2015, 3(3) Column
Photonics Research 第3卷 第3期
In underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC), a channel is characterized by abundant scattering/absorption effects and optical turbulence. Most previous studies on UOWC have been limited to scattering/absorption effects. However, experiments in the literature indicate that underwater optical turbulence (UOT) can cause severe degradation of UOWC performance. In this paper, we characterize an UOWC channel with both scattering/absorption and UOT taken into consideration, and a spatial diversity receiver scheme, say a single-input–multiple-output (SIMO) scheme, based on a light-emitting-diode (LED) source and multiple detectors is proposed to mitigate deep fading. The Monte Carlo based statistical simulation method is introduced to evaluate the bit-error-rate performance of the system. It is shown that spatial diversity can effectively reduce channel fading and remarkably extend communication range.
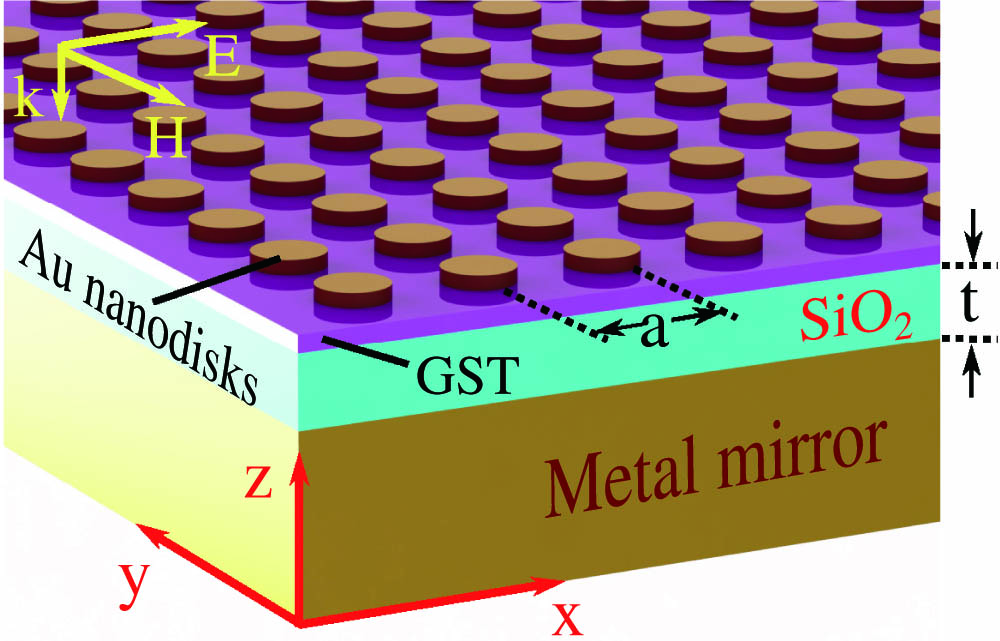
Oceanic propagation Fiber optics and optical communications A tunable plasmonic perfect absorber with a tuning range of ~ 650 nm Ge 2 Sb 2 Te 5
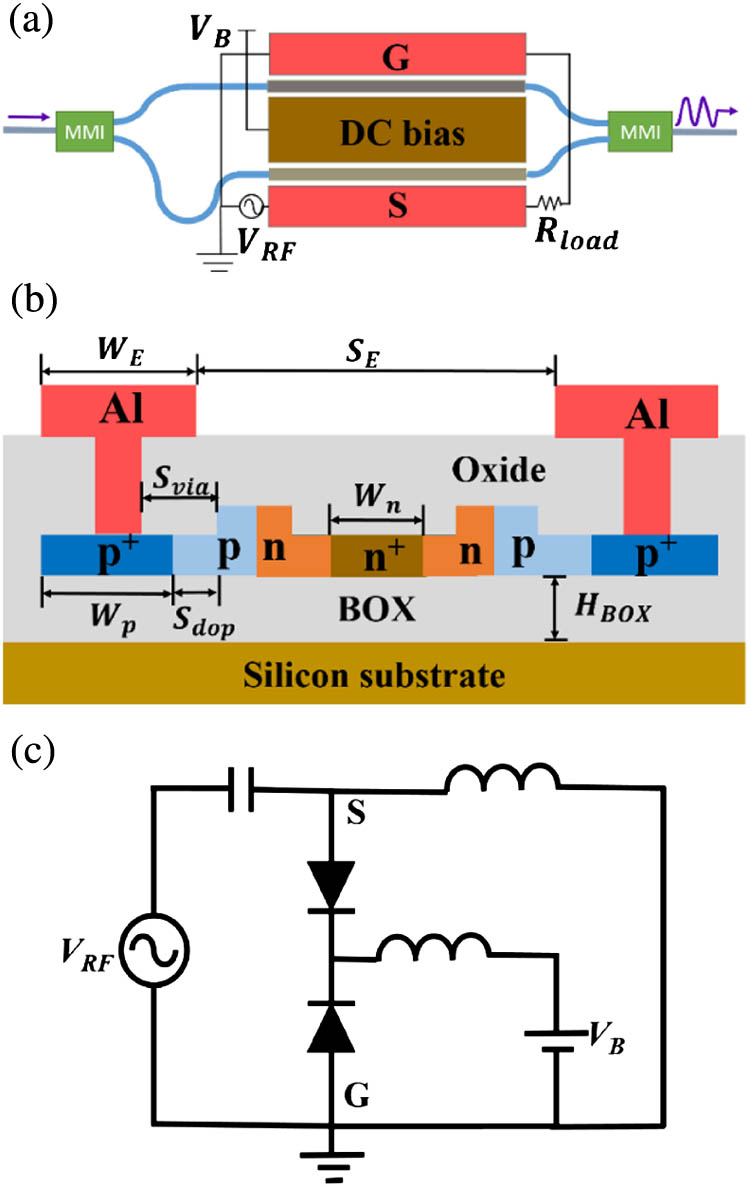
Spectral properties Plasmonics Subwavelength structures, nanostructures Multilayer design We demonstrate binary phase shift keying (BPSK) modulation using a silicon Mach–Zehnder modulator with a π V π 4.5 V
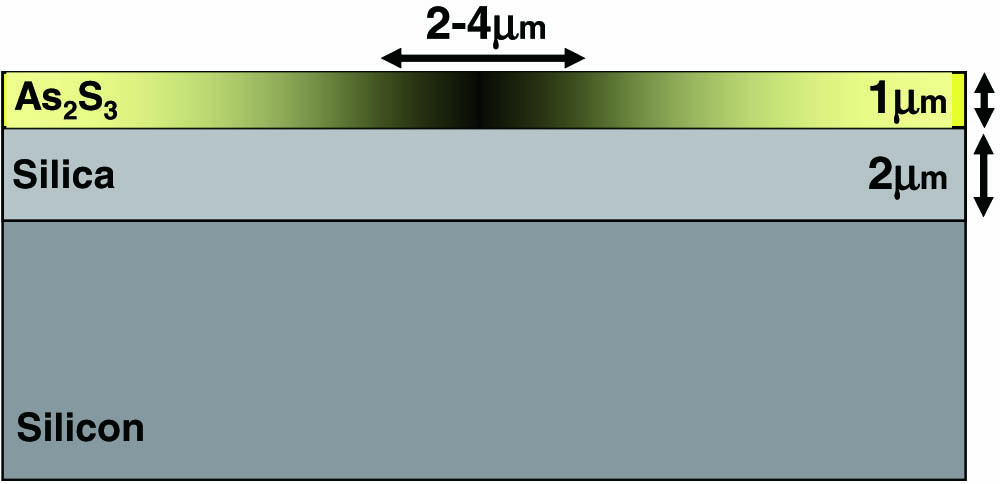
Integrated optics devices Integrated optoelectronic circuits Waveguide modulators Planar ring resonator waveguides are fabricated in thin films of As 2 S 3 Q Q
Glass waveguides Photosensitive materials Resonators An ultrathin, planar, broadband metalens composed of metal rectangular split-ring resonators (MRSRRs) has been designed, which shows dual-polarity characteristics for different types of circularly polarized (CP) light incidence. The designed metalens can be considered as the focusing lens and the diverging lens under left-handed CP and right-handed CP light incidence, respectively. The phase discontinuity of the cross-polarized transmission light is produced by optical-axis rotation through modulating two arms’ lengths of the MRSRR. The MRSRR metalens possesses a wavelength-controllable focal length and a relatively larger chromatic aberration compared with the conventional lenses. And the focal length changes from 9 to 7 μm with incident wavelength from 740 to 950 nm. The dual-polarity flat metalens opens a door for new applications of phase discontinuity devices, and it will promote the fabricating capability of on-chip or fiber-embedded optical devices.
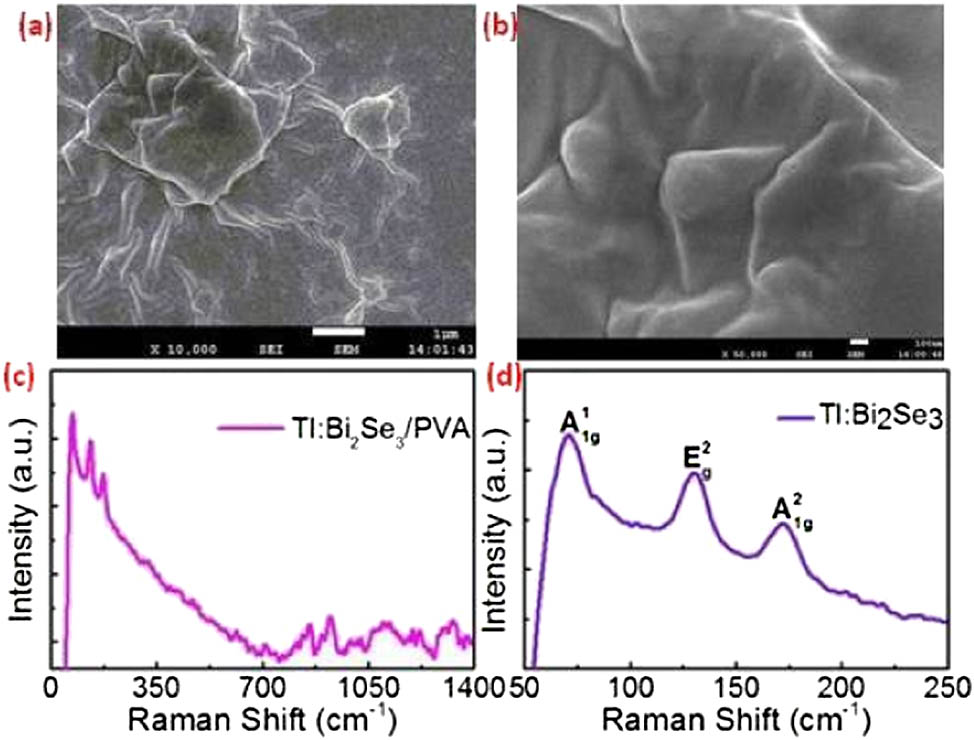
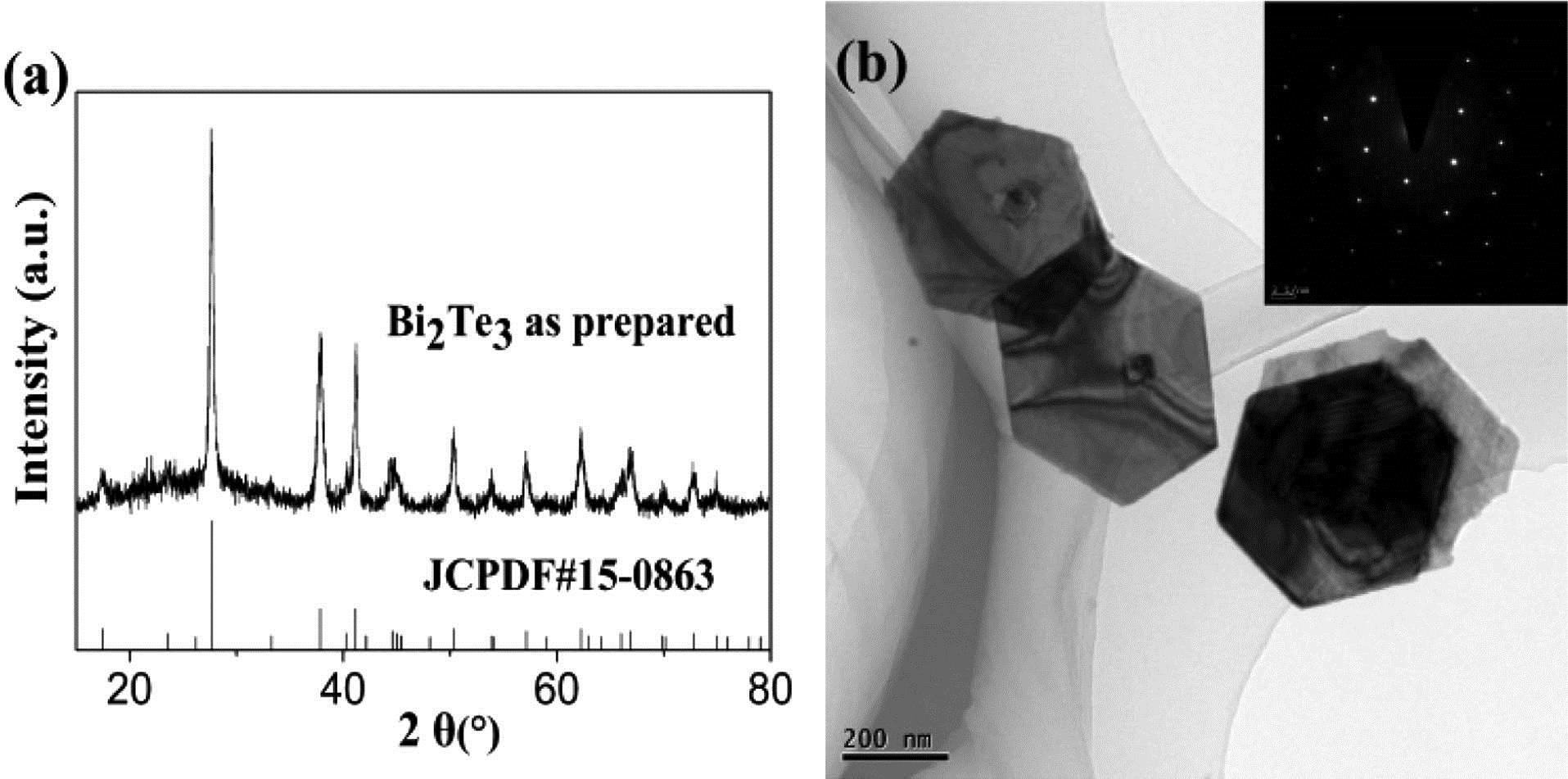
Lenses Metamaterials Phase modulation We reported diverse soliton operations in a thulium/holmium-doped fiber laser by taking advantage of a tapered fiber-based topological insulator (TI) Bi 2 Te 3 ~ 53.5 %
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Ultrafast lasers Lasers and laser optics Mode-locked lasers Nonlinear optical materials Conversion of out-of-phase to in-phase order in coupled laser arrays with second harmonics Download:841次
Download:841次
 Download:841次
Download:841次A novel method for converting an array of out-of-phase lasers into one of in-phase lasers that can be tightly focused is presented. The method exploits second-harmonic generation and can be adapted for different laser arrays geometries. Experimental and calculated results, presented for negatively coupled lasers formed in a square, honeycomb, and triangular geometries are in good agreement.
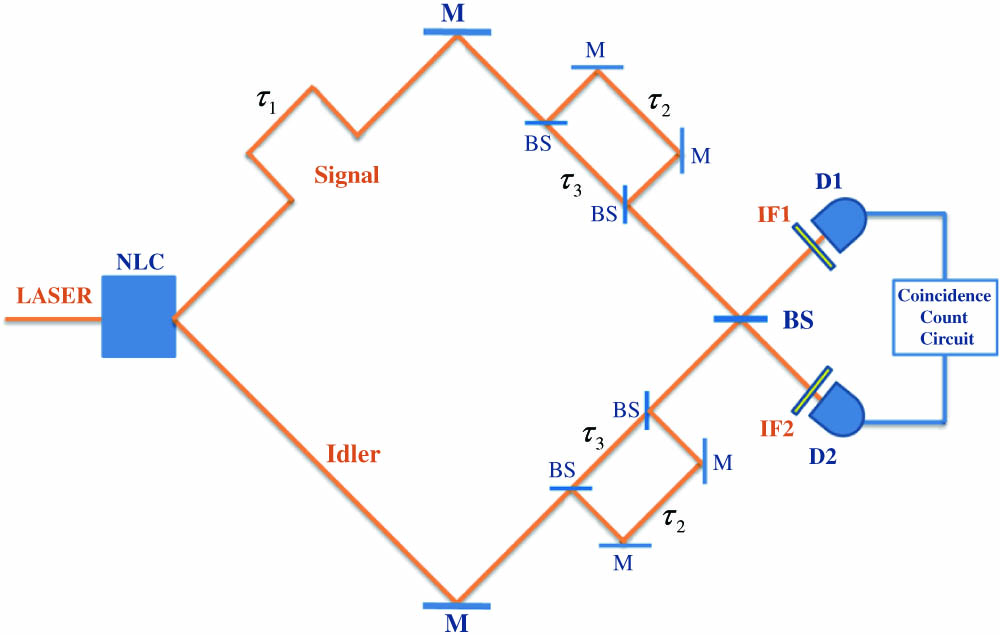
Lasers, distributed-feedback Laser coupling Lasers, solid-state Nonlinear optics Quantum beats can be produced in fourth-order interference such as in a Hong–Ou–Mandel (HOM) interferometer by using photons with different frequencies. Here we present theoretically the appearance of interference of quantum beats when the HOM interferometer is combined with a Franson-type interferometer. This combination can make the interference effect of photons with different colors take place not only within the coherence time of downconverted fields but also in the region beyond that. We expect that it can provide a new method in quantum metrology, as it can realize the measurement of time intervals in three scales.
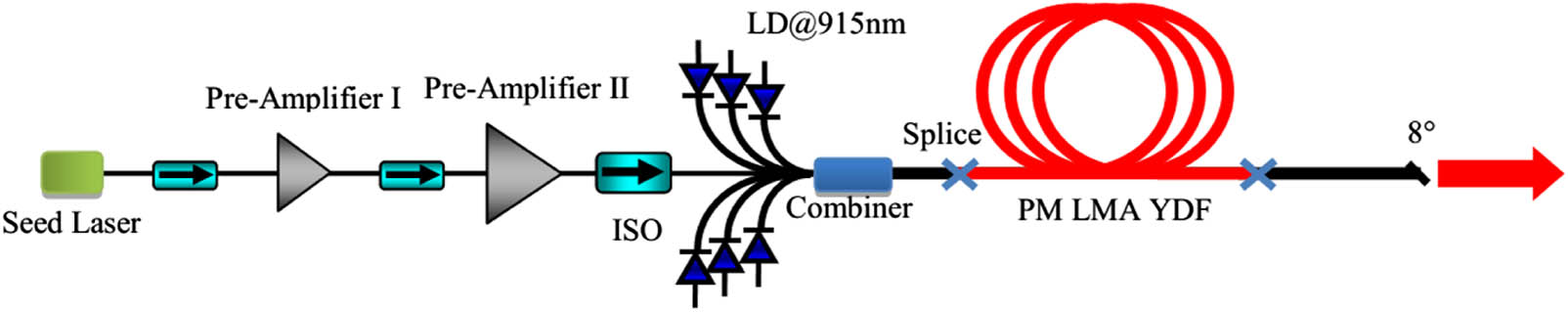
Coherent optical effects Photon statistics Quantum detectors We report on the high-power amplification of a 1064 nm linearly polarized laser in an all-fiber polarization-maintained master oscillator power amplifier, which can operate at an output power level of 1.3 kW. The beam quality (M 2 < 1.2
Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Fibers, polarization-maintaining Fibers, single-mode Dual-wavelength rectangular pulse erbium-doped fiber laser based on topological insulator saturable absorber Download:1184次
Download:1184次
 Download:1184次
Download:1184次We reported on the generation of the dual-wavelength rectangular pulse in an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) with a topological insulator saturable absorber. The rectangular pulse could be stably initiated with pulse width from 13.62 to 25.16 ns and fundamental repetition rate of 3.54 MHz by properly adjusting the pump power and the polarization state. In addition, we verified that the pulse shape of the dual-wavelength rectangular pulse can be affected by the total net cavity dispersion in the fiber laser. Furthermore, by properly rotating the polarization controllers, the harmonic mode-locking operation of the dual-wavelength rectangular pulse was also obtained. The dual-wavelength rectangular pulse EDFL would benefit some potential applications, such as spectroscopy, biomedicine, and sensing research.
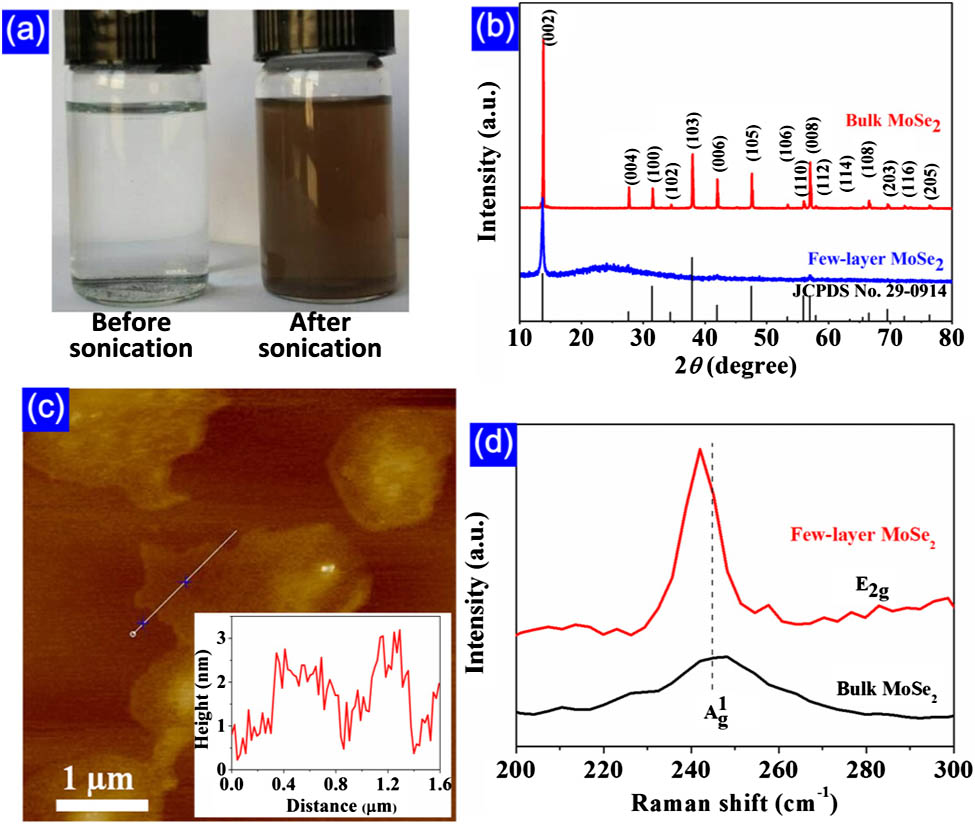
Mode-locked lasers Nonlinear optics, fibers Nonlinear optical materials In this paper, both nonlinear saturable absorption and two-photon absorption (TPA) of few-layer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) were observed at 1.56 μm wavelength and further applied to mode-locked ultrafast fiber laser for the first time to our knowledge. Few-layer MoSe2 nanosheets were prepared by liquid-phase exfoliation method and characterized by x ray diffractometer, Raman spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The obtained few-layer MoSe2 dispersion is further composited with a polymer material for convenient fabrication of MoSe2 thin films. Then, we investigated the nonlinear optical (NLO) absorption property of the few-layer MoSe2 film using a balanced twin-detector measurement technique. Both the saturable absorption and TPA effects of the few-layer MoSe2 film were found by increasing the input optical intensity. The saturable absorption shows a modulation depth of 0.63% and a low nonsaturable loss of ~ 3.5 % ~ 260 MW / cm 2
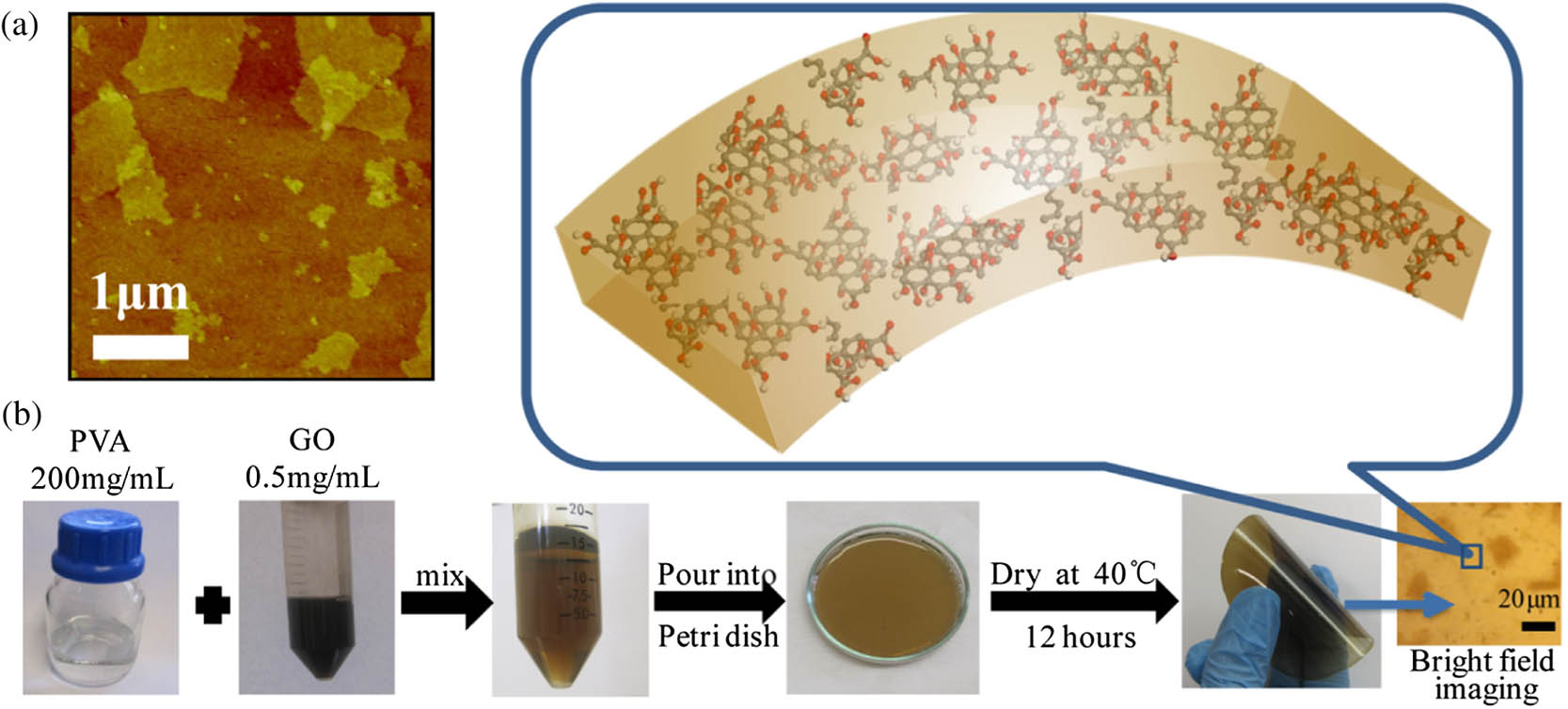
Nanomaterials Nonlinear optical materials Lasers, fiber Mode-locked lasers We report a simple solution-processed method for the fabrication of low-cost, flexible optical limiting materials based on graphene oxide (GO) impregnated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) sheets. Such GO–PVA composite sheets display highly efficient broadband optical limiting activities for femtosecond laser pulses at 400, 800, and 1400 nm with very low limiting thresholds. Femtosecond pump–probe measurement results revealed that nonlinear absorption played an important role for the observed optical limiting activities. High flexibility and efficient optical limiting activities of these materials allow these composite sheets to be attached to nonplanar optical sensors in order to protect them from light-induced damage.
Thin films, optical properties Nonlinear optical materials Ultrafast nonlinear optics Spectroscopy, time-resolved Few-layer MoS2 grown by chemical vapor deposition as a passive Q-switcher for tunable erbium-doped fiber lasers Download:1025次
Download:1025次
 Download:1025次
Download:1025次We report an erbium-doped fiber laser passively Q-switched by a few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS 2 MoS 2 MoS 2 MoS 2
Lasers, Q-switched Lasers, erbium Nanomaterials In this paper, we reported a multiwavelength passively Q Yb 3 + : GdAl 3 ( BO 3 ) 4 Bi 2 Te 3 Bi 2 Te 3 Bi 2 Te 3 Bi 2 Te 3
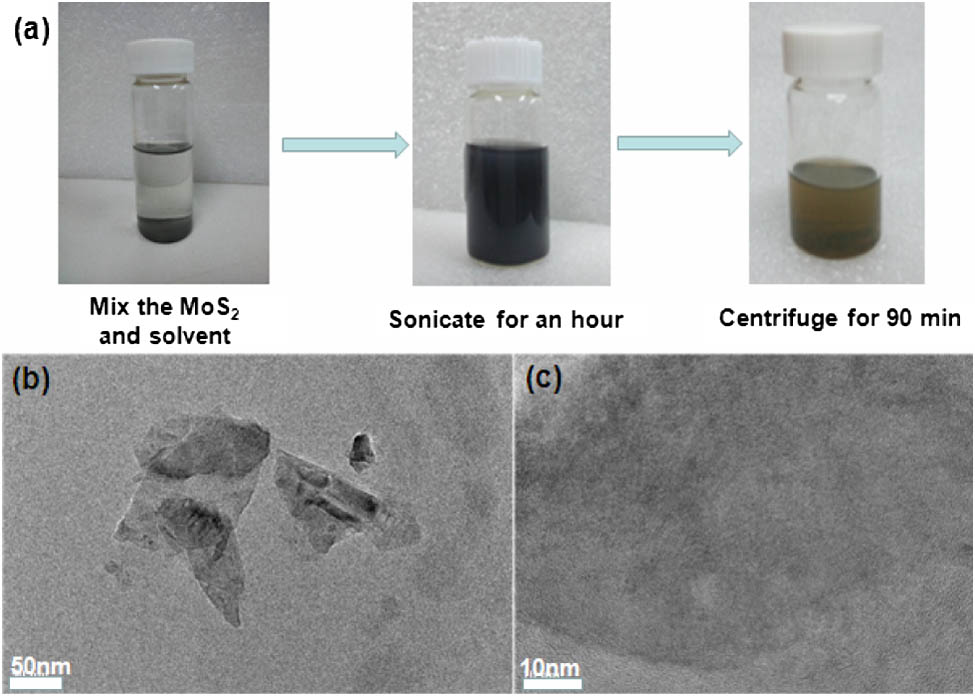
Lasers, diode-pumped Lasers, Q-switched Lasers, solid-state Lasers, ytterbium Deposition of two-dimensional (2D) MoS2 materials on the tapered fiber allows various photonic applications including saturable absorbers and four-wave mixing. Ethanol catalytic deposition (ECD) of MoS2 on the optical tapered fiber was proposed and demonstrated in this work. Different from the conventional optical driven deposition using water or organic solvent, the ECD method utilized the high volatility of the ethanol solvent, which significantly increased the movement speed of the MoS2 nanosheets and thus boosted the deposition rate and reduced the minimum power threshold to drive the deposition. We believe the ECD method should be able to be applied to other similar 2D materials such as other types of transition metal chalcogenides.
Nonlinear optical materials Deposition and fabrication Nonlinear optical devices 公告
动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-25
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 2): 封面|超紧凑片上偏振控制器动态信息 丨 2024-04-11
PR Highlight (Vol. 11, Iss. 12): 亮点 | 十亿像素级、高通量的无透镜偏振编码叠层成像技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 3): 封面 | 基于时空编码神经网络的像差感知超分辨成像动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 1) 光涡旋与手性器件微纳3D打印动态信息 丨 2024-03-14
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 1): 同步双脉冲激光烧蚀中的气泡相互作用效应激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦