imaging.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 110.0180 Microscopy 100.2000 Digital image processing 170.1530 Cell analysis We experimentally demonstrate that optical tweezers can be used to accelerate the self-assembly of colloidal particles at a water–air interface in this Letter. The thermal flow induced by optical tweezers dominates the growth acceleration at the interface. Furthermore, optical tweezers are used to create a local growth peak at the growing front, which is used to study the preferential incorporation positions of incoming particles. The results show that the particles surfed with a strong Marangoni flow tend to fill the gap and smoothen the steep peaks. When the peak is smooth, the incoming particles incorporate the crystal homogeneously at the growing front.
140.7010 Laser trapping 350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation 230.5298 Photonic crystals An elliptical initial polarization state is essential for generating mode-locked pulses using the nonlinear polarization rotation technique. In this work, the relationship between the ellipticity ranges capable of maintaining mode-locked operation against different pump power levels is investigated. An increasing pump power, in conjunction with minor adjustments to the polarization controller’s quarter waveplate, results in a wider ellipticity range that can accommodate mode-locked operation. Other parameters such as noise, pulsewidth, and average output power are also observed to vary as the ellipticity changes.
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 060.2410 Fibers, erbium 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers In this Letter, ceramic Nd:YAG is charactrizeby electron spin resonance (ESR) measurements. The ESR results indicate that the polycrystalline ceramic Nd:YAG has barely native defects and impurity ions localization defects, compared to an Nd:YAG crystal with the same Nd doping concentration, due to its density structure by sintering in a vacuum pure raw material and additives during the fabrication. It may conclude that the high quality ceramic Nd:YAG may have greater ability on optical characteristic, mechanical performance, and laser damage than that of the crystals, which is a promising candidate to use on laser diode-pumped solid-state lasers.
160.3380 Laser materials 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state Effect of various red phosphorescent dopants in single emissive white phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices Download:779次
Download:779次
 Download:779次
Download:779次In order to realize single emissive white phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices (PHOLEDs) with three color phosphorescent dopants (red, green, and blue), the energy transfer between the host material and the three dopants, as well as the among the three dopants themselves, should be considered and optimized. To explore the effect of red phosphorescent dopant on the color rendering index (CRI), the authors investigate the wavelength position of the maximum emission peak from three phosphorescent dopants. The CRI and luminous efficiency of white PHOLED in which Ir ( pq ) 2 ( acac ) Ir ( piq ) 3 Ir ( btp ) 2 ( acac ) Ir ( pq ) 2 ( acac ) Ir ( pq ) 2 ( acac )
160.4890 Organic materials 300.1030 Absorption 260.2160 Energy transfer The plasmonic mode in graphene metamaterial provides a new approach to manipulate terahertz (THz) waves. Graphene-based split ring resonator (SRR) metamaterial is proposed with the capacity for modulating transmitted THz waves under normal and oblique incidence. Here, we theoretically demonstrate that the resonant strength of the dipolar mode can be significantly enhanced by enlarging the arm-width of the SRR and by stacking graphene layers. The principal mechanism of light–matter interaction in graphene metamaterial provides a dynamical modulation based on the controllable graphene Fermi level. This graphene-based design paves the way for a myriad of important THz applications, such as optical modulators, absorbers, polarizers, etc.
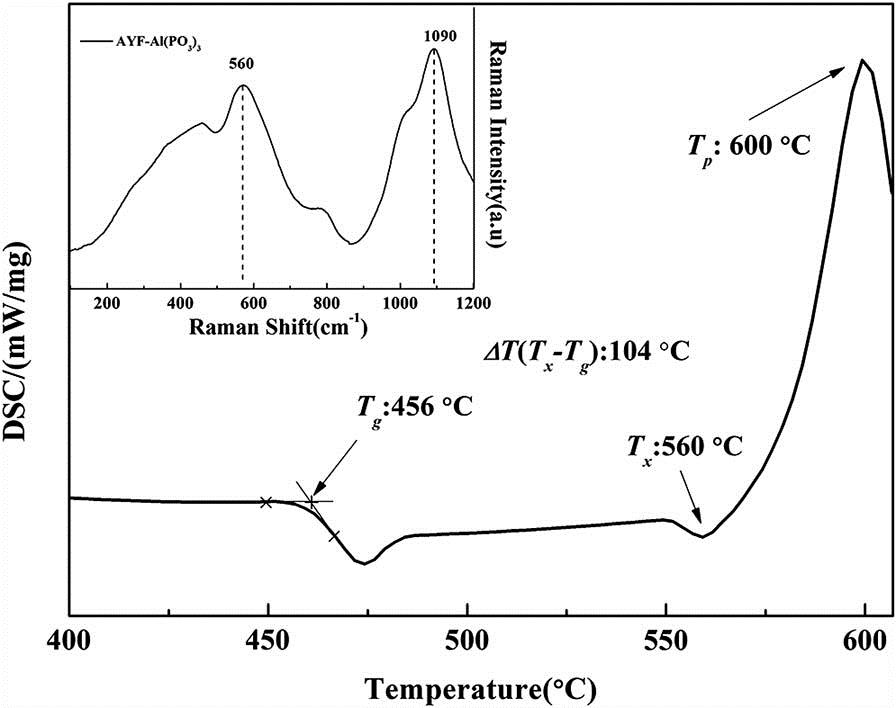
160.3918 Metamaterials 120.7000 Transmission 130.4110 Modulators In this work, we investigate a new type of fluoride glasses modified by Al ( PO 3 ) 3 Tm 3 + / Ho 3 + PO 3 Tm 3 + Ho 3 + Tm 3 + Ho 3 + 118.74 s 1 σ emi × τ
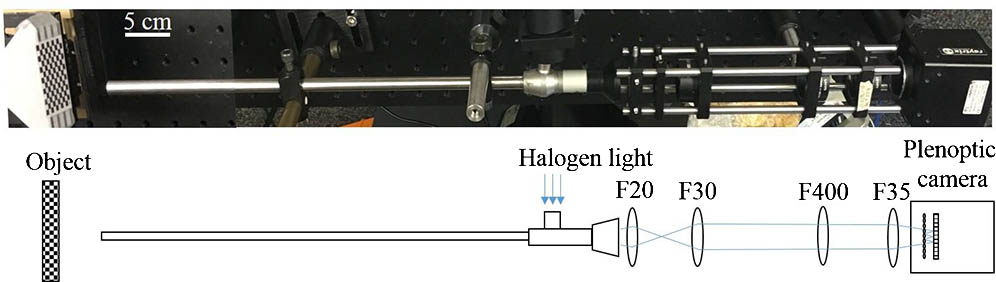
160.4670 Optical materials 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 060.2390 Fiber optics, infrared 070.4790 Spectrum analysis An endoscopic imaging system using a plenoptic technique to reconstruct 3-D information is demonstrated and analyzed in this Letter. The proposed setup integrates a clinical surgical endoscope with a plenoptic camera to achieve a depth accuracy error of about 1 mm and a precision error of about 2 mm, within a 25 mm × 25 mm
170.2150 Endoscopic imaging 170.4580 Optical diagnostics for medicine 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation Five conical harmonic beams are generated from the interaction of femtosecond mid-infrared (mid-IR) pulses at a nominal input wavelength of 1997 nm with a 2D LiNbO 3
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 050.1940 Diffraction We show how to optimally protect quantum states and freeze coherence under incoherent channels using a quantum weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. In particular, we present explicit formulas for the conditions for freezing quantum coherence in a given quantum state.
270.1670 Coherent optical effects 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise The cavity ring-down (CRD) technique is adopted for simultaneously measuring s p s p s p s p s p
310.0310 Thin films 310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology We review over a decade of technology evolution and advancement of intra-datacenter optical interconnect, mainly driven by the explosive bandwidth growth of web and cloud-based services. Emerging trends and technology options to scale interface bandwidth beyond 400 Gb/s will also be discussed.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦