强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(7): 071001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Thin Film Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
4 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
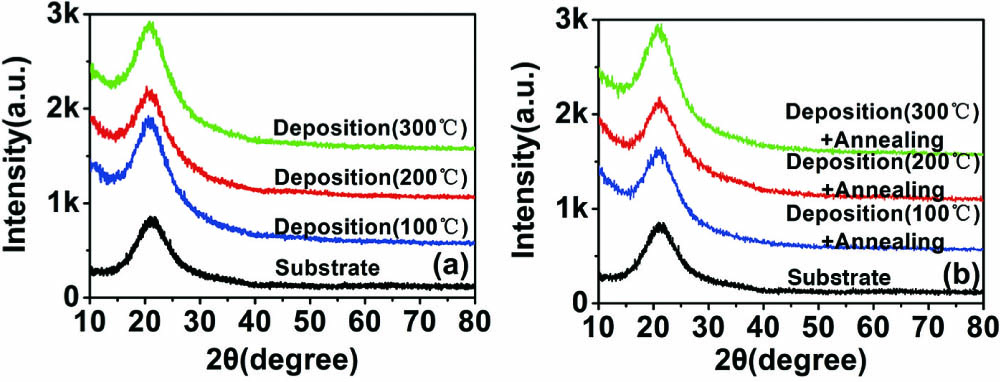
Ultrathin Ge films with thickness of about 15 nm at different deposition temperatures were prepared by electron beam evaporation. Spectral measurement results showed that as the deposition temperature increased from 100°C to 300°C, the transmittance of the films in the wavelength range from 350 nm to 2100 nm decreased. After annealing in air at 500°C, the transmittance significantly increased and approached that of uncoated fused quartz. Based on the Tauc plot method and Mott–Davis–Paracrystalline model, the optical band gap of Ge films was calculated and interpreted. The difference in optical band gap reveals that the deposition temperature has an effect on the optical band gap before annealing, while having little effect on the optical band gap after annealing. Furthermore, due to oxidation of Ge films, the optical band gap was significantly increased to ~5.7 eV after annealing.
Ge films transmittance optical band gap deposition temperature annealing Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(10): 103101
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所精密光学制造与检测中心, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所薄膜光学实验室, 上海 201800
利用时间分辨激光光度计实时测量纳秒脉冲激光诱导熔石英体损伤过程中的透射、反射和散射变化量;通过在同一区域多次动态测量直至损伤产生,获得了多脉冲累积破坏的时间分辨过程。结果表明:在损伤出现前的脉冲辐照过程中,熔石英透过率已明显下降,后向反射率同步上升,甚至可达70%;后向反射率的上升量与透过率的损失量几乎相同;在多脉冲辐照过程中,只要脉冲辐照中出现后向反射,就会产生损伤;受激布里渊散射对多脉冲诱导熔石英体损伤具有促进作用。
激光光学 激光损伤 激光材料 光学性质 熔石英
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Thin Film Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
A time-resolved high-power laser photometer, which measures the real-time variations of transmission, internal reflection, and scattering simultaneously with picosecond time resolution, was developed to investigate the material response sequence during high-power nanosecond laser irradiation in thick fused silica. It was found that the transient transmission decreased sharply, accompanied by an increase in internal reflection at the rising edge of the laser pulse. The transient transmission recovered, while laser damage did not occur, but it did not recover if the scattering increased, indicating the occurrence of laser damage. The reason for the sharp decrease of transmission and the relationship between the transmission drop and laser damage were discussed.
160.4760 Optical properties 140.3330 Laser damage 160.3380 Laser materials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
4 IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
The spatial resolved method, which measures the laser-induced damage fluence by identifying the location of the damage point in the Gaussian beam three-dimensional direction, is demonstrated. The advantages and practicality of this method have been explained. Taking a triple frequency beam splitter as an example, the defect damage fluence can be accurately calculated by the spatial resolved method. The different defect damage performance of the triple frequency splitter is distinguished under irradiations of only the 355 and 532 nm lasers. The spatial resolved method provides a way to obtain precise information of optical film defect information.
140.3330 Laser damage 140.3295 Laser beam characterization Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(3): 031403

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
4 National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Materials Surface Engineering Technology, Guangdong Institute of New Materials, Guangzhou 510650, China
Laser-induced modification at 355 nm of deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP) crystals following exposure to nanosecond (ns) and sub-ns laser irradiation is investigated in order to probe the absorption mechanism in damage initiation. Laser damage resistance is greatly improved by sub-ns laser conditioning, whereas only a little improvement occurred after ns laser conditioning at the same laser fluence. Moreover, scattering and transmittance variations after the two types of laser conditioning indicate similar reduction of linear absorption. However, by contrast, large differences on nonlinear absorption modification are discovered using Z-scan measurement. This characteristic absorption modification by laser irradiation provides evidence that a nonlinear absorption mechanism plays a key role in damage initiation at 355 nm.
160.4670 Optical materials 190.4180 Multiphoton processes Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 051601
1 长春理工大学理学院, 吉林 长春 130022
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
提出一种基于高斯脉冲激光空间分辨测量光学元件表面激光损伤阈值的方法。通过设定激光能量密度差对高斯光斑进行能量密度分区, 统计并分析每个能量密度分区的能量密度以及损伤密度分布, 设定一个零损伤密度所对应的激光能量密度作为所测样品的激光损伤阈值。同时利用国际标准1-on-1激光损伤阈值测试方法对同一样品进行激光损伤阈值测试, 并将两种测试方法获得的损伤阈值进行了比较分析, 证明基于高斯脉冲激光空间分辨的激光损伤阈值测试方法, 解决了国际标准1-on-1激光损伤阈值测试中将高斯光斑内空间能量密度以及损伤点的不均匀分布等效地视作均匀分布所带来的问题。
测量 激光损伤阈值 空间分辨
1 中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所 中国科学院强激光材料重点实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
针对晶体表面的损伤特性,采用小光斑扫描激光预处理技术预辐照DKDP晶体元件,并采用表面损伤自动探测系统实时分析每个脉冲辐照后晶体表面的损伤情况,比较预处理和未预处理区域的损伤点密度确定表面预处理效果,并进一步模拟分析表面各类缺陷在纳秒强激光辐照下的动态过程,解释激光预处理对精抛表面提升作用的微观机制并分析它对粗抛表面提升不明显的原因。实验结果表明,激光预处理技术对粗抛表面的提升作用并不明显,但是可以大幅度抑制精抛表面的损伤点密度。在本文的实验条件下,晶体表面的抗激光损伤能力可以提升约60%。比较体材料和精抛表面的预处理效果发现: 当体材料的抗破坏能力通过预处理提升后,精抛表面的抗激光损伤能力也会提升,由此可见精抛表面的激光预处理效果与体材料性能相关。
激光损伤 激光预处理 损伤阈值 预处理效果 氘化磷酸二氢钾(DKDP) laser damage laser conditioning damage threshold laser conditioning effects dopted deuterium KDP (DKDP)
中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所 强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 210800
回顾了国内在激光预处理技术研究方面取得的进展。综述了基于激光预处理技术提升基频介质膜、磷酸二氢钾/高掺氘磷酸二氢钾(KDP/DKDP)晶体等光学元件抗激光损伤性能的机理、效果和关键技术。针对高功率激光驱动器中关键光学元件激光负载能力的提高, 建立了大口径光学元件激光预处理平台, 实现了基频介质膜元件的激光预处理工程化作业。比较了纳秒和亚纳秒脉冲宽度激光对DKDP晶体损伤性能的影响。基于亚纳秒激光预处理后, 纳秒激光辐照至14.4 J/cm2(5 ns)尚未出现"本征"损伤的实验结果, 提出了用于DKDP晶体的亚纳秒激光预处理方案, 并指出亚纳秒激光预处理技术将成为高功率激光三倍频晶体抗激光损伤性能达标的关键技术。
激光预处理 激光与物质相互作用 高功率激光 激光损伤阈值 介质膜 磷酸二氢钾(KDP)晶体 高掺氘磷酸二氢钾(DKDP)晶体 laser conditioning high power laser system laser induced damage threshold dielectric coating potassium dihydrogen phosphate(KDP) crystal doped deuterium KDP(DKDP) crystal 光学 精密工程
2016, 24(12): 2938
1 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
3 中国科学技术大学近代物理系核探测与核电子学国家重点实验室, 合肥 230026
对金属介质多层膜样品进行不同温度的退火处理。实验发现,当退火温度为350 ℃时,在样品Au层与SiO2层的界面处出现过渡层,样品具有很强的抗化学清洗能力。利用透射电子显微镜观测与能谱仪分析发现,过渡层的出现主要是Cr原子从Au层底部扩散到SiO2层的结果。过渡层可以增强Au层与SiO2层间的粘附力,阻挡酸溶液的渗入,使得金属介质多层膜的抗化学清洗能力得到增强。
材料 界面扩散 化学清洗 退火 粘附力 中国激光
2016, 43(10): 1003002





