2015, 13(12) Column
Atmospheric Optics and Oceanic Optics Detectors Diffraction and Gratings Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Geometric Optics Instrumentation, Measurement and Metrology Lasers and Laser Optics Machine Vision Materials Nonlinear optics Nonlinear Optics Optical Devices Quantum Optics Thin Films Ultrafast Optics
Chinese Optics Letters 第13卷 第12期
Second generation solar adaptive optics for 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at the Fuxian Solar Observatory Download:1276次
Download:1276次
 Download:1276次
Download:1276次A second generation solar adaptive optics (AO) system is built and installed at the 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) of the Fuxian Solar Observatory (FSO) in 2015. The AO high-order correction system consists of a 151-element deformable mirror (DM), a correlating Shack–Hartmann (SH) wavefront sensor (WFS) with a 3500 Hz frame rate, and a real-time controller. The system saw first light on Mar. 16, 2015. The simultaneous high-resolution photosphere and chromosphere images with AO are obtained. The on-sky observational results show that the contrast and resolution of the images are apparently improved after the wavefront correction by AO.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.0115 Imaging through turbulent media We propose and demonstrate a pseudo Fabry–Pérot filter in the terahertz frequency range of 0.1–0.5 THz. It consists of alternative liquid crystal layers and metallic slats. Separate sharp resonant peaks are shown in the simulated transmission spectra, and their positions shift toward higher frequencies when the refractive index of liquid crystal decreases. The measured transmission spectra are consistent with corresponding simulations. Via thermally tuning the refractive index of the filled liquid crystal, the resonant transmission frequencies shift accordingly. The work supplies a novel design for tunable terahertz filters, which would play important roles in terahertz imaging, sensing, high speed communication, and security applications.
040.2235 Far infrared or terahertz 120.2230 Fabry-Perot 120.2440 Filters 160.3710 Liquid crystals This Letter proposes a brand-new filament diameter measurement method based on what is called “dual diffraction,” in that a grating is added behind the filament to make full use of its subdivision and amplification characteristics. Higher measurement accuracy is achieved by this method compared with the traditional diffraction method. To verify its accuracy, three standard filaments with nominal values of 100.2, 120.1, and 140.8 μm are measured by the dual diffraction method and traditional diffraction method under the same experimental conditions. The relative measurement errors of the new method are less than 0.75%, and its average relative error is reduced by 56% compared with the traditional diffraction method.
050.1940 Diffraction 050.2770 Gratings 120.4820 Optical systems A combination of light-emitting diode (LED) identification and a time-division multiplexing scheme is proposed in this Letter for indoor location-based service. With the scheme, the arrangement of white LED lamps and the structure of a data frame are designed to realize high-accuracy indoor positioning and location-based payload data transmission simultaneously. The results of the experiment demonstrate that the indoor positioning accuracy is 10 cm and 2 Mb/s data transmission with high signal quality is realized.
060.4510 Optical communications 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 040.5160 Photodetectors Fabrication and sensing characteristics of intrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometers in fiber tapers Download:924次
Download:924次
 Download:924次
Download:924次This Letter presents intrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometers in the fiber tapers fabricated by the femtosecond laser micromachining technique. The sensing of temperatures as high as 1000°C based on the fiber device is characterized, with a sensitivity of 15.28 pm / ° C 73.05 dB / RIU
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 050.2230 Fabry-Perot Multiple-object Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor design for a wide field of view on the retina Download:838次
Download:838次
 Download:838次
Download:838次In order to detect the aberration from a wide field of view (FOV) on the retina with adaptive optics, we present a multiple-object Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor (MOSHWFS) design. The simulated results indicate that the wavefront from our MOSHWFS can be reconstructed for multiple objects, and the measurement error can be less than λ / 7 λ / 14 0.798 λ 0.895 λ
080.1010 Aberrations (global) 330.7321 Vision coupled optical systems 330.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices A new optical method based on frequency-shift feedback and laser confocal microscopy is presented to noninvasively measure a microstructure inside a sample. Due to the limit of axial resolution caused by poor signal detection ability, conventional laser feedback cannot precisely measure the microstructure. In this Letter, the light scattered by the sample is frequency shifted before feedback to the laser to obtain a magnification. Weak signals that change with the microstructure can be detected. Together with the tomography ability of laser confocal microscopy, the inner microstructure can be measured with high axial resolution.
120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology 120.4820 Optical systems 180.1790 Confocal microscopy 180.5810 Scanning microscopy Ultrafast laser system based on noncollinear optical parametric amplification for laser spectroscopy Download:1048次
Download:1048次
 Download:1048次
Download:1048次We report the experimental demonstration of transform-limited sub-6 fs pulses at an optimal central wavelength by a tunable noncollinear optical parametric amplification (NOPA) source. Meanwhile, a white light continuum in the near-infrared (NIR) range from 900 to 1100 nm is also successfully generated by focusing the unconverted 800 nm beam during NOPA generation on a sapphire rod. Both visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe experiments are realized using the same laser system. As examples, ultrafast photo-induced exciton dynamics inside two kinds of materials are investigated by the visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe spectroscopy, respectively.
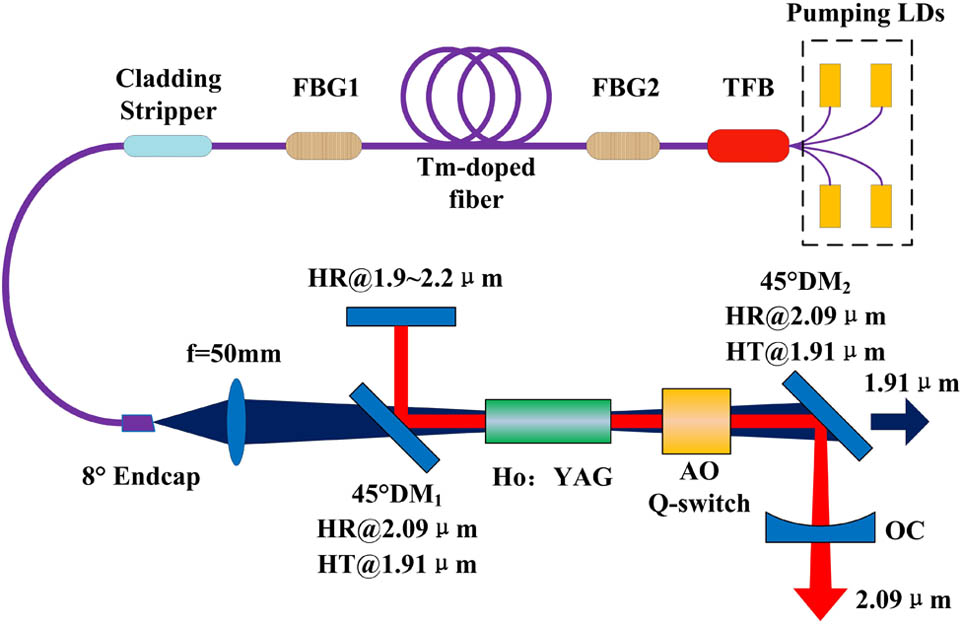
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7150 Ultrafast spectroscopy 320.6629 Supercontinuum generation 300.6530 Spectroscopy, ultrafast A high-power, high-energy Ho:YAG oscillator resonantly pumped by a Tm-doped fiber laser is presented. A maximum continuous output power of 38 W with a slope efficiency of 51.9% is achieved at the wavelength of 2.09 μm, and M 2 ≈ 1.48 Q TEM 00
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.5680 Rare earth and transition metal solid-state lasers We propose and demonstrate a laser-diode-pumped, maglev rotating Nd:YAG disk laser. The disk of the laser crystal is attached to a maglev pyrolytic graphite disk and is rotated by compressed gas. In this rotating disk laser, the detrimental thermal effects are alleviated and the laser can be operated in the single transverse electromagnetic ( TEM ) 00 ~ 4 Hz
140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3570 Lasers, single-mode 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.6810 Thermal effects The existing two-dimensional vision measurement methods ignore lens distortion, require the plane to be perpendicular to the optical axis, and demand a complex operation. To address these issues, a new approach based on local sub-plane mapping is presented. The plane calibration is performed by dividing the calibration plane into sub-planes, and there exists an approximate affine invariance between each small sub-plane and the corresponding image plane. Thus, the coordinate transformation can be performed precisely, without lens distortion correction. The real comparative experiments show that the proposed approach is robust and yields a higher accuracy than the traditional methods.
150.0150 Machine vision 150.1488 Calibration In this Letter, new concepts of fluorescence phase-change materials and fluorescence phase-change multilevel recording are proposed. High-contrast fluorescence between the amorphous and crystalline states is achieved in nickel- or bismuth-doped Ge 2 Sb 2 Te 5
160.2900 Optical storage materials 310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 210.4770 Optical recording Research on light scattering from a large chiral sphere shows that the rainbow phenomenon is different from that of an isotropic sphere. A chiral sphere with certain chirality generates three first-order rainbows. In this Letter, we present a geometric optics interpretation for the phenomenon and make a calculation of the rainbow angles. The ray traces inside the sphere are determined by the reflection and refraction laws of light at the achiral–chiral interface and the chiral–achiral interface. The calculated rainbow angles achieve good agreements with those obtained by the analytical solutions. The effects of chirality and the refractive index of the sphere on rainbow angles are analyzed.
160.1585 Chiral media 080.0080 Geometric optics 290.5850 Scattering, particles The influence of group velocity dispersion (GVD) on the self-focusing of femtosecond laser pulses is investigated by numerically solving the extended nonlinear Schr?dinger equation. By introducing the GVD length LGVD into the semi-empirical, self-focusing formula proposed by Marburger, a revised one is proposed, which can not only well explain the influence of GVD on the collapse distance, but also is in good agreement with the numerical results, making the self-focusing formula applicable for more cases.
190.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 190.0190 Nonlinear optics 190.3270 Kerr effect 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Intensity modulation of light by light in a periodically poled MgO-doped lithium niobate crystal Download:733次
Download:733次
 Download:733次
Download:733次In this Letter, we investigate a method for controlling the intensity of a light by another light in a periodically poled MgO-doped lithium niobate (PPMgLN) crystal with a transverse applied external electric field. The power of the emergent light can be modulated by the power ratio of the incident ordinary and extraordinary beams. The light intensity control is experimentally demonstrated by the Mach–Zehnder interference configuration, and the results are in good agreement with the theoretical predictions.
190.4223 Nonlinear wave mixing 230.6120 Spatial light modulators Pulsed collimated blue light at 420.3 nm is generated in hot Rb vapor by upconverting the 778.10 nm pumping beam through four wave mixing process. The energy conversion efficiency exceeds 1% when a 45 cm-long, 170°C heated Rb cell is used. The influence of cell temperature, wavelength, and energy of a pumping laser are fully examined. The efficiency of the photon conversion is found to be more sensitive to the blue detuning of the pump light and less sensitive to the red detuning of the pump light. This phenomenon can be explained by stimulated hyper-Raman scattering involved in the four-wave mixing process.
190.4380 Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing 190.4180 Multiphoton processes 190.7220 Upconversion 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Linear variable filters fabricated by ion beam etching with triangle-shaped mask and normal film coating technique Download:718次
Download:718次
 Download:718次
Download:718次In this Letter, we propose a method of fabricating linear variable filters by ion beam etching with masking mechanisms. A triangle-shaped mask is designed and set between the ion source and sample. During the ion etching, the sample is moved back and forth repeatedly with a constant velocity for the purpose of obtaining the linearly varied thickness of the cavity. Combined with ion beam assistant thermal oxidative electron beam evaporation deposition technology, we finish the fabrication of linear variable filters, whose filtering range is from 500 to 580 nm. The measured results indicate that the transmittance and bandwidth at the peak wavelength are around 40% and 3 nm.
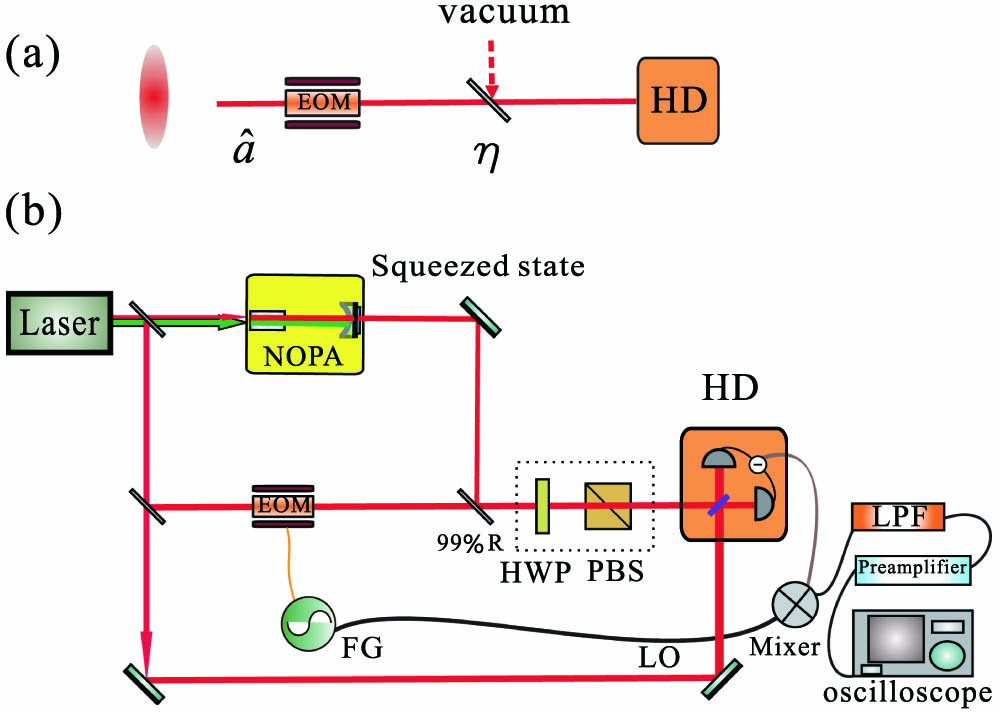
230.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 220.4610 Optical fabrication 310.4165 Multilayer design The distribution of a modulated squeezed state over a quantum channel is the basis for quantum key distribution (QKD) with a squeezed state. In this Letter, a modulated squeezed state is distributed over a lossy channel. The Wigner function of the distributed state is measured to observe the evolution of the quantum state over a lossy channel, which shows that the squeezing level and the displacement amplitude of the quantum state are decreased along with the increase of the channel loss. We also measure the squeezing level in the frequency domain by the frequency shift technique. The squeezing of the modulated squeezed state at the modulation frequency is observed in this way. The presented results supply a reference for a QKD with a squeezed state.
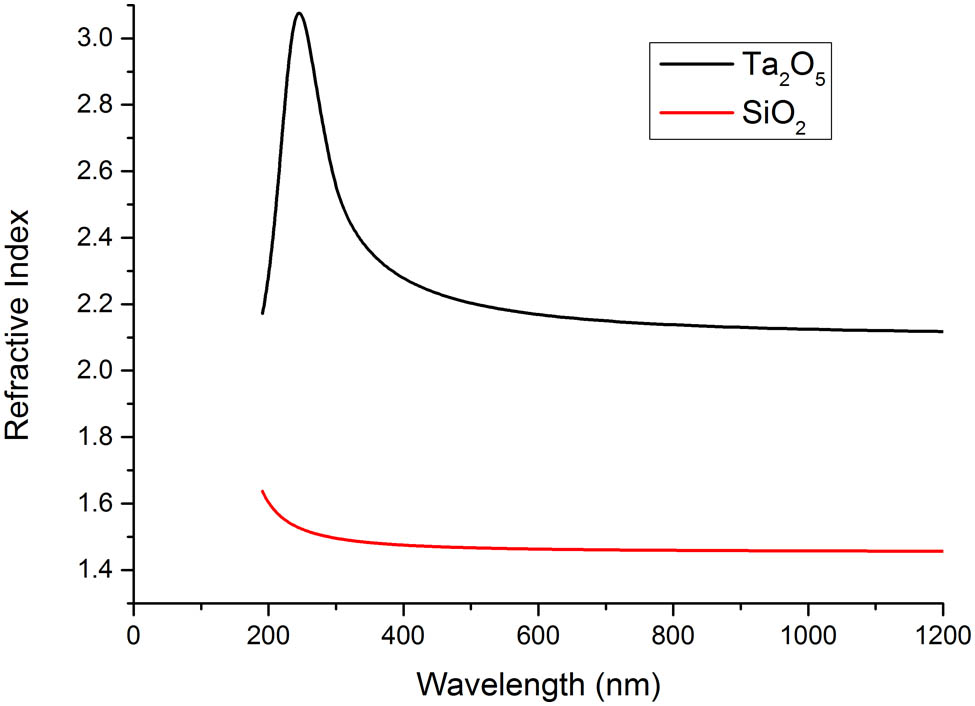
270.0270 Quantum optics 270.5565 Quantum communications 270.6570 Squeezed states In our investigation, lead germanium telluride, which is a pseudo-binary alloy of IV-VI narrow-gap semiconductor compounds of PbTe and GeTe, can be used in the fabrication of mid-wavelength infrared narrow bandpass filters as a high-index coating material, due to its high refractive index, lower absorption, and tunability of fundamental absorption edges. It is demonstrated that a half-width of 160 nm and a better rejection ratio can be obtained for a simple 8-layer double cavity filter with a central wavelength at 4 μm, compared with a half-width of 390 nm for those conveniently fabricated using Ge as high-index material.
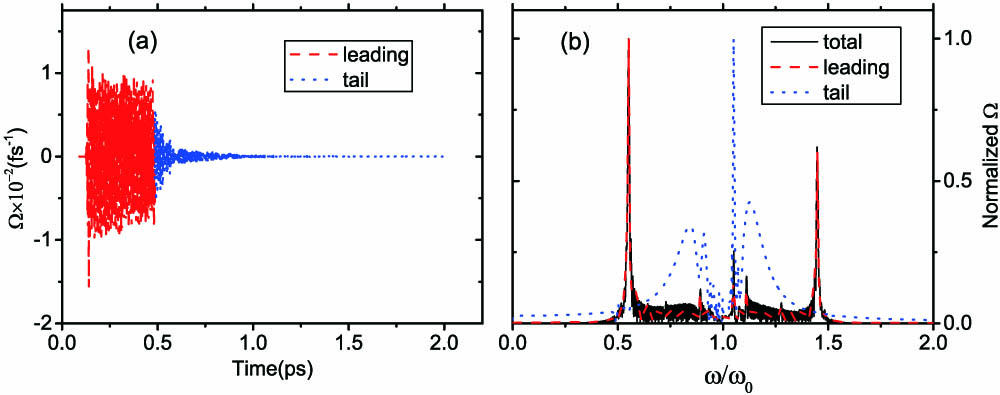
310.1620 Interference coatings 310.3840 Materials and process characterization 310.6188 Spectral properties 310.4165 Multilayer design We investigate the reflected field for few-cycle ultra-short laser pulses propagating through resonant media embedded within wavelength-scale structures. Full-wave Maxwell–Bloch equations are solved numerically by using the finite-difference time-domain method. The results show that the spectral feature of the reflected spectrum is determined by the Bragg reflection condition, and that the periodic structure of a dense atomic system can be regarded as a one-dimensional photonic crystal and even as a highly reflective multilayer film. Our study explains the suppression of the frequency shifts in the reflected spectrum based on the Bragg reflection theory and provides a method to control the frequency and frequency intervals of the spectral spikes in the reflected spectrum.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 320.7150 Ultrafast spectroscopy 020.1335 Atom optics 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦