1 中国科学院半导体研究所全固态光源实验室,北京 100083
2 北京市全固态激光先进制造工程技术研究中心,北京 100083
3 中央民族大学 理学院,北京 100081
4 中国科学院大学 材料科学与光电技术学院,北京 100049
透明硬脆材料由于其优异的力学性能、热稳定性、耐腐蚀性以及光电性能,广泛应用于半导体与电子领域。传统透明硬脆材料切片方法效率低、材料损耗大,制约了硬脆材料的推广应用。激光剥离技术是近年来新兴的一种透明硬脆材料切片新方法,较传统金刚线切割方法大幅提升硬脆材料的切片效率和材料利用率,目前已发展成为硬脆材料激光加工领域学术研究与产业应用的焦点。文中深入分析透明硬脆材料激光剥离物理过程,归纳激光剥离过程关键科学问题:透明硬脆材料对激光的非线性吸收、激光作用下材料内部微观结构演化与缺陷扩展规律,以及激光光场调控对材料改质影响机制等。基于这些科学问题,综述了近年来激光剥离不同类型透明硬脆材料的研究进展,目前用于激光剥离的材料已涵盖了SiC、Si、GaN、金刚石等半导体材料,蓝宝石、多晶Al2O3、氧化锆等陶瓷材料,激光剥离技术已发展出超快激光双脉冲诱导剥离、超快激光-化学辅助剥离、多激光复合剥离等。激光剥离物理过程是一个典型的激光-材料-热学-力学多学科交叉问题,尽管在实验结果方面获得了显著突破和迅猛发展,但目前对于工艺机理仍缺乏深入的理论与数值建模研究。未来透明硬脆材料激光剥离技术将会朝着百微米以下超薄厚度剥离、改质层低损伤、工艺自适应等方向发展,将为半导体与电子等领域快速发展提供更大的技术支撑。
超快激光 硬脆材料 剥离 非线性吸收 缺陷扩展 光场调控 ultrafast laser hard and brittle materials splitting nonlinear absorption defect extension optical field modulation 红外与激光工程
2024, 53(1): 20230487
吉林大学电子科学与工程学院集成光电子学国家重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012
近年来,红外微光学器件由于在红外传感与成像、红外探测等领域中具有重要的应用价值而得到了飞速发展,直接在硬脆材料衬底上制备的红外微光学器件更是在苛刻环境应用领域中具有不可代替的作用。针对此需求,已经有研究人员提出了多种高精密制造方法。其中,飞秒激光加工由于真三维加工等独特优势已经被广泛应用于各种复杂三维微纳结构的制备,也为解决硬脆材料红外微光学器件的制备问题提供了新的思路。从飞秒激光加工技术、常用红外光学材料以及基于飞秒激光加工的硬脆材料红外微光学器件的制备和应用方面入手,梳理了近些年此领域的发展情况,重点介绍了折射器件和衍射器件等红外微光学器件以及飞秒激光加工技术在红外传感与成像、红外探测等领域中的应用,并对飞秒激光加工硬脆材料红外微光学器件的发展趋势进行了展望。
激光技术 飞秒激光 硬脆材料 红外微光学器件 红外微光学应用
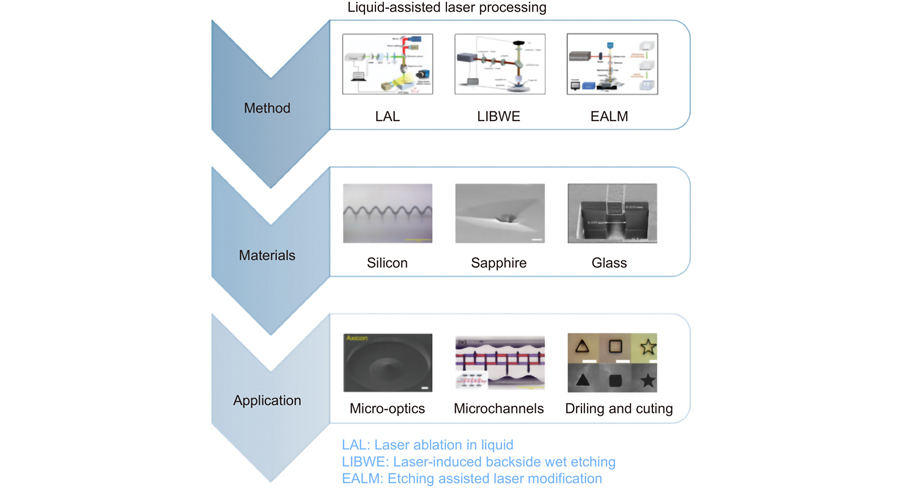
吉林大学电子科学与工程学院,集成光电子学国家重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012
Overview: With the development of industry, laser fabrication has become one of the important technologies for welding, cutting, surface processing, and other advanced manufacturing areas. At the same time, the pursuit of structures miniaturization, devices integration, and high precision has put forward more stringent requirements for laser fabrication technologies. Due to the advantages of stable mechanical and chemical properties and unique photoelectric properties, hard and brittle materials have been widely used in aerospace, the photoelectric industry, et al. Laser fabrication is an ideal technology for hard and brittle materials processing due to its high precision, high energy, and non-contact properties. In order to achieve the removal of hard and brittle materials, high laser energy is usually required, resulting in low fabrication accuracy and poor surface quality. As an improved laser processing method, liquidassisted laser fabrication can effectively improve fabrication accuracy and surface quality. The processing characteristics and material removal principles of three different liquid-assisted laser processing technologies are summarized in this review. According to the different functions of the medium through which the laser penetrates and the kinds of liquid, liquid-assisted laser fabrication technology can be divided into Laser ablation in liquid (LAL), laser-induced backside wet etching (LIBWE), and etching-assisted laser modification (EALM). The auxiliary liquid of Laser ablation in liquid is mostly water, which mainly plays the role of cooling and removing debris. The auxiliary liquids used by laser-induced backside wet etching include organic solvents, acid-base solutions, inorganic salts, and other liquids, which play different roles according to different liquids. The etching-assisted laser modification mainly uses an acid or alkaline solution as an auxiliary liquid to remove laser-modified materials. Different methods and auxiliary liquids have different mechanisms in the methods. Therefore, almost any material can be processed by choosing suitable methods and auxiliary liquids, including photosensitive glass, silicon crystal, sapphire, and other transparent hard brittle materials. Here, we summarize the fabrication technologies and fabrication parameters for different materials. The development and applications of liquid-assisted laser fabrication technologies in the fields of micro-optical components, microfluidic devices, and drilling and cutting are introduced. Finally, the challenges of the technology are discussed.
激光加工 硬脆材料 液体辅助制造 微/纳米结构 laser fabrication hard and brittle materials liquid assisted fabrication micro/nano structures
1 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所,安徽 合肥 230031
2 中国科学技术大学,安徽 合肥 230026
激光抛光技术具有非接触式加工、不产生机械应力、抛光精度高等优点,特别适用于脆硬材料的表面加工。本文阐述了激光抛光工艺的特点和作用机理,介绍了激光抛光工艺中各参数对加工质量的影响,综述了各国对于硬脆材料的激光抛光技术的研究成果和现状。着重介绍了激光热抛光和激光冷抛光的区别和特点,以及抛光原理和研究进展。
材料 热效应 光化学效应 激光抛光 硬脆材料 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(13): 1300003





