2017, 15(1) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第15卷 第1期
Microwave photonic components and subsystems can replace or complement their electronic counterparts with a net gain in functionality, bandwidth, size, mass, complexity, and cost, facilitating the innovative implementation of radio frequency (RF) systems due to broad bandwidth, low loss, light weight, flat frequency response, favorable isolation, and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) provided by photonic technologies. Much attention has been recently paid to this area, which results in impressive progresses. Hence, we designed a focus issue intended to introduce the recent advancements in this field, especially the works by some distinguished research groups.
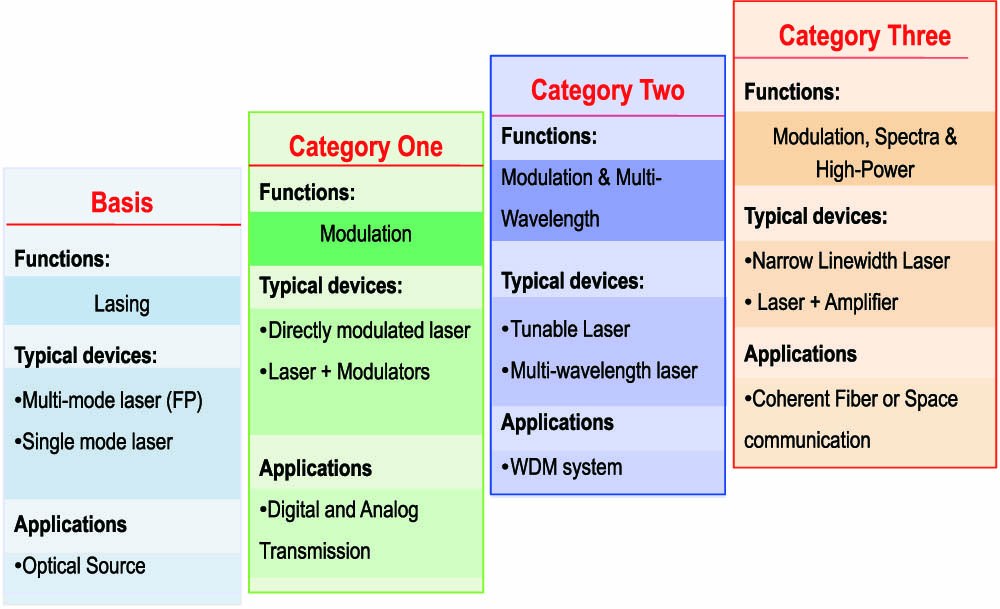
This Review reviews semiconductor lasers with an emphasis on high-speed information technologies. Semiconductor lasers are classified based on their applications in optical communications. Different types of semiconductor lasers are discussed in terms of principle, history, advantages, and limitations.
250.4110 Modulators 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics This Letter introduces the design and simulation of a microstrip-line-based electro-optic (EO) polymer optical phase modulator (PM) that is further enhanced by the addition of photonic crystal (PhC) structures that are in close proximity to the optical core. The slow-wave PhC structure is designed for two different material configurations and placed in the modulator as a superstrate to the optical core; simulation results are depicted for both 1D and 2D PhC structures. The PM characteristics are modeled using a combination of the finite element method and the optical beam propagation method in both the RF and optical domains, respectively. The phase-shift simulation results show a factor of 1.7 increase in an effective EO coefficient (120 pm/V) while maintaining a broadband bandwidth of 40 GHz.
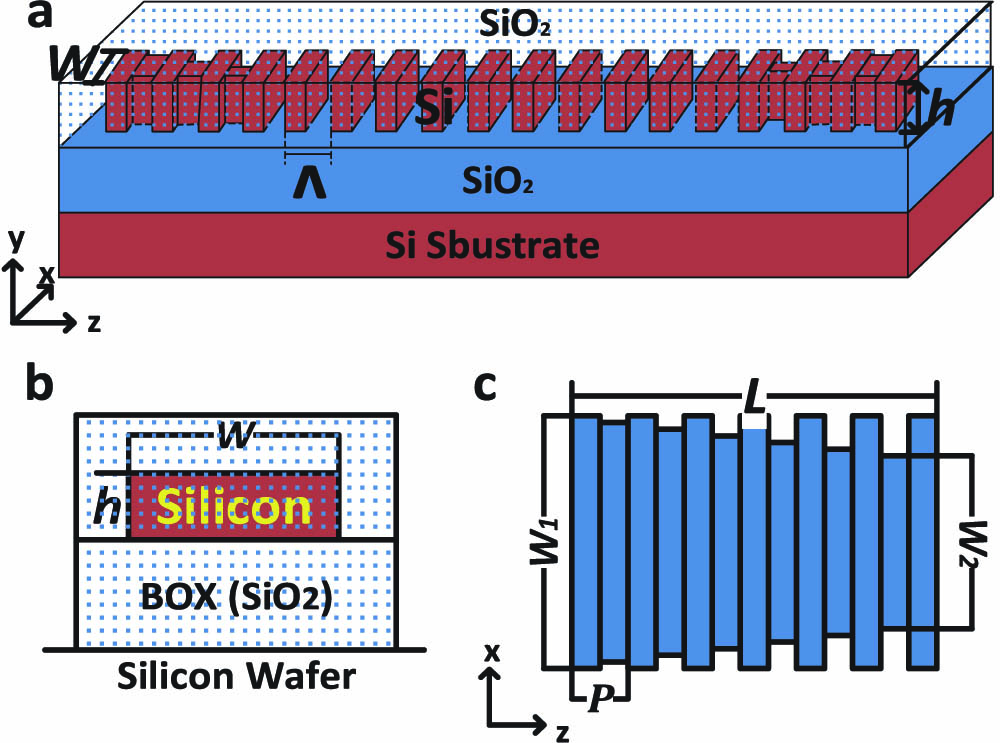
230.0230 Optical devices 250.0250 Optoelectronics 130.0130 Integrated optics 130.0250 Optoelectronics 130.4110 Modulators 130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 130.5460 Polymer waveguides 160.2100 Electro-optical materials 160.4236 Nanomaterials Subwavelength grating waveguide devices in silicon-on-insulators for integrated microwave photonics (Invited Paper) Download:879次
Download:879次
 Download:879次
Download:879次We provide an overview of our recent work on developing subwavelength grating (SWG) waveguide devices as an enabling technology for integrated microwave photonics. First, we describe wavelength-selective SWG waveguide filters, including ring resonators, Bragg gratings, and contradirectional couplers. Second, we discuss the development of an index variable optical true time delay line that exploits spatial diversity in an equal-length waveguide array. These SWG waveguide components are fundamental building blocks for realizing more complex structures for advanced microwave photonic signal processing.
050.2770 Gratings 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics DFB laser arrays based on the REC technique and their applications in radio-over-fiber systems (Invited Paper) Download:1054次
Download:1054次
 Download:1054次
Download:1054次We review the recent work of distributed-feedback (DFB) multi-wavelength semiconductor laser arrays (MWLAs) based on the reconstruction equivalent chirp (REC) technique. The experimental results show that the proposed MWLA has very high wavelength precision (< ± 0.1 nm
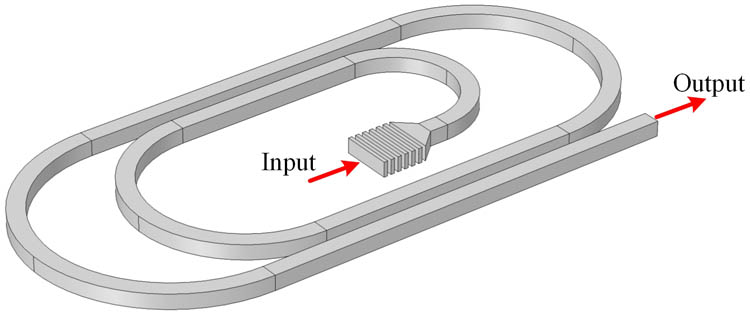
140.2010 Diode laser arrays 050.2770 Gratings Optical biosensors with a high sensitivity and a low detection limit play a highly significant role in extensive scenarios related to our daily life. Combined with a specific numerical simulation based on the transfer matrix and resonance condition, the idea of novel single-waveguide-based microresonators with a double-spiral-racetrack (DSR) shape is proposed and their geometry optimizations and sensing characteristics are also investigated based on the Vernier effect. The devices show good sensing performances, such as a high quality factor of 1.23 × 10 5 1.8 × 10 5
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 230.5750 Resonators 230.3990 Micro-optical devices 230.3120 Integrated optics devices Photonic generation of background-free millimeter-wave ultra-wideband signals (Invited Paper) Download:702次
Download:702次
 Download:702次
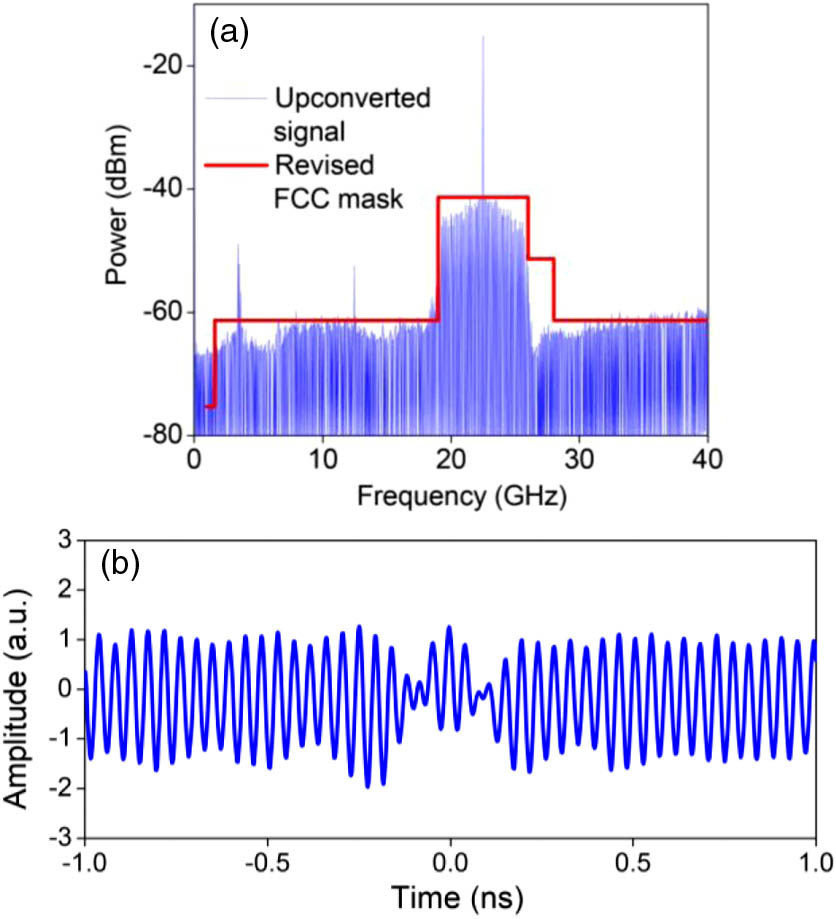
Download:702次We review the recent progress of photonic generation of millimeter wave (MMW)-ultra-wideband (UWB) signals. To fully satisfy the standard defined by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the baseband signal (background signal) and the residual local oscillator (LO) signal should be well controlled. We discuss several schemes in this work for generating background-free MMW-UWB signals that are fully compliant with the FCC requirement.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 060.2310 Fiber optics A 4 × 4
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 060.2840 Heterodyne Ultra-low phase noise performance is required for frequency agile local oscillators, which are the core for high resolution imagers, spectrum analyzers, and high speed data communications. A forced opto-electronic oscillator (OEO) benefits from frequency stabilization techniques for realizing a clean and low phase noise source at microwave and millimeter wave frequencies. Forced oscillation techniques of self-injection locking and self-phase lock loop are combined to provide an ultra-low oscillator phase noise both close-in and far-away from the carrier frequency, while a tunable yttrium iron garnet microwave filter combined with a wavelength tuned transversal filter are employed to implement both coarse and fine frequency tuning for a tunable X-band OEO. A phase noise of 137 dBc / Hz
060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems 230.4910 Oscillators 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics We propose a high-Q Q
140.3410 Laser resonators 230.0250 Optoelectronics 140.3570 Lasers, single-mode Full-duplex transmission of IEEE 802.11ac-compliant MIMO WLAN signals over a 2-km 7-core fiber Download:888次
Download:888次
 Download:888次
Download:888次In this Letter, we experimentally demonstrate a full-duplex transmission system of IEEE 802.11ac-compliant multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) signals over a 2-km 7-core fiber for in-building wireless local-area network (WLAN) distributed antenna systems. For full-duplex 3 × 3 6 × 6
350.3950 Micro-optics 060.4230 Multiplexing 060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems Photonics-assisted compressive sampling system for wideband spectrum sensing (Invited Paper) Download:986次
Download:986次
 Download:986次
Download:986次Compressive sampling (CS) has attracted considerable attention in microwave and radio frequency (RF) fields in recent years. It enables the acquisition of high-frequency signals at a rate much smaller than their Nyquist rates. Combined with photonics technology, traditional CS systems can significantly enlarge their operating bandwidth, which offers great potential for spectrum sensing in cognitive radios. In this Letter, we review our recent work on photonic CS systems for wideband spectrum sensing. First, a proof-of-concept photonics-assisted CS system is demonstrated; it is capable of acquiring numerous radar pulses in an instantaneous bandwidth spanning from 500 MHz to 5 GHz with a 500-MHz analog-to-digital converter (ADC). To further reduce the acquisition bandwidth, multi-channel photonics-assisted CS systems are proposed for the first time, enabling the acquisition of multi-tone signals with frequencies up to 5 GHz by using 120-MHz ADCs. In addition, the system bandwidth is increased from 5 to 20 GHz by employing time-interleaved optical sampling.
060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems 230.0250 Optoelectronics 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics Performance evaluation of optical beamforming-based wideband antenna array (Invited Paper) Download:838次
Download:838次
 Download:838次
Download:838次A wideband-generalized pattern multiplication approach to evaluate the performance of an optical beamforming-based wideband antenna array is proposed and experimentally demonstrated, which enables the far-field measurement of a large wideband array with a small anechoic chamber. Because the optimum reception of a wideband microwave signal is highly related to the time-domain distortions of the beamforming system, a correlation-receiver-based radiation pattern is applied to take the fidelity of the wideband signals into account. A four-element optical beamforming system is built to verify the feasibility of the proposed method. The results achieved by the proposed method agree well with the conventional direct measurements.
280.5110 Phased-array radar 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics A full-band direct-conversion receiver using a microwave photonic in-phase and quadrature (I/Q) mixer is proposed and experimentally evaluated in terms of radio frequency (RF) range, port isolation, phase imbalance, conversion gain, noise figure, spurious-free dynamic range, and error vector magnitude. The proposed microwave photonic I/Q mixer shows significant advantages in local oscillator leakage and I/Q phase imbalance over entire RF bands, which are recognized as major drawbacks of conventional direct-conversion receivers.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing 250.4110 Modulators To design a compact erbium-doped fiber laser, a high-concentration erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is needed. However, increasing the erbium ion (Er 3 + Er 3 + Er 3 + Er 3 + Er 3 +
060.2290 Fiber materials 060.2320 Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2410 Fibers, erbium 060.3510 Lasers, fiber Flat mirror for millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging systems using an inexpensive metasurface Download:737次
Download:737次
 Download:737次
Download:737次Flat mirrors, also known as flat parabolic surfaces, for millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging systems are demonstrated. This flat mirror is based on the metasurface in which an inexpensive printed circuit board technology is used to realize copper patterns printed on an FR4 substrate. Compared to the conventional reflector antennas used today in diverse applications (for homeland security, medical systems, communication, etc.), the suggested mirror has major advantages in process simplicity, mechanical flexibility, frequency alignment, weight, and cost. The theoretical background, simulation results, experimental results, and proof of concept are given in this Letter.
110.6795 Terahertz imaging 160.3918 Metamaterials 230.4040 Mirrors 240.6700 Surfaces We present a lamp-pumped Nd: phosphate glass laser amplifier delivering up to 1 J of pulse energy at 1053 nm with a repetition rate of 1 Hz and an injected pulse energy of 2.5 mJ. The amplifier system employs a beam-shaping module and a four-pass, lamp-pumped amplifier. The thermally induced wavefront distortion is mitigated and a uniform gain distribution is obtained by a four-lamp-pumped laser head in the amplifier. Thus, an excellent beam quality is obtained.
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.5560 Pumping 140.6810 Thermal effects 140.3295 Laser beam characterization A novel black phosphorus (BP) solution saturable absorber (SA) is fabricated by the liquid-phase-exfoliated method and successfully used for passively Q Nd : YVO 4
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials A dual-wavelength fiber laser operating at the 1550 nm region using a side-polished arc-shaped fiber with deposited ZnO nanoparticles is proposed and demonstrated. The arc-polished fiber is fabricated by using a simple but novel approach in which a silicon carbide paper polishes one side of a conventional single-mode fiber. An arc-polished fiber with a length of 2.25 mm and an insertion loss of 0.95 dB is obtained and deposited with ZnO nanoparticles by the drop-cast method. A stable dual-wavelength output is obtained at 1562.5 and 1563.4 nm at peak powers of 9.3 10.1 dBm
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3500 Lasers, erbium Beat note analysis and spectral modulation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers with radio frequency injection Download:962次
Download:962次
 Download:962次
Download:962次We demonstrate the electrical beat note analysis and radio frequency (RF) injection locking of a continuous wave (cw) terahertz quantum cascade laser (QCL) emitting around 3 THz (~ 100 μm ~ 180 MHz
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 040.0040 Detectors 350.0350 Other areas of optics 060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications We provide the first demonstration of pure red emission in the visible light region via three-photon excitation in monodisperse Na 3 ZrF 7 : Er ~ 22 nm Na 3 ZrF 7 : Er Er 3 + S 3 / 2 4 → F 4 15 / 2 F 9 / 2 4 → F 4 15 / 2 Er 3 + Er 3 + 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4760 Optical properties
Static light scattering properties of a ZnO nanosphere aqueous suspension at visible and near-infrared wavelengths Download:892次
Download:892次
 Download:892次
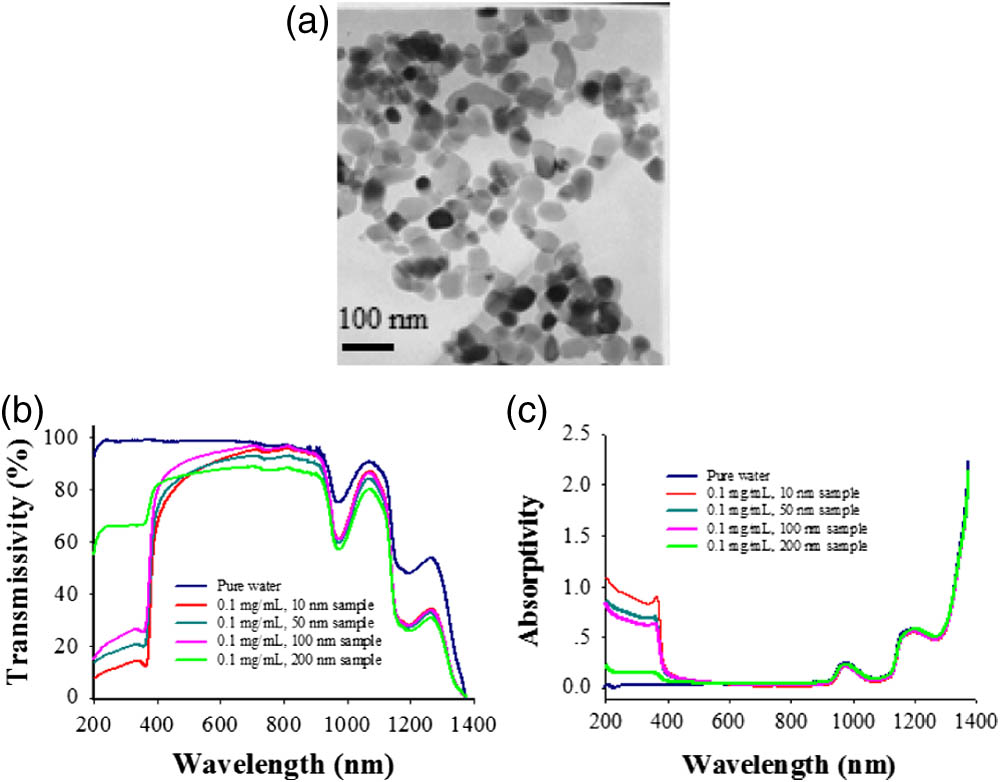
Download:892次The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres with four different particle diameters of 10, 50, 100, and 200 nm suspended in water are investigated theoretical and experimentally in the spectral range of the entire visible range and part of the near-infrared region. The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres suspended in water are described by employing three main parameters: the angular distribution of the scattering intensity I α scat σ scat
290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5825 Scattering theory 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
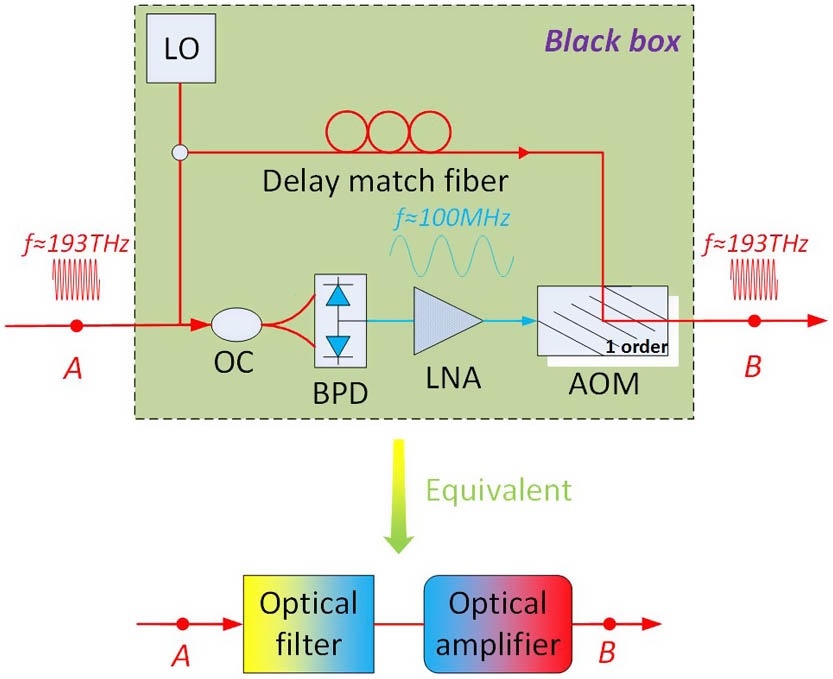
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦